AACE International Planning & Scheduling Professional (PSP) AACE-PSP Exam Practice Test
Baseline schedule can be submitted only__________.
Answer : A
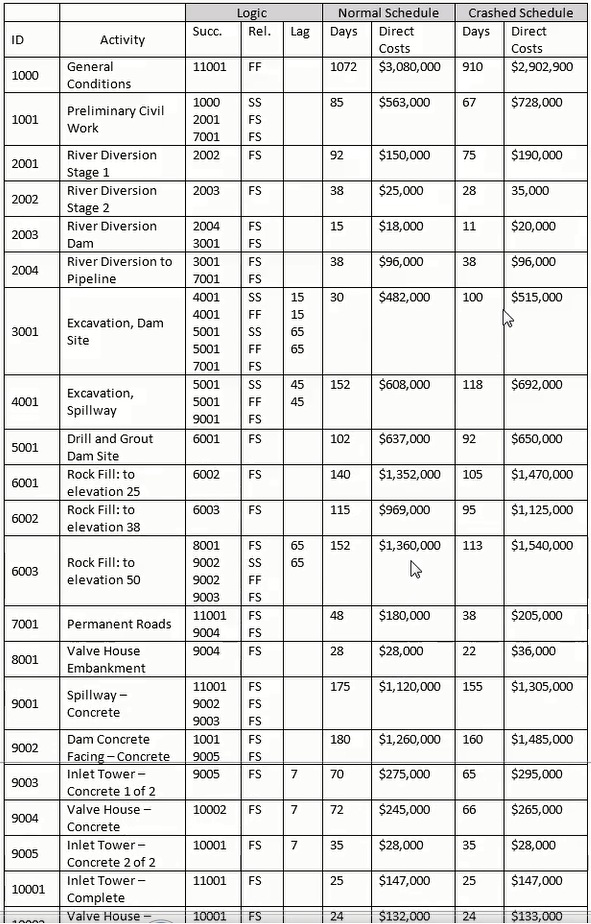
Determine the correct formula and date for the late finish for Activity 2001.

Answer : B
Activity Details (2001 - 'River Diversion Stage 1'):
Successor: 2002 ('River Diversion Stage 2').
Relationship: Finish-to-Start (FS) with no lag.
Normal schedule duration for Activity 2001 = 92 days.
Backward Pass Calculation for Late Finish (LF):
The Late Finish (LF) of Activity 2001 is derived from the Late Start (LS) of its successor, Activity 2002.
Formula: LF.2001 = LS.2002 - 1 day.
Date Calculation:
Given: LS.2002 = 08-30-01 (as per data in the schedule).
LF.2001 = LS.2002 - 1 day = 08-30-01 - 1 day = 08-29-01.
Cross-Verification with Answer Options:
Option A: Incorrect. Misrepresents the Late Finish formula.
Option C: Incorrect. Adds 1 day instead of subtracting.
Option D: Incorrect. Incorrect date application.
Option B: Correct. Matches both formula and calculation.
Prior to the beginning work on Activity 6001, the scope is changed by executed change order to increase the activity duration by thirty days and rock fill by 100.000 cubic meters If the project has progressed as scheduled up to the point of the executed change order, what activities would be changed on the next project update?
Answer : D
The change order impacts Activity 6001 by increasing its duration and workload. As per Critical Path Method (CPM) principles, this would also affect predecessor activities like 1000, which directly influence the start of 6001.
Updates to the schedule will ripple through linked activities, but only those immediately affected by the change---1000 and 6001---would be revised in the immediate update.
Reference: PSP Study Guide, Section 2.3.4 -- Schedule Change Management, and Appendix A -- Sample Problems on CPM Network adjustments highlight how scope changes propagate through linked activities.
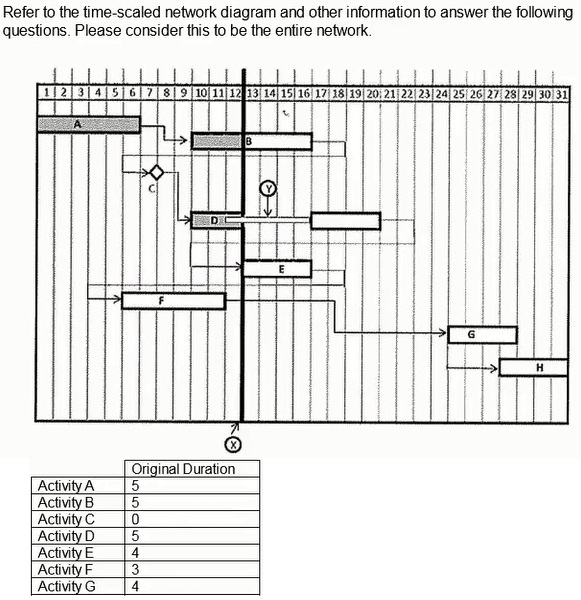
What is the actual duration as of the status date or data date of Activity B?
Answer : A
Understand Activity B's Status:
Activity B has an original duration of 5 days.
As of the data date/status date, the diagram shows progress beyond 5 days.
Review Actual Duration:
The progress bar indicates that 7 days have already been worked on Activity B.
Actual duration as of the status date = 7 days.
Cross-Verification:
Option B: Incorrect. Progress exceeds 3 days.
Option C: Incorrect. Progress is not 0 days.
Option D: Incorrect. Progress is more than 4 days.
Option A: Correct. Matches the observed progress on the diagram.
PSP Study Guide (2019), Section on Network Diagrams and Status Updates.
AACE Recommended Practices, RP 10S-90.
What project cost elements would NOT normally be reflected in the Activity 1000?
Answer : A
Activity-specific costs in CPM schedules typically include direct expenses like materials (C), field-related overhead (D), and specific schedule management tasks (B).
Home office expenses are classified as indirect costs and are not associated with any specific activity within the project schedule. They are accounted for in broader financial statements rather than in the activity-based budget.
Reference: PSP Study Guide, Section 1.3.10 -- Cost Estimate Development, explains how costs are categorized and assigned in schedules.
Determine the correct formula and date for the late finish for Activity 9004.
Answer : D
Analyze the Data and Logic:
Activity 9004 ('Valve House Embankment'): This activity has a direct Finish-to-Start (FS) relationship with Activity 10002, with a lag of 7 days.
Late Start (LS) and Late Finish (LF): In backward pass calculations, the late finish of the successor activity is adjusted for lag and task duration to determine the late start of the predecessor activity.
Formula for Late Finish (LF):
The Late Finish of Activity 9004 is derived by taking the Late Start (LS) of Activity 10002, subtracting the lag of 7 days, and subtracting 1 day to calculate the exact finish date.
Correct Date Calculation:
Given the Late Start (LS) of Activity 10002:
LS.10002 = 11-28-03.
Apply the formula: LF.9004 = LS.10002 - Lag.7 - 1 day = 11-28-03 - 7 days - 1 day = 11-20-03.
Cross-Verification with Answer Options:
Option A: Incorrect. Misrepresents the formula.
Option B: Incorrect. Incorrect application of logic and lag adjustments.
Option C: Incorrect. Omits the correct lag consideration.
Option D: Correct. Matches both formula and calculated date.
The project goals_________.
Answer : C