AIWMI Certified Credit Research Analyst - Level 2 CCRA-L2 CCRA - Level 2 Exam Practice Test
Scott is a credit analyst with one of the credit rating agencies in Indi
a. He was looking in Oil and Gas Industry companies and has presented brief financials for following 4 entities:
Two credit analysts are discussing the DM-approach to credit risk modeling. They make the following statements:
Analyst A: A portfolio's standard deviation of credit losses can be determined by considering the standard deviation of credit losses of individual exposures in the portfolio and summing them all up.
Analyst B: I do not fully agree with that. Apart from individual standard deviations, one also needs to consider the correlation of the exposure with the rest of the portfolio so as to account for diversification effects. Higher correlations among credit exposures will lead to higher standard deviation of the overall portfolio.
Answer : C
The following information pertains to bonds:
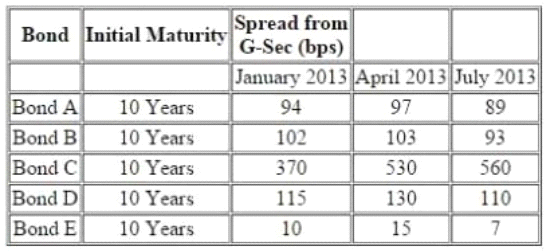
Further following information is available about a particular bond 'Bond F'
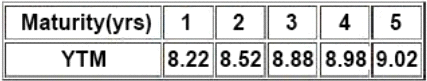
There is a 10.25% risky bond with a maturity of 2.25% year(s) its current price is INR105.31, which ccorresponds to YTM of 9.22%. The following are the benchmark YTMs.
Assume that the general market rates have increased. An issuer, Revolution Ltd has plans to roll over its existing commercial paper and forth coming reset dates for its floating rate bonds are very near. Which of the following ratios for revolution will get impacted?
Answer : A
Mark Construction Company (MCC) has bagged a contract for construction of a large dam and hydro power project on river Shivna in Madhya Pradesh (MP). The project is also of relevance from the irrigation perspective due to its location and as per the agreement MCC will have to undertake construction of web of canals, approach road to dam, power house and other ancillary units. MCC is promoted by Mr. Thomas Mark, who is a MP from the ruling party which recently formed government in MP. Historically, MCC has been engaged into construction of rural roads, small bridges and railway platforms on contract basis for the Government. MCC will have a separate special purpose vehicle (SPV) floated for this venture.
The hydro power project comes under the public private partnership scheme of the Government of MP, where in the private partner builds owns operates and transfers (BOOT) the hydro power plant. The detailed terms of the hydro power project agreement are as follows:
1. The construction of the dam, canals and hydro power plant shall be undertaken by the contractor. The
Government of MP will have to acquire land which will submerge on construction of dam and shall rehabilitate the owners of land.
2. MCC shall have right to operate the hydro power project from date of commencement of commercial operations (DCCO) for a period of 20 years and shall transfer the project to Government thereafter. Further,
SPV shall be tax exempt for a period of five years from DCCO i.e. FY17-FY21.
3. The power project is of 600 megawatts (MW) shall comprise 4 units of 150 MW each. The estimated cost of project is about INR3, 500 Million to be spent over a period of 4 year(s) the project is estimated to be commercially operational by April 1, 2016 with two units operational on same day and one unit each will be operational on April 1, 2017 and April 1, 2018.
4. Means of finance:
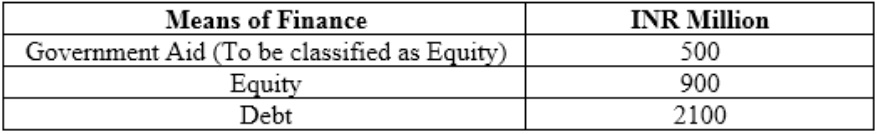
Means of Finance INR Million
Government Aid (To be classified as Equity) 500Equity 900 Debt 2100
5. Amount if expenditure estimated in various years is as follows:
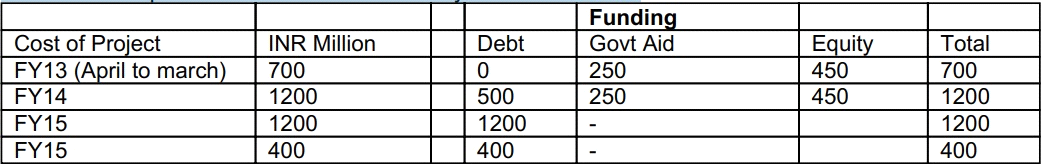
Debt shall bear a fixed rate of interest of 10% and all interest till DCCO shall be added to the principal. The expected principal along with capitalized interest is expected to be INR2, 400 Million (i.e.INR2100 Million debt plus INR300 Million capitalized interest). The repayment of the same shall be in 12 equated annual installments starting from FY17.
