AICPA CPA Regulation CPA-Regulation CPA Exam Questions
DAC Foundation awarded Kent $75,000 in recognition of lifelong literary achievement. Kent was not required to render future services as a condition to receive the $75,000. What condition(s) must have been met for the award to be excluded from Kent's gross income?
I Kent was selected for the award by DAC without any action on Kent's part.
II Pursuant to Kent's designation, DAC paid the amount of the award either to a governmental unit or to a charitable organization.
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. Generally, the fair market value of prizes and awards is taxable income. However, an exclusion from income for certain prizes and awards applies where the winner is selected for the award without entering into a contest (i.e., without any action on their part) and then assigns the award directly to a governmental unit or charitable organization. Therefore, conditions 'I' and 'II' must be met in order for Ken to exclude the award from his gross income.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. 'II' is a necessary condition as well. See Explanation: above.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. 'I' is a necessary condition as well. See Explanation: above.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. 'I' and 'II' are both necessary conditions. See Explanation: above.
A cash basis taxpayer should report gross income:
Answer : D
Choice 'd' is correct. A cash basis taxpayer should report gross income for the year in which income is either actually or constructively received, whether in cash or in property.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Income also be constructively received in property - not only actually in cash.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Income also be constructively received - not only actually.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. Income also be received in property - not only cash.
Baum, an unmarried optometrist and sole proprietor of Optics, buys and maintains a supply of eyeglasses and frames to sell in the ordinary course of business. In 1999, Optics had $350,000 in gross business receipts and its year-end inventory was not subject to the uniform capitalization rules. Baum's 1999 adjusted gross income was $90,000 and Baum qualified to itemize deductions. During 1999, Baum recorded the following information:
Business expenses:

What amount should Baum report as 1999 net earnings from self-employment?
Answer : D
Choice 'd' is correct. Baum should report $281,750 as 1999 net earnings from self-employment (line 12 of the Form 1040), calculated as follows:

Choices 'a', 'b', and 'c' are incorrect. Self-employment tax and self-employment health insurance expenses are adjustments from total gross income. They are not deducted from self-employment earnings (i.e., not reported net on line 12 of the Form 1040).
Note: There are many distracters in this question, all relating to items that are either deductible as part of itemized deductions or not deductible. Be careful to read the requirement of the question before spending unnecessary time on the question. The statement that Baum's year-end inventory was not subject to the uniform capitalization rules is a distracter as well. There is not enough information given in the facts to apply the rules if he had been subject to them.
On December 31, 1989, a building owned by Pine Corp. was totally destroyed by fire. The building had fire insurance coverage up to $500,000. Other pertinent information as of December 31, 1989 follows:
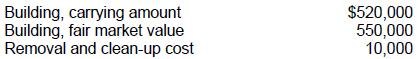
During January 1990, before the 1989 financial statements were issued, Pine received insurance proceeds of $500,000. On what amount should Pine base the determination of its loss on involuntary conversion?
Answer : B
Choice 'b' is correct. $530,000 basis of involuntary converted building.

Tom and Joan Moore, both CPAs, filed a joint 1994 federal income tax return showing $70,000 in taxable income. During 1994, Tom's daughter Laura, age 16, resided with Tom. Laura had no income of her own and was Tom's dependent.
Determine the amount of income or loss, if any that should be included on page one of the Moores' 1994 Form 1040.
During 1994, the Moores received a $2,500 federal tax refund and a $1,250 state tax refund for 1993 overpayments. In 1993, the Moores were not subject to the alternative minimum tax and were not entitled to any credit against income tax. The Moores' 1993 adjusted gross income was $80,000 and itemized deductions were $1,450 in excess of the standard deduction. The state tax deduction for 1993 was $2,000.
Answer : E
'E' is correct. $1,250. The Moores itemized deductions in 1993 because such deductions were $1,450 in excess of the standard deduction. The amount of state taxes deducted in 1993 was $2,000, which (along with the fact that the Moores were not subject to alternative minimum tax, which may have reduced their tax benefit) indicates that the Moores received a tax benefit in 1993 from deducting the $1,250 state tax refund they received in 1994. The $1,250 is taxable in 1994.
