APA Fundamental Payroll Certification FPC-Remote Exam Questions
Under the CCPA, use the following information to calculate the MAXIMUM child support order deduction allowed for an employee supporting a second family and in arrears.
Answer : B
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
Under the Consumer Credit Protection Act (CCPA):
If the employee supports a second family and is in arrears, the maximum garnishment limit is 55% of disposable earnings.
Calculate Disposable Earnings:
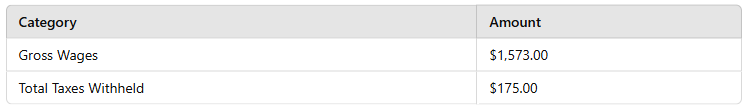
Gross wages: $1,573.00
Less taxes withheld: $175.00
Disposable earnings = $1,573.00 - $175.00 = $1,398.00
Calculate Maximum Child Support Deduction (55% of disposable earnings):
$1,398.00 55% = $768.90
Thus, the correct answer is B. $768.90.
As of December 31, 2024, what is the MAXIMUM amount, if any, a 49-year-old employee can contribute to a 401(k) plan?
Answer : B
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
For 2024, the 401(k) contribution limit is:
$23,000.00 for employees under 50 years old.
$30,500.00 for employees 50 and older (includes $7,500 catch-up contribution).
Since the employee is 49 years old, they do not qualify for the catch-up contribution, so the maximum contribution is $23,000.00.
IRS -- 401(k) Contribution Limits for 2024
Payroll.org -- Retirement Plan Payroll Compliance
All of the following activities are examples of an internal control EXCEPT:
Answer : A
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
Internal controls are processes used to ensure accuracy, security, and compliance in payroll operations. Effective internal controls include:
Option B (Segregating job duties) Prevents fraud by ensuring no one person has full control over payroll.
Option C (Rotating job duties) Reduces fraud risk and enhances cross-training.
Option D (Restricting system access) Protects sensitive payroll data.
Option A (Storing backup files on-site) is incorrect because internal control best practices recommend off-site or cloud backups to protect against data loss from disasters.
Payroll.org -- Payroll Internal Control Procedures
IRS -- Best Practices for Payroll Security
All of the following workflow mapping descriptions are correct EXCEPT:
Answer : D
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
Workflow mapping is a visual representation of payroll processes to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
Option A (Logical thought processes) ensures clarity and eliminates assumptions.
Option B (Depictions of sequences) accurately describes workflow design.
Option C (Steps follow without delay) ensures process efficiency.
Option D is incorrect because it describes Service Level Agreements (SLA), not workflow mapping.
Payroll.org -- Payroll Workflow Mapping Guide
Process Improvement Standards -- Payroll System Optimization
All of the following statements are correct regarding independent contractors EXCEPT that they:
Answer : A
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
Independent contractors do NOT receive a salary. They:
Invoice for services rendered rather than receiving fixed wages.
Risk profit or loss (Option B) based on how they manage expenses.
Can hire assistants (Option C) to help complete tasks.
Can end the relationship at any time (Option D) unless bound by a contract.
Option A (Receive a salary) is incorrect because salaries are paid only to employees, not independent contractors.
IRS -- Independent Contractor vs. Employee Classification
Payroll.org -- Guidelines for Contractor Payments and Taxation
The best practice is to start the annual reconciliation after the:
Answer : A
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
Annual payroll reconciliation ensures that payroll records match tax filings. The best practice is to start reconciliation after completing the W-2 audit, as this verifies:
Employee earnings and tax withholdings
Federal and state tax deposits
Year-end adjustments
Option B is incorrect because quarterly reconciliation is separate from annual reconciliation.
Option C is incorrect because reconciliation should start after verifying W-2s, not just at the year-end.
Option D is incorrect because reconciliation should be based on the prior year, not the first payroll of the new year.
IRS -- Year-End Payroll Reporting Guide
Payroll.org -- Annual Reconciliation Best Practices
A state's minimum wage is $0.60 higher than the federal minimum wage. Under the FLSA, for an employee age 20, what is the MINIMUM hourly rate an employer can pay the employee?
Answer : D
The federal minimum wage is $7.25 per hour.
A state's minimum wage is $0.60 higher, so $7.25 + $0.60 = $7.85.
FLSA requires the higher of state or federal minimum wage.
FLSA Minimum Wage Provisions (Department of Labor)