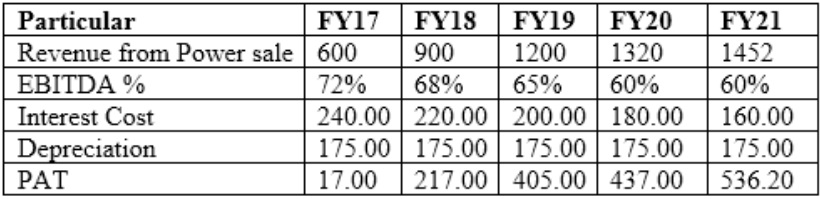
Brief projections for the period of FY17 to FY21 are given below:
Developments as on March 31, 2015
The project manager for the SPV made following comments at a press conferee on March 31, 2015:
As you all are aware, we were running bang on schedule till we last met on December 21, 2014. From today we are just left with one more year to complete the project in time. However, the flash floods which struck our dam site on this March 15, 2015 have created havoc in the region. I shall not point out the loss of lives in the region as you all are well aware of those. Our project has also been badly hit due to the same and we have been assessing the damage over the last one week. After analyzing damage, we have made changes in project schedule. Now we will be making only one unit of 150 MW operational on April 1, 2016 and 1 unit each will be added in each of subsequent year(s).
Development as on September 30, 2015
Post the flash floods, lot of environmentalists started raising issues of changes in environment due to construction of large number of dams. A few Public Interest Litigations (PILs) have been filed in various courts.
Honorable High Court of MP on September 27, 2015, banned construction of any dams in the region and banned permissions for new dams till next hearing scheduled on November 30, 2015. MCC in its press release has indicated that they will apply to the higher court on the matter.
As a credit analyst on March 31, 2012, which of the following sets of risks are you going to put in your credit appraisal note?
Answer : C
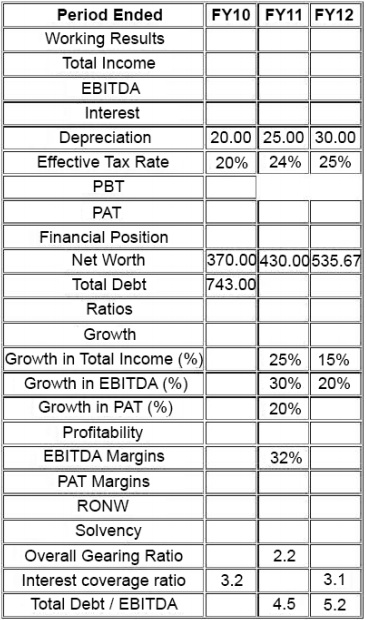
Ms. Mary Brown is a credit rating analyst. She had prepared a detailed report on one of her client, FlyHigh
Airlines Ltd, a company operating chartered aircrafts in Indi
a. As she was heading for a meeting with her superior on the matter, coffee spilled over her set of prepared paper(s). As she was getting late for meeting, instead of preparing entire set she could recollect few numbers from her memory and reconstructed following partial financial table:
An analyst comparing two competitors Comp Systems and Big Tables gathers the data below:
Cash Conversions Cycle:
Comp Systems: 18 days and Big Tables 32 days
Defense Interval Ratio:
Comp Systems: 50 and Big Tables: 20
What can the analyst conclude regarding the liquidity of these companies?
Answer : C
Mark Construction Company (MCC) has bagged a contract for construction of a large dam and hydro power project on river Shivna in Madhya Pradesh (MP). The project is also of relevance from the irrigation perspective due to its location and as per the agreement MCC will have to undertake construction of web of canals, approach road to dam, power house and other ancillary units. MCC is promoted by Mr. Thomas Mark, who is a MP from the ruling party which recently formed government in MP. Historically, MCC has been engaged into construction of rural roads, small bridges and railway platforms on contract basis for the Government. MCC will have a separate special purpose vehicle (SPV) floated for this venture.
The hydro power project comes under the public private partnership scheme of the Government of MP, where in the private partner builds owns operates and transfers (BOOT) the hydro power plant. The detailed terms of the hydro power project agreement are as follows:
1. The construction of the dam, canals and hydro power plant shall be undertaken by the contractor. The
Government of MP will have to acquire land which will submerge on construction of dam and shall rehabilitate the owners of land.
2. MCC shall have right to operate the hydro power project from date of commencement of commercial operations (DCCO) for a period of 20 years and shall transfer the project to Government thereafter. Further,
SPV shall be tax exempt for a period of five years from DCCO i.e. FY17-FY21.
