AICPA CPA Business Environment and Concepts CPA-Business CPA Exam Practice Test
Formation of which of the following types of business does not require the filing of documents with the state?

Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. A sole proprietorship can be formed without filing with the state. Formation of either a corporation or a limited partnership requires a filing.
Choices 'a', 'b', and 'd' are incorrect per the Explanation: above.
When evaluating capital budgeting analysis techniques, the payback period emphasizes:
Answer : A
Choice 'a' is correct. The payback period is the time period required for cash inflows to recover the initial investment. The emphasis of the technique is on liquidity (i.e., cash flow).
Choices 'b', 'c', and 'd' are incorrect, per the above Explanation:.
A vendor offered Wyatt Co. $25,000 compensation for losses resulting from faulty raw materials.
Alternately, a lawyer offered to represent Wyatt in a lawsuit against the vendor for a $12,000 retainer and 50% of any award over $35,000. Possible court awards with their associated probabilities are:
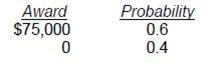
Compared to accepting the vendor's offer, the expected value for Wyatt to litigate the matter to verdict provides a:
Answer : A
Choice 'a' is correct.
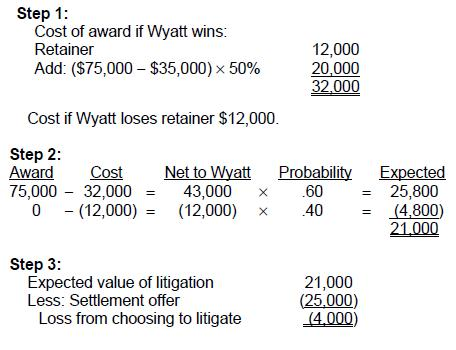
Choices 'b', 'c', and 'd' are incorrect based on the above Explanation:.
In a member managed LLC, the apparent authority of a member to bind the LLC in dealing with third parties:
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. This is really an agency question on apparent authority. Apparent authority is authority that a third party reasonably believes an agent has. If the third party is aware of a restriction on the agent's authority, the third party cannot reasonably believe that the agent has the restricted authority.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Submitting a claim to arbitration is an extraordinary act and so is not within a member's apparent authority.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Apparent authority is derived from what the reasonable person believes is the authority of a member, not the express powers and purposes contained in the operating agreement.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. A formal resolution of the members will not be effective to destroy apparent authority if third parties are unaware of the resolution.
Considering the SCOR Model of supply chain operations, which of the following key management processes does implementing changes in engineering fall into?
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. The 'make' process encompasses all the activities that turn the raw materials into finished products that are produced to meet a planned demand. Implementing changes in the engineering process falls into the 'make' process.
Choices 'a', 'b', and 'd' are incorrect, per the above Explanation: .
During a recession:
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. During a recession, potential output (real GDP) will exceed actual output (real GDP).
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Real GDP is falling during a recession.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. The natural rate of unemployment will not be affected by the various phases of the business cycle. Actual unemployment will change with the cycle.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. Actual output will not exceed potential output except at the peak of the cycle, and perhaps not then.
Youngsten Electric is contemplating new projects for the next year that will require $30,000,000 of new financing. In keeping with its capital structure, Youngsten plans to use debt & equity financing as follows:
* Issue $10,000,000 of 20-year bonds at a price of 101.5, with a coupon of 10%, and flotation costs of 2.5% of par value.
* Use internal funds generated from earnings of $20,000,000.
The equity market is expected to earn 15%. U.S. treasury bonds currently are yielding 9%. The beta coefficient for Youngsten's common stock is estimated to be .8. Youngsten is subject to a 40% corporate income tax rate. Youngsten has a price/earnings ratio of 10, a constant dividend payout ratio of 40%, and an expected growth rate of 12%.
Assume Youngsten has an after-tax cost of debt of 9% and an after-tax cost of equity of 15%.
Youngsten's weighted average cost of capital is:
Answer : B
Choice 'b' is correct. The WACC is computed by multiplying the required returns on equity and debt by the percentage of equity and debt used to finance that particular project. Youngsten will use 33% debt ($10 million of $30 million total project cost) and 67% equity ($20 million of $30 million total project cost).
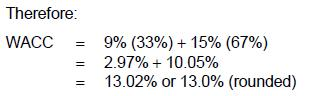
Choices 'a', 'c', and 'd' are incorrect, per the above calculation.