Tom and Joan Moore, both CPAs, filed a joint 1994 federal income tax return showing $70,000 in taxable income. During 1994, Tom's daughter Laura, age 16, resided with Tom. Laura had no income of her own and was Tom's dependent.
Determine the amount of income or loss, if any that should be included on page one of the Moores' 1994 Form 1040.
In 1992, Joan received an acre of land as an inter-vivos gift from her grandfather. At the time of the gift, the land had a fair market value of $50,000. The grandfather's adjusted basis was $60,000. Joan sold the land in 1994 to an unrelated third party for $56,000.
Answer : A
'A' is correct. $0. Property received by gift has two bases: one for computing gain and another for computing loss. Joan's basis for gain is the grandfather's adjusted basis ($60,000). Using this basis for gain, Joan has a loss of: $56,000 - $60,000 = ($4,000 loss). Joan's basis for loss is the fair market value of the property on the date of the gift ($50,000). Using this basis for loss, Joan has a gain of: $56,000 - $50,000 = $6,000 gain. In this unusual situation, Joan has neither a gain nor a loss, although the transaction must be reported.
Tom and Joan Moore, both CPAs, filed a joint 1994 federal income tax return showing $70,000 in taxable income. During 1994, Tom's daughter Laura, age 16, resided with Tom. Laura had no income of her own and was Tom's dependent.
Determine the amount of income or loss, if any that should be included on page one of the Moores' 1994 Form 1040.
Tom received $10,000, consisting of $5,000 each of principal and interest, when he redeemed a Series EE savings bond in 1994. The bond was issued in his name in 1990 and the proceeds were used to pay for Laura's college tuition. Tom had not elected to report the yearly increases in the value of the bond.
Answer : A
'A' is correct. $0. Generally, if a taxpayer does not make an election to accrue interest income from Series EE bonds, the interest is taxable at the time the bonds are cashed. However, an exception applies in this case because Tom Moore meets the criteria (assume he was 24 years or older in 1990). Savings bonds is tax-exempt when:
(1) It is used to pay for qualified higher-education expenses for the taxpayer, spouse, or dependents;
(2) There is taxpayer or joint ownership with spouse;
(3) The taxpayer is age 24 (or over) when the bonds are issued; and
(4) The bonds are acquired after 1989.
Don Wolf became a general partner in Gata Associates on January 1, 1989, with a 5% interest in Gata's profits, losses, and capital. Gata is a distributor of auto parts. Wolf does not materially participate in the partnership business. For the year ended December 31, 1989, Gata had an operating loss of $100,000.
In addition, Gata earned interest of $20,000 on a temporary investment. Gata has kept the principal temporarily invested while awaiting delivery of equipment that is presently on order. The principal will be used to pay for this equipment. Wolf's passive loss for 1989 is:
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. Wolf's passive loss for 1989 is $5,000 ($100,000 operating loss 5% interest in partnership).
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Wolf did not materially participate in the partnership, so the loss was passive.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Wolf's passive loss of $5,000 could not be reduced by his distributive share of the partnership's 'interest income' totaling $1,000. Interest income is considered 'portfolio income,' and neither the partnership nor a partner can offset it against passive losses.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. No items of income or deduction from portfolio income or activities in which the taxpayer materially participates may be combined or offset with passive losses unless the activity generating the loss is completely disposed of in a taxable transaction.
Tom and Joan Moore, both CPAs, filed a joint 1994 federal income tax return showing $70,000 in taxable income. During 1994, Tom's daughter Laura, age 16, resided with Tom. Laura had no income of her own and was Tom's dependent.
Determine the amount of income or loss, if any that should be included on page one of the Moores' 1994 Form 1040.
Tom's 1994 wages were $53,000. In addition, Tom's employer provided group-term life insurance on Tom's life in excess of $50,000. The value of such excess coverage was $2,000.
Answer : A
'N' is correct. $55,000. The value of employer-provided group term life insurance for which the face amount exceeds $50,000 is taxable income to the insured employee and the $53,000 in wages would both be included on page one, Form 1040.