3. The power project is of 600 megawatts (MW) shall comprise 4 units of 150 MW each. The estimated cost of project is about INR3, 500 Million to be spent over a period of 4 year(s) the project is estimated to be commercially operational by April 1, 2016 with two units operational om same day and one unit each will be operational on April 1, 2017 and April 1, 2018.
4. Means of finance:
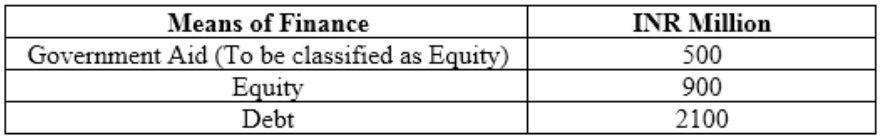
Means of Finance INR Million
Government Aid (To be classified as Equity) 500Equity 900 Debt 2100
5. Amount if expenditure estimated in various years is as follows:
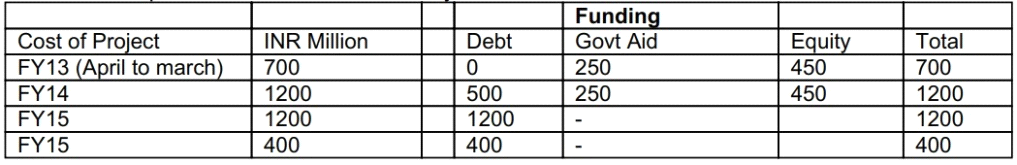
Debt shall bear a fixed rate of interest of 10% and all interest till DCCO shall be added to the principal. The expected principal along with capitalized interest is expected to be INR2, 400 Million (i.e.INR2100 Million debt plus INR300 Million capitalized interest). The repayment of the same shall be in 12 equated annual installments starting from FY17.
Brief projections for the period of FY17 to FY21 are given below:
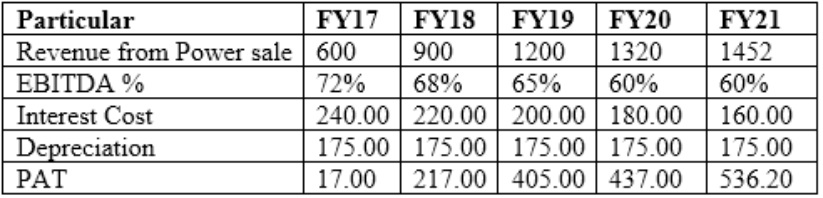
Developments as on March 31, 2015
The project manager for the SPV made following comments at a press conferee on March 31, 2015:
As you all are aware, we were running bang on schedule till we last met on December 21, 2014. From today we are just left with one more year to complete the project in time. However, the flash floods which struck our dam site on this March 15, 2015 have created havoc in the region. I shall not point out the loss of lives in the region as you all are well aware of those. Our project has also been badly hit due to the same and we have been assessing the damage over the last one week. After analyzing damage, we have made changes in project schedule. Now we will be making only one unit of 150 MW operational on April 1, 2016 and 1 unit each will be added in each of subsequent year(s).
Development as on September 30, 2015
Post the flash floods, lot of environmentalists started raising issues of changes in environment due to construction of large number of dams. A few Public Interest Litigations (PILs) have been filed in various courts.
Honorable High Court of MP on September 27, 2015, banned construction of any dams in the region and banned permissions for new dams till next hearing scheduled on November 30, 2015. MCC in its press release has indicated that they will apply to the higher court on the matter.
After the developments of March 31, 2015, assuming revenues are directly linked to the power production and the EBITDA margins remain intact for the year, as were projected, compute the revised interest coverage ratio dfor FY17 and FY18?
Answer : B
The following information pertains to bonds:
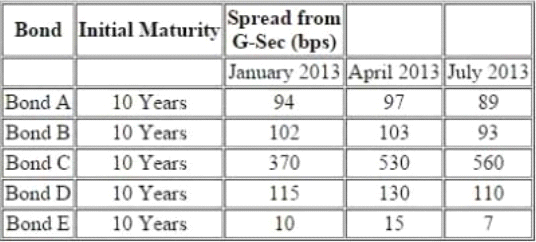
Further following information is available about a particular bond 'Bond F'
There is a 10.25% risky bond with a maturity of 2.25% year(s) its current price is INR105.31, which corresponds to YTM of 9.22%. The following are the benchmark YTMs.
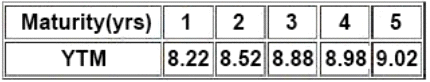
Compute interpolated spread for Bond F based on the information provided in the vignette:
Answer : A
Following is information related banks:
Auckland Ltd is a public sector bank operating with about 120 branches across Indi
a. The bank has been in business since 1971 and has about 40% branches in rural areas and about 75% of all branches are in
Western India. On the basis of the size, Auckland Ltd will be ranked at number 31 amongst 40 banks in India.
