APICS CPIM-8.0 Certified in Planning and Inventory Management (CPIM 8.0) Exam Practice Test
In which of the following phases of the product life cycle is product price most effective in influencing demand?
Answer : A
Product price is most effective in influencing demand in the introduction phase of the product life cycle, when the product is new and unfamiliar to the market. In this phase, customers are not aware of the product's benefits, features, or quality, and may be reluctant to try it. Therefore, a lower price can help attract customers and stimulate demand, as well as deter potential competitors from entering the market. A lower price can also help the product gain market share and establish a loyal customer base. As the product moves to the growth, maturity, and decline phases, price becomes less effective in influencing demand, as other factors, such as product differentiation, quality, promotion, and customer satisfaction, become more important. Reference:
* Product Life Cycle Explained: Stage and Examples
* The 6 Stages of the Product Life Cycle [+Examples]
* Product Life Cycle - Definition, Stages, Usage
Which of the following circumstances would cause a move from acceptance sampling to 100% inspection?
Answer : C
Acceptance sampling is a statistical quality control technique that involves inspecting a sample of products or materials from a lot and deciding whether to accept or reject the lot based on the sample results1. Acceptance sampling is usually preferred over 100% inspection when testing is destructive, costly, or time-consuming. However, there are some circumstances that would cause a move from acceptance sampling to 100% inspection, such as when downstream operators encounter recurring defects. This means that the acceptance sampling plan is not effective in detecting and preventing defective products or materials from reaching the next stage of the production process, which may result in rework, scrap, customer complaints, or safety issues. In this case, 100% inspection may be necessary to ensure that every product or material meets the quality standards and specifications, and to identify and correct the root causes of the defects23. Reference: 1 Acceptance sampling - Wikipedia 4 2 100% Inspection or Sampling Inspection? Which is Best5 3 CPIM Exam Reference - Association for Supply Chain Management 1
Which of the following capacity planning methods uses the master production schedule (MPS) as its primary input?
Answer : B
Rough-cut capacity planning (RCCP) is a type of capacity planning method that uses the master production schedule (MPS) as its primary input. RCCP is a technique for checking the feasibility of the MPS by comparing the available capacity of critical resources (such as machines, labor, or materials) with the capacity required by the MPS. RCCP helps to identify and resolve any potential capacity problems or bottlenecks at an aggregate level, before committing to the MPS. RCCP can also be used to evaluate alternative MPS scenarios and to support the sales and operations planning (S&OP) process12. Reference: 1 Rough Cut Capacity Planning (RCCP) - Definition, Example, and ... 3 2 CPIM Exam Reference - Association for Supply Chain Management
Exhibit:
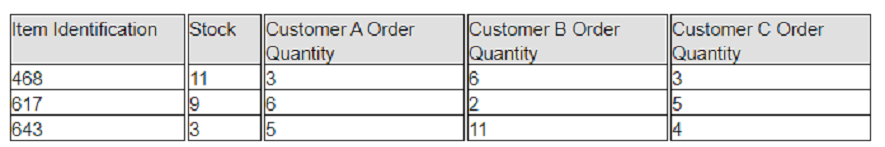
A company has prioritized customers A, B, and C, filling orders in that sequence. What are the impacts to customer service levels for customers B and C?
Answer : B
Customer service level is the percentage of customer orders that are fulfilled on time and in full1. A company that prioritizes customers A, B, and C, filling orders in that sequence, will have different impacts on the service levels for customers B and C, depending on the availability of stock and the order quantities. Based on the table in the exhibit, customer B will have a higher service level than customer C, because customer B will receive all the ordered units for item 468 and item 617, while customer C will only receive partial units for item 468 and none for item 617. Customer C will also receive none of the ordered units for item 643, while customer B will receive some of them. Therefore, customer B will have a higher percentage of orders fulfilled on time and in full than customer C. Reference: 1 Customer Service Level: Definition, Standards, Measuring | SupportYourApp 2
Improvements in an Input/output control (I/O control) system will most likely lead to:
Answer : C
Improvements in an input/output control (I/O control) system will most likely lead to a reduction in queue size and queue time. An I/O control system is a method of managing the flow of work orders in a production system by matching the input rate to the output rate. The input rate is the number of work orders that are released to the shop floor in a given period. The output rate is the number of work orders that are completed and shipped to the customers in a given period. An I/O control system aims to keep the input rate equal to the output rate, or slightly lower, to avoid overloading the system and creating excess inventory. By improving the I/O control system, the production system can achieve a smoother and more balanced flow of work orders, which reduces the queue size and queue time at each work center. Queue size is the number of work orders that are waiting to be processed at a work center. Queue time is the amount of time that a work order spends in the queue before being processed. A reduction in queue size and queue time can improve the production efficiency, quality, and flexibility, as well as the customer service and satisfaction. The other options are not correct, as they are not the most likely outcomes of improvements in an I/O control system, but rather possible effects of other factors or methods:
Flattened bills of material (BOMs) are the result of simplifying the product structure and reducing the number of components or levels in a BOM. Flattened BOMs can reduce the complexity and lead time of the production process, but they are not directly related to the I/O control system.
A change in operation sequencing is the result of altering the order or priority of the work orders or operations in a production system. A change in operation sequencing can affect the production flow and capacity, but it is not necessarily caused by the I/O control system.
Fewer engineering change notifications are the result of minimizing the changes in the product design or specification during the production process. Fewer engineering change notifications can reduce the disruption and cost of the production process, but they are not directly related to the I/O control system.Reference:
[CPIM Part 2 - Section A - Topic 2 - Capacity Planning]
Input/Output Control | SpringerLink
Input/Output Control - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Input/Output Control - InventoryOps.com