APICS Certified in Planning and Inventory Management (Part 2) CPIM-Part-2 Exam Questions
Which of the following factors is considered a carrying cost?
Answer : C
The other options are not considered carrying costs, because they are not related to holding inventory in stock. Setup is the cost of preparing a machine or a process for production. Transportation is the cost of moving goods from one place to another. Scrap rate is the percentage of defective or unusable units produced in a process. These costs are more related to production or distribution activities than inventory holding activities.
The production plan relates to a firm's financial planning because it is used to:
Answer : D
The production plan is a statement of the resources needed to meet the aggregate demand plan over a medium-term horizon. The production plan is the output of the supply planning step in the sales and operations planning (S&OP) process. The production plan relates to a firm's financial planning because it is used to identify future cash needs. Cash needs are the amount of money that a firm requires to operate and grow its business. Cash needs can be influenced by various factors, such as sales revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, capital expenditures, inventory levels, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and taxes. The production plan can help to estimate the cash inflows and outflows associated with these factors, and to determine the optimal balance between them. The production plan can also help to identify the potential sources and uses of cash, such as borrowing, investing, or paying dividends. By identifying future cash needs, the production plan can help to improve the firm's liquidity, profitability, and solvency.
Ergonomic workstation design should incorporate:
Answer : B
Ergonomic workstation design should incorporate the reduction of repetitive motion, as this can help prevent musculoskeletal disorders, fatigue, and errors. Repetitive motion can cause strain on the muscles, tendons, and nerves, leading to pain, inflammation, and loss of function. Ergonomic workstation design can reduce repetitive motion by optimizing the layout of the workstation, tools, and materials, using automation or mechanization where possible, and varying the tasks performed by the worker.Reference: CPIM Part 2 Exam Content Manual, Domain 8: Manage Quality, Continuous Improvement, and Technology, Section A: Quality Management, Subsection 3: Quality Tools and Techniques, Page 37.
Work Center 1 has an available capacity of 1,200 hours per month. Which of the following amounts represents the cumulative difference between the required capacity and the available capacity of Months 1 through 37
Answer : B
To find the cumulative difference between the required capacity and the available capacity of Months 1 through 37, we need to sum up the differences for each month. The difference for each month is calculated by subtracting the available capacity from the required capacity. The available capacity of Work Center 1 is given as 1,200 hours per month, while the required capacity for each month is given in the table below:
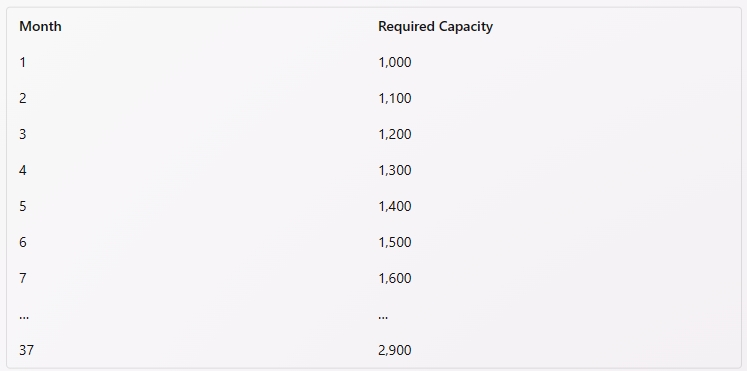
The difference for each month is then:

The cumulative difference is the sum of all the differences:
-200 -100 +0 +100 +200 +300 +400 + ... +1,700 =150
What is the shortest manufacturing lead time required for 10 units of Item A assuming that it must complete Operations 10, 20, and 30 in a work cell, and these operations require no set up time''?
Answer : B
Manufacturing lead time = Preprocessing time + Processing time + Postprocessing time
In this question, we are given the following information:
The product is Item A, which requires Operations 10, 20, and 30 in a work cell
The order quantity is 10 units
The operations require no set up time
The processing times for each operation are:
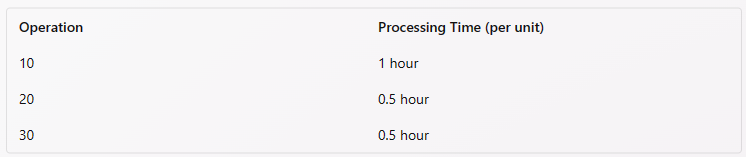
To find the shortest manufacturing lead time, we need to assume that the preprocessing and postprocessing times are zero, and that the operations can be performed in parallel. This means that the work cell can process 10 units of Item A simultaneously, without any waiting or transportation time.
Therefore, the shortest manufacturing lead time is equal to the longest processing time among the three operations. Since Operation 10 has the longest processing time of 1 hour per unit, the shortest manufacturing lead time is:
Manufacturing lead time = 1 hour x 10 units = 10 hours
However, this answer is not among the options given. Therefore, we need to consider another possibility: that the work cell can only process one unit of Item A at a time, and that the operations must be performed in sequence. This means that each unit of Item A must complete Operation 10 before moving to Operation 20, and then to Operation 30. In this case, the shortest manufacturing lead time is equal to the sum of the processing times for all three operations multiplied by the order quantity. Therefore, the shortest manufacturing lead time is:
Manufacturing lead time = (1 hour + 0.5 hour + 0.5 hour) x 10 units = 20 hours
However, this answer is also not among the options given. Therefore, we need to consider one more possibility: that the work cell can process one unit of Item A at a time, but that the operations can be performed in parallel with overlapping times. This means that as soon as one unit of Item A finishes Operation 10, it moves to Operation 20, while another unit of Item A starts Operation 10. Similarly, as soon as one unit of Item A finishes Operation 20, it moves to Operation 30, while another unit of Item A starts Operation 20. In this case, the shortest manufacturing lead time is equal to the sum of the processing times for all three operations plus the processing times for each operation multiplied by the order quantity minus one. Therefore, the shortest manufacturing lead time is:
Manufacturing lead time = (1 hour + 0.5 hour + 0.5 hour) + (1 hour + 0.5 hour + 0.5 hour) x (10 units - 1) = 12 hours
This answer is among the options given and it is the shortest possible manufacturing lead time under these assumptions. Therefore, the correct answer is B. 12 hours.
A 58 environment should be maintained for which of the following reasons?
Answer : B
A 5S environment is a type of workplace organization method that uses a list of five Japanese words: seiri (sort), seiton (set in order), seiso (shine), seiketsu (standardize), and shitsuke (sustain). The goal of 5S is to create a clean, uncluttered, safe, and well organized workplace that helps reduce waste and optimize productivity. A 5S environment should be maintained for the following reason:
To support standard work: Standard work is a set of documented procedures that define the best way to perform a task or process. Standard work helps to ensure quality, efficiency, safety, and consistency. A 5S environment supports standard work by providing a clear and visible layout of the work area, tools, materials, and instructions. A 5S environment also helps to maintain the condition and performance of the equipment and facilities. A 5S environment enables workers to follow standard work easily and effectively.
One way to mitigate liability risk in the supply chain is to:
Answer : B
The other options are not effective ways to mitigate liability risk in the supply chain. Negotiating lower component cost may reduce the procurement expenses, but it may also compromise the quality and safety of the components, which may increase the liability risk. Pushing inventory to supplier locations may reduce the inventory carrying costs and risks, but it may also increase the dependency and vulnerability on the suppliers, which may expose the company to more liability risk. Using LTL shipments more frequently may reduce the transportation costs and emissions, but it may also increase the handling and damage risks of the products, which may affect the customer satisfaction and liability.