Microsoft Developing Solutions for Microsoft Azure AZ-204 Exam Practice Test
A company uses Azure SQL Database to store data for an app. The data includes sensitive information.
You need to implement measures that allow only members of the managers group to see sensitive information.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
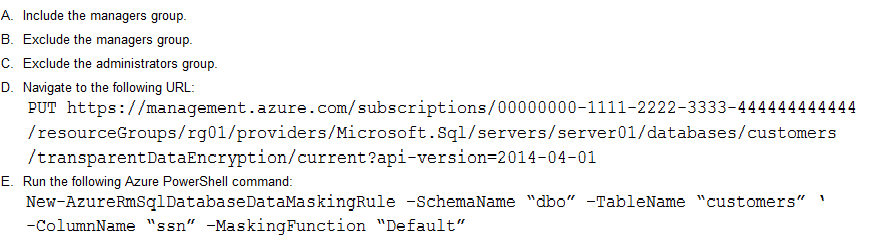
Answer : B, E
Dynamic data masking helps prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data by enabling customers to designate how much of the sensitive data to reveal with minimal impact on the application layer.
SQL users excluded from masking - A set of SQL users or AAD identities that get unmasked data in the SQL query results.
Note: The New-AzureRmSqlDatabaseDataMaskingRule cmdlet creates a data masking rule for an Azure SQL database.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/azurerm.sql/new-azurermsqldatabasedatamaskingrule?view=azurermps-6.13.0
You develop an app that allows users to upload photos and videos to Azure storage. The app uses a storage REST API call to upload the media to a blob storage account named Account1. You have blob storage
containers named Container1 and Container2.
Uploading of videos occurs on an irregular basis.
You need to copy specific blobs from Container1 to Container2 in real time when specific requirements are
met, excluding backup blob copies.
What should you do?
Answer : B
The Start-AzureStorageBlobCopy cmdlet starts to copy a blob.
Example 1: Copy a named blob
C:\PS>Start-AzureStorageBlobCopy -SrcBlob 'ContosoPlanning2015' -DestContainer 'ContosoArchives' -SrcContainer 'ContosoUploads'
This command starts the copy operation of the blob named ContosoPlanning2015 from the container named ContosoUploads to the container named ContosoArchives.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/powershell/module/azure.storage/start-azurestorageblobcopy?view=azurermps-6.13.0
You are developing a web application that uses Azure Cache for Redis. You anticipate that the cache will frequently fill and that you will need to evict keys.
You must configure Azure Cache for Redis based on the following predicted usage pattern: A small subset of elements will be accessed much more often than the rest.
You need to configure the Azure Cache for Redis to optimize performance for the predicted usage pattern.
Which two eviction policies will achieve the goal?
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Answer : B, C
B: The allkeys-lru policy evict keys by trying to remove the less recently used (LRU) keys first, in order to make space for the new data added. Use the allkeys-lru policy when you expect a power-law distribution in the popularity of your requests, that is, you expect that a subset of elements will be accessed far more often than the rest.
C: volatile-lru: evict keys by trying to remove the less recently used (LRU) keys first, but only among keys that have an expire set, in order to make space for the new data added.
Note: The allkeys-lru policy is more memory efficient since there is no need to set an expire for the key to be evicted under memory pressure.
https://redis.io/topics/lru-cache
You are writing code to create and run an Azure Batch job.
You have created a pool of compute nodes.
You need to choose the right class and its method to submit a batch job to the Batch service.
Which method should you use?
Answer : C
A Batch job is a logical grouping of one or more tasks. A job includes settings common to the tasks, such as priority and the pool to run tasks on. The app uses the BatchClient.JobOperations.CreateJob method to create a job on your pool.
The Commit method submits the job to the Batch service. Initially the job has no tasks.
{
CloudJob job = batchClient.JobOperations.CreateJob();
job.Id = JobId;
job.PoolInformation = new PoolInformation { PoolId = PoolId };
job.Commit();
}
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/quick-run-dotnet
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are developing an Azure Service application that processes queue data when it receives a message from a mobile application. Messages may not be sent to the service consistently.
You have the following requirements:
Queue size must not grow larger than 80 gigabytes (GB).
Use first-in-first-out (FIFO) ordering of messages.
Minimize Azure costs.
You need to implement the messaging solution.
Solution: Use the .Net API to add a message to an Azure Service Bus Queue from the mobile application. Create an Azure Windows VM that is triggered from Azure Service Bus Queue.
Does the solution meet the goal?
Answer : B
Don't use a VM, instead create an Azure Function App that uses an Azure Service Bus Queue trigger.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/functions-create-storage-queue-triggered-function
You are developing an Azure Function that calls external APIs by providing an access token for the API. The access token is stored in a secret named token in an Azure Key Vault named mykeyvault.
You need to ensure the Azure Function can access to the token. Which value should you store in the Azure Function App configuration?
A.
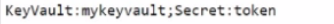
B.

C.

D.

Answer : D
You are developing a software solution for an autonomous transportation system. The solution uses large data sets and Azure Batch processing to simulate navigation sets for entire fleets of vehicles.
You need to create compute nodes for the solution on Azure Batch.
What should you do?
Answer : D
A Batch job is a logical grouping of one or more tasks. A job includes settings common to the tasks, such as priority and the pool to run tasks on. The app uses the BatchClient.JobOperations.CreateJob method to create a job on your pool.
Note:
Step 1: Create a pool of compute nodes. When you create a pool, you specify the number of compute nodes for the pool, their size, and the operating system. When each task in your job runs, it's assigned to execute on one of the nodes in your pool.
Step 2 : Create a job. A job manages a collection of tasks. You associate each job to a specific pool where that job's tasks will run.
Step 3: Add tasks to the job. Each task runs the application or script that you uploaded to process the data files it downloads from your Storage account. As each task completes, it can upload its output to Azure Storage.
Incorrect Answers:
C: To create a Batch pool in Python, the app uses the PoolAddParameter class to set the number of nodes, VM size, and a pool configuration.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/batch/quick-run-dotnet