In a tax year where the taxpayer pays qualified education expenses, interest income on the redemption of qualified U.S. Series EE Bonds may be excluded from gross income. The exclusion is subject to a modified gross income limitation and a limit of aggregate bond proceeds in excess of qualified higher education expenses. Which of the following is (are) true?
I The exclusion applies for education expenses incurred by the taxpayer, the taxpayer's spouse, or any person whom the taxpayer may claim as a dependent for the year.
II "Otherwise qualified higher education expenses" must be reduced by qualified scholarships not includible in gross income.
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. Interest earned on Series EE bonds issued after 1989 may qualify for exclusion. One requirement is that the interest is used to pay tuition and fees for the taxpayer, spouse, or dependent enrolled in higher education. The interest exclusion is reduced by qualified scholarships that are exempt from tax and other nontaxable payments received for educational expenses (other than gifts and inheritances).
Tom and Joan Moore, both CPAs, filed a joint 1994 federal income tax return showing $70,000 in taxable income. During 1994, Tom's daughter Laura, age 16, resided with Tom. Laura had no income of her own and was Tom's dependent.
Determine the amount of income or loss, if any that should be included on page one of the Moores' 1994 Form 1040.
The Moores had no capital loss carryovers from prior years. During 1994, the Moores had the following stock transactions, which resulted in a net capital loss:
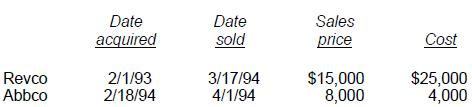
Answer : J
'J' is correct. $3,000. The capital loss on Revco ($10,000 loss) is added to the capital gain on Abbco ($4,000) to produce a net capital loss of ($6,000). The Moores can claim $3,000 of the loss on their 1994 income tax return and carry the balance forward to 1995.
Don Wolf became a general partner in Gata Associates on January 1, 1989, with a 5% interest in Gata's profits, losses, and capital. Gata is a distributor of auto parts. Wolf does not materially participate in the partnership business. For the year ended December 31, 1989, Gata had an operating loss of $100,000.
In addition, Gata earned interest of $20,000 on a temporary investment. Gata has kept the principal temporarily invested while awaiting delivery of equipment that is presently on order. The principal will be used to pay for this equipment. Wolf's passive loss for 1989 is:
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. Wolf's passive loss for 1989 is $5,000 ($100,000 operating loss 5% interest in partnership).
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Wolf did not materially participate in the partnership, so the loss was passive.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Wolf's passive loss of $5,000 could not be reduced by his distributive share of the partnership's 'interest income' totaling $1,000. Interest income is considered 'portfolio income,' and neither the partnership nor a partner can offset it against passive losses.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. No items of income or deduction from portfolio income or activities in which the taxpayer materially participates may be combined or offset with passive losses unless the activity generating the loss is completely disposed of in a taxable transaction.
Parker, whose spouse died during the preceding year, has not remarried. Parker maintains a home for a dependent child. What is Parker's most advantageous filing status?
Answer : D
Choice 'd' is correct. A qualifying widow (er) is a taxpayer who may use the joint tax return standard deduction and rates (but not the exemption for the deceased spouse) for each of two taxable years following the year of death of his or her spouse, unless he or she remarries. The surviving spouse must maintain a household that, for the whole entire taxable year, was the principal place of abode of a son, stepson, daughter, or stepdaughter (whether by blood or adoption). The surviving spouse must also be entitled to a dependency exemption for such individual. Parker may file as a qualifying widow (er) since her spouse died in the previous tax year, she did not remarry and she maintained a home for a dependent child. Since, qualifying widow (er) is the most advantageous status and Parker qualifies, Parker would file as a qualifying widow (er).
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Even though Parker would qualify as single, filing single would give Parker a high tax liability than the qualifying widow (er) status and therefore is not most advantageous.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Parker would not qualify as head of household for the first two years after the death of Parker's spouse because one of the requirements for Head of Household status is that the taxpayer is NOT a surviving spouse. (Also, note that the likely reason for this requirement is that filing as Head of Household status would give the qualifying surviving spouse taxpayer a higher tax liability than the Qualifying Widow(er) status, which would be less advantageous.)
