ARDMS Abdomen Sonography Examination AB-Abdomen Exam Practice Test
Which laboratory value stays elevated longest and is considered the most reliable in diagnosing pancreatitis?
Answer : A
Lipase is the most sensitive and specific laboratory marker for diagnosing acute pancreatitis. It rises earlier, remains elevated longer (up to 14 days), and is more pancreas-specific than amylase