HashiCorp Certified: Vault Associate (002) Vault-Associate Exam Practice Test
You have a 2GB Base64 binary large object (blob) that needs to be encrypted. Which of the following best describes the transit secrets engine?
Security requirements demand that no secrets appear in the shell history. Which command does not meet this requirement?
Answer : B
The command that does not meet the security requirement of not having secrets appear in the shell history is B. vault kv put secret/password value-itsasecret. This command would store the secret value ''itsasecret'' in the key/value secrets engine at the path secret/password, but it would also expose the secret value in the shell history, which could be accessed by other users or malicious actors. This is not a secure way of storing secrets in Vault.
The other commands are more secure ways of storing secrets in Vault without revealing them in the shell history. A. generate-password | vault kv put secret/password value would use a pipe to pass the output of the generate-password command, which could be a script or a tool that generates a random password, to the vault kv put command, which would store the password in the key/value secrets engine at the path secret/password. The password would not be visible in the shell history, only the commands. C. vault kv put secret/password value=@data.txt would use the @ syntax to read the secret value from a file named data.txt, which could be encrypted or protected by file permissions, and store it in the key/value secrets engine at the path secret/password. The file name would be visible in the shell history, but not the secret value. D. vault kv put secret/password value-SSECRET_VALUE would use the -S syntax to read the secret value from the environment variable SECRET_VALUE, which could be set and unset in the shell session, and store it in the key/value secrets engine at the path secret/password. The environment variable name would be visible in the shell history, but not the secret value.
[Write Secrets | Vault | HashiCorp Developer]
Which of the following statements are true about Vault policies? Choose two correct answers.
Answer : C, E
Vault does not need to be restarted in order for a policy change to take effect, as policies are stored and evaluated in memory. Any change to a policy is immediately reflected in the system, and any token or role that has that policy attached will be affected by the change.
What command creates a secret with the key "my-password" and the value "53cr3t" at path "my-secrets" within the KV secrets engine mounted at "secret"?
Answer : A
The vault kv put command writes the data to the given path in the K/V secrets engine. The command requires the mount path of the K/V secrets engine, the secret path, and the key-value pair to store. The mount path can be specified with the -mount flag or as part of the secret path. The key-value pair can be given as an argument or read from a file or stdin. The correct syntax for the command is:
vault kv put -mount=secret my-secrets/my-password 53cr3t
or
vault kv put secret/my-secrets my-password=53cr3t
A user issues the following cURL command to encrypt data using the transit engine and the Vault AP:
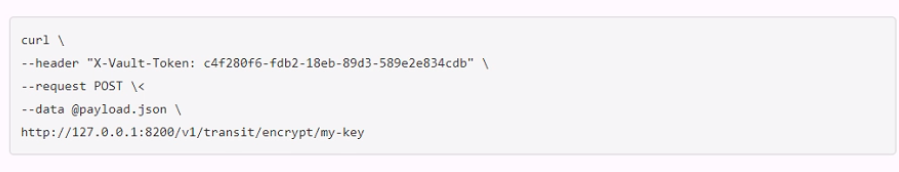
Which payload.json file has the correct contents?
A.
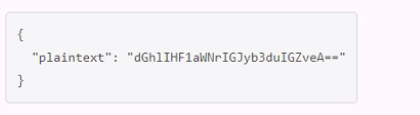
B.
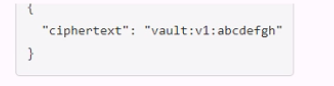
C.
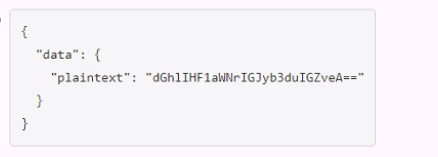
D.
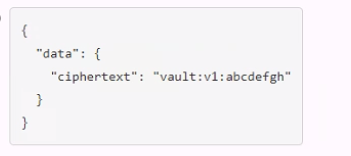
A developer mistakenly committed code that contained AWS S3 credentials into a public repository. You have been tasked with revoking the AWS S3 credential that was in the code. This credential was created using Vault's AWS secrets engine and the developer received the following output when requesting a credential from Vault.
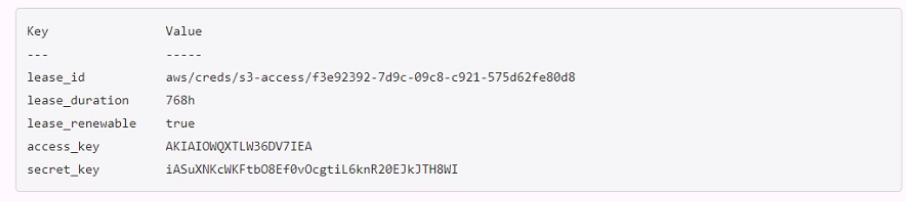
Which Vault command will revoke the lease and remove the credential from AWS?
Answer : A