Choice 'c' is incorrect. Parker would not qualify to file married filing separately.
Doris and Lydia are equal partners in the capital and profits of Agee & Nolan, but are otherwise unrelated. The following information pertains to 300 shares of Mast Corp. stock sold by Lydia to Agee & Nolan:
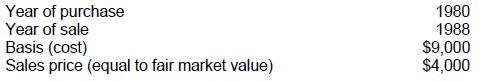
The amount of long-term capital loss that Lydia realized in 1988 on the sale of this stock was:
Answer : A
Choice 'a' is correct. $5,000 long term capital loss 'realized' in 1988 by Lydia. Be careful, and always check the question being asked. In this case, the question is how much of a capital loss Lydia realized in 1988.

Choice 'b' is incorrect. $3,000 represents the portion of the $5,000 realized loss that would currently be recognized unless there were additional capital transactions resulting in gains. Remember that the deduction for capital losses for an individual is limited to $3,000 each year.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. $2,500 represents the pre-1986 portion of the $5,000 realized loss that would have given rise to a recognized loss. Pre-1986 law required $2 of net long term loss to give the benefit of $1 of tax deduction. Current law gives a dollar-for-dollar deduction limited to $3,000 in any year.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. $0 would have been the amount of loss recognized if Lydia owned more than a 50% interest in the partnership. Losses realized on transactions between a partnership and a partner owning more than a 50% interest are not deductible as the parties would be considered related and any realized loss would be disallowed.
Which payment(s) is(are) included in a recipient's gross income?
I . Payment to a graduate assistant for a part-time teaching assignment at a university. Teaching is not a requirement toward obtaining the degree.
II . A grant to a Ph.D. candidate for his participation in a university-sponsored research project for the benefit of the university.
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct.
The uniform capitalization method must be used by:
I Manufacturers of tangible personal property.
II Retailers of personal property with $2 million dollars in average annual gross receipts for the 3 preceding years.
Answer : A
Choice 'a' is correct. I only.
Rule: The uniform capitalization rules apply to the following:
1. Real or tangible personal property produced by the taxpayer for use in a trade or business.
2. Real or tangible personal property produced by the taxpayer for sale to customers.
3. Real or personal property acquired by the taxpayer for resale.
4. However, the uniform capitalization rules do not apply to property acquired for resale if the taxpayer's annual gross receipts for the preceding three tax years do not exceed $10,000,000 (not $2 million).
In 19X4, Smith, a divorced person, provided over one half the support for his widowed mother, Ruth, and his son, Clay, both of whom are U.S. citizens. During 19X4, Ruth did not live with Smith. She received $9,000 in Social Security benefits. Clay, a 25 year-old full-time graduate student, and his wife lived with Smith. Clay had no income but filed a joint return for 19X4, owing an additional $500 in taxes on his wife's income. How many exemptions was Smith entitled to claim on his 19X4 tax return?
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. Smith is entitled to an exemption for himself. He is also entitled to an exemption for his mother Ruth (qualifying relative). Ruth has $9,000 in Social Security payments during 19X4, but since that is her only income, the Social Security is not taxable, and nontaxable income does not count in calculating whether an exemption can be taken for a dependent. Clay cannot be taken as a dependent because he filed a joint return with his wife. Since the joint return was filed for a purpose other than simply claiming a refund, the joint return prevents Smith from claiming an exemption for Clay. An exemption cannot be taken for Clay's wife because she filed a joint return with Clay. Smith is entitled to two exemptions.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Clay cannot be taken as a dependent because he filed a joint return with his wife. Since the joint return was filed for a purpose other than simply claiming a refund, the joint return prevents Smith from claiming an exemption for Clay. An exemption cannot be taken for Clay's wife because she filed a joint return with Clay.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Clay cannot be taken as a dependent because he filed a joint return with his wife. Since the joint return was filed for a purpose other than simply claiming a refund, the joint return prevents Smith from claiming an exemption for Clay. An exemption cannot be taken for Clay's wife because she filed a joint return with Clay.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. Smith is entitled to an exemption for his mother, Ruth. Ruth has $9,000 in Social Security payments during 19X4, but because that is her only income, the Social Security income is not taxable, and nontaxable income does not count in calculating whether an exemption can be taken for a dependent.