Although top management has appointment period of 5 years, generally they retire on ach sieving age of 60 years with an average tenure of only 2 years at the top job.
Profit and Loss Account
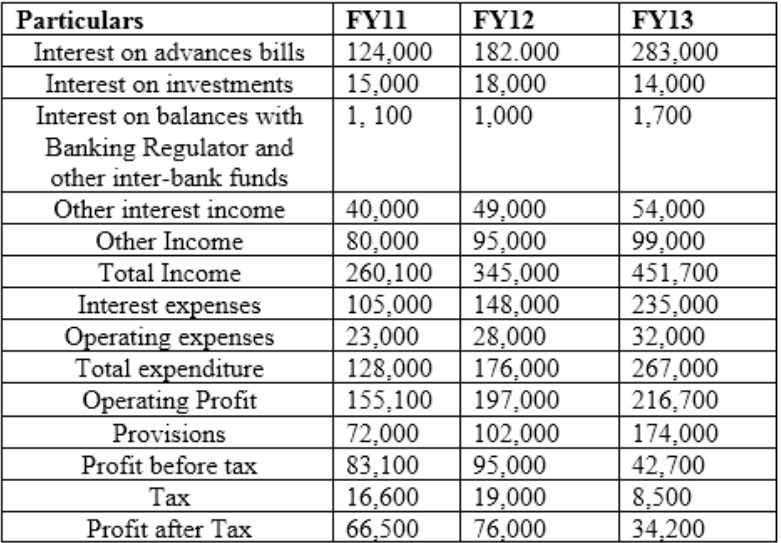
Balance Sheet
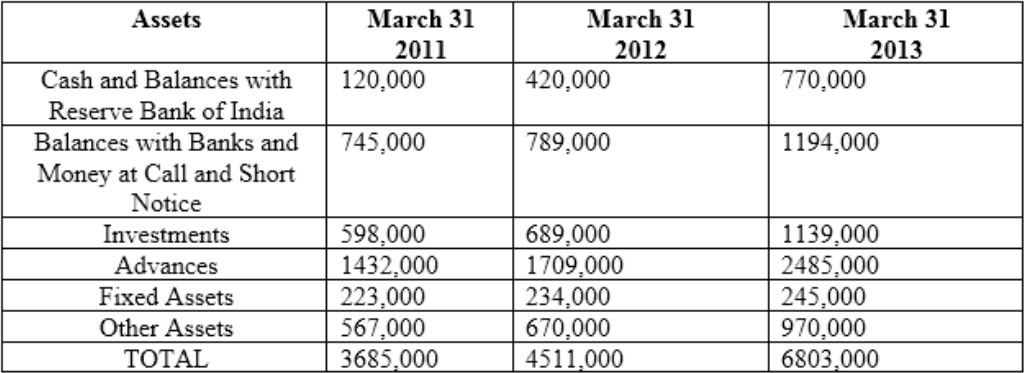
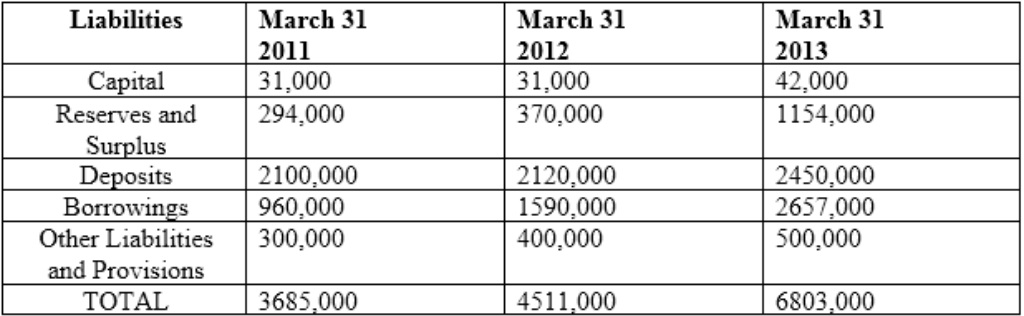
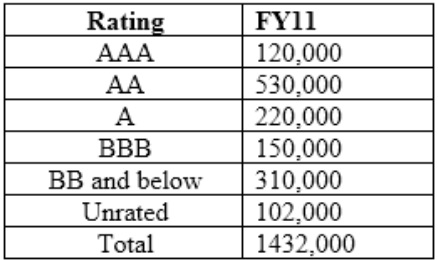
The rating wise break-up of assets for FY11 is as follows:
The ROTA for Auckland deteriorated from ___in FY12 to___ in FY13.
Answer : C