Individual Taxation - Gross Income
Which of the following sales should be reported as a capital gain?
Answer : D
Choice 'd' is correct. Government bonds held by an individual investor are considered capital assets in the hands of the investor. When these types of security investments are sold, the resulting gain or loss is reported as capital.
Choice 'a' is incorrect. In this case, we must assume that the BEST answer is option 'd' (as that option would ALWAYS result in capital gain or loss treatment) and that the examiners are assuming that the equipment is depreciable equipment that has been used in a business for over one year. [If the equipment had been considered a personal asset by the examiners and had sold for a gain, it would also be a capital asset that sold for a capital gain, and there would be two correct answers. Remember that the correct answer is the option that best answers the question.] Depreciable equipment used in a business and held for over one year falls under the category of Section 1245 property. When Section 1245 assets are sold at a gain, all the accumulated depreciation on the asset is recaptured as ordinary income (the same category as the depreciation expense was deducted against), and any remaining gain (typically, in practice, this is not the case, though, as the asset would have had to sell for an amount greater than its purchase price) is capital gain under Code Section 1231. [Note that Section 1245 applies only to gains. If the asset had sold for a loss, the loss would have been ordinary under Section 1231.]
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Real property sold by a dealer is considered inventory and results in ordinary income or ordinary losses upon sale. Inventory is not a capital asset and is not afforded the capital gain benefits.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. Inventory is not a capital asset and is not afforded the capital gain benefits. The sale of inventory results in ordinary income or loss (e.g., gross profit on sales) being reported on the tax return, as inventory is an asset held for sale in the ordinary course of business.
Among which of the following related parties are losses from sales and exchanges not recognized for tax purposes?
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. Losses from sales and exchanges are not recognized for tax purposes between grandfather and granddaughter.
Rule: Losses are disallowed on sales between related parties. 'Related' includes brothers and sisters, husband-wife, lineal descendants (father, son, grandfather), and entities that are more than 50% owned by individuals, corporations, trusts and/or partnerships.
Choices 'a', 'b', and 'd' are incorrect, because losses from sales and exchanges are recognized for all 'in-laws.'
Barkley owns a vacation cabin that was rented to unrelated parties for 10 days during the year for $2,500. The cabin was used personally by Barkley for three months and left vacant for the rest of the year. Expenses for the cabin were as follows:
Real estate taxes $1,000
Maintenance and utilities $2,000
How much rental income (loss) is included in Barkley's adjusted gross income?
Answer : A
RULE: If a vacation residence is rented for less than 15 days per year, it is treated as a personal residence. The rental income is excluded from income, and mortgage interest (first or second home) and real estate taxes are allowed as itemized deductions. Depreciation, utilities, and repairs are not deductible.
Choice 'a' is correct. Applying the rule above, if a vacation residence is rented for less than 15 days per year, it is treated as a personal residence. The rental income ($2,500 in this case) is excluded from income. A Schedule E is not filed for this property (i.e., no income is reported, the taxes are reported as itemized deductions, and the maintenance and utilities are not deductible), so the effect on AGI is zero.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. This assumes that the property taxes are reported as itemized deductions but that the rental income ($2,500) less the maintenance and utilities ($2,000) are reported net on Schedule E.
Per the above RULE, the rental income is excluded from income, and the maintenance and utilities are not deductible.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. This assumes that all of the items shown are reported net on the Schedule E-$2,500 - $1,000 - $2,000 = ($500). Per the above RULE, the rental income is excluded from income, the maintenance and utilities are not deductible, and the property taxes are reported on Schedule A as an itemized deduction.
Choice 'd' is incorrect, per the above rule and discussion.
In which of the following situations may taxpayers file as married filing jointly?
Answer : A
RULE: In order to file a joint return, the parties must be MARRIED at the end of the year. Exception: If the parties are married but are LEGALLY SEPARATED under the laws of the state in which they reside, they cannot file a joint return (they will file either under the single or head of household filing status).
Choice 'a' is correct. Per the above rule, taxpayers who are married but lived apart during the year are allowed to file a joint return for the year. The fact that they did not live together during the year has no bearing on the issue.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Per the above rule, taxpayers who are married but lived under a legal separation agreement at the end of the year may not file a joint return. They will generally file either under the single or head of household filing status.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. Per the above rule, taxpayers who were divorced during the year may not file a joint return together, as they are not married at the end of the year. [Note, however, that they may become married again in the year and file a joint return with the new spouse.]
Choice 'd' is incorrect. Per the above rule, taxpayers who were legally separated but lived together for the entire year may not file a joint return. They will generally file either under the single or head of household filing status.
Fred Berk bought a plot of land with a cash payment of $40,000 and a mortgage of $50,000. In addition, Berk paid $200 for a title insurance policy. Berk's basis in this land is:
Answer : D
Choice 'd' is correct. $90,200 is Berk's basis in the land.
Rule: The basis of the property acquired will be the property's cost consisting of the amount of cash paid plus any amount of related debt assumed. Cost will be adjusted to reflect any additional costs incurred in purchasing the property.

Choices 'a', 'b', and 'c' are incorrect, per the above rule.
Gibson purchased stock with a fair market value of $14,000 from Gibson's adult child for $12,000. The child's cost basis in the stock at the date of sale was $16,000. Gibson sold the same stock to an unrelated party for $18,000. What is Gibson's recognized gain from the sale?
Answer : B
Choice 'b' is correct. Losses are disallowed on most related party sales transactions even if they were made at an arm's length (FMV) price. The basis (and related gain or loss) of the (second) buying relative depends on whether the second relative's resale price is higher, lower, or between the first relative's basis and the lower selling price to the second relative. In this case, the $4,000 capital loss on the sale by Gibson's adult child to Gibson [$12,000 SP - $16,000 Basis] is disallowed. Gibson's basis is determined by his selling price to a third party. In this case, the selling price is $18,000, which is HIGHER than the original basis of Gibson's adult child. Gibson's basis in the stock is, therefore, his adult child's basis of $16,000. Gibson's recognized basis is calculated as follows:
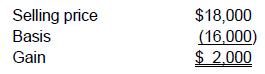
Choice 'a' is incorrect. There would be a zero gain or loss if the selling price were between the adult child's basis and Gibson's purchase price, but this is not the case in the facts.
Choice 'c' is incorrect. This answer option uses the fair market value of the stock at the date of purchase as the basis. As is discussed above, the rules do not provide for this treatment. [$18,000 SP - $14,000 FMV = $4,000]
Choice 'd' is incorrect. This would be the answer if the basis were Gibson's purchase price of $12,000; however, because the stock sold for more than Gibson's child's basis and the child had a disallowed loss on the sale to Gibson, Gibson is allowed to use his child's original basis of $16,000 as his basis for the stock on the date of the second sale. [$18,000 SP - $12,000 PP = $6,000]
Parker, whose spouse died during the preceding year, has not remarried. Parker maintains a home for a dependent child. What is Parker's most advantageous filing status?
Answer : D
Choice 'd' is correct. A qualifying widow (er) is a taxpayer who may use the joint tax return standard deduction and rates (but not the exemption for the deceased spouse) for each of two taxable years following the year of death of his or her spouse, unless he or she remarries. The surviving spouse must maintain a household that, for the whole entire taxable year, was the principal place of abode of a son, stepson, daughter, or stepdaughter (whether by blood or adoption). The surviving spouse must also be entitled to a dependency exemption for such individual. Parker may file as a qualifying widow (er) since her spouse died in the previous tax year, she did not remarry and she maintained a home for a dependent child. Since, qualifying widow (er) is the most advantageous status and Parker qualifies, Parker would file as a qualifying widow (er).
Choice 'a' is incorrect. Even though Parker would qualify as single, filing single would give Parker a high tax liability than the qualifying widow (er) status and therefore is not most advantageous.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. Parker would not qualify as head of household for the first two years after the death of Parker's spouse because one of the requirements for Head of Household status is that the taxpayer is NOT a surviving spouse. (Also, note that the likely reason for this requirement is that filing as Head of Household status would give the qualifying surviving spouse taxpayer a higher tax liability than the Qualifying Widow(er) status, which would be less advantageous.)
Choice 'c' is incorrect. Parker would not qualify to file married filing separately.
Among which of the following related parties are losses from sales and exchanges not recognized for tax purposes?
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. Losses from sales and exchanges are not recognized for tax purposes between grandfather and granddaughter.
Rule: Losses are disallowed on sales between related parties. 'Related' includes brothers and sisters, husband-wife, lineal descendants (father, son, grandfather), and entities that are more than 50% owned by individuals, corporations, trusts and/or partnerships.
Choices 'a', 'b', and 'd' are incorrect, because losses from sales and exchanges are recognized for all 'in-laws.'
Smith made a gift of property to Thompson. Smith's basis in the property was $1,200. The fair market value at the time of the gift was $1,400. Thompson sold the property for $2,500. What was the amount of Thompson's gain on the disposition?
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. The general rule for the basis on gifted property is that the donee receives the property with a rollover cost basis (equal to the donor's basis). An exception exists where the fair market value of the property at the time of the gift is less than the donor's basis. That is not the case in this question; thus, the calculation of the gain on the disposition of the property is:

Choice 'a' is incorrect. This choice could be correct if the facts of the question met the exception whereby no gain or loss is recognized when a donee sells gifted property for an amount between the donor's basis and the fair market value at the date of the gift.
Choice 'b' is incorrect. This choice uses the basis as the fair market value of the property. Fair market value of property at date of death is used as the basis for inherited property, not gifted property.
Choice 'd' is incorrect. This choice assumes that Thompson's basis is zero. His basis is $1,200 as indicated above.
The uniform capitalization method must be used by:
I Manufacturers of tangible personal property.
II Retailers of personal property with $2 million dollars in average annual gross receipts for the 3 preceding years.
Answer : A
Choice 'a' is correct. I only.
Rule: The uniform capitalization rules apply to the following:
1. Real or tangible personal property produced by the taxpayer for use in a trade or business.
2. Real or tangible personal property produced by the taxpayer for sale to customers.
3. Real or personal property acquired by the taxpayer for resale.
4. However, the uniform capitalization rules do not apply to property acquired for resale if the taxpayer's annual gross receipts for the preceding three tax years do not exceed $10,000,000 (not $2 million).
Allen owns 100 shares of Prime Corp., a publicly-traded company, which Allen purchased on January 1, 2001, for $10,000. On January 1, 2003, Prime declared a 2-for-1 stock split when the fair market value (FMV) of the stock was $120 per share. Immediately following the split, the FMV of Prime stock was $62 per share. On February 1, 2003, Allen had his broker specifically sell the 100 shares of Prime stock received in the split when the FMV of the stock was $65 per share. What amount should Allen recognize as long-term capital gain income on his Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return, for 2003?
Answer : C
Choice 'c' is correct. The receipt of a nontaxable stock dividend will require the shareholder to spread the basis of his original shares over both the original shares and the new shares received, resulting in the same total basis but a lower basis per share of stock helD. Therefore, Allen's total basis remains the same, $10,000, but is now split between 200 shares (a 2-for-1 split and he originally owned 100 shares).
Therefore, his basis per share goes from $100/share ($10,000/100) to $50/share ($10,000/200).
Consequently, his basis in the 100 shares sold is 100 x $50 = $5,000. Calculate his gain as follows:
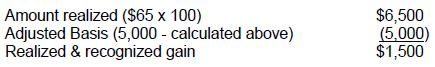
Choices 'a', 'b', and 'd' are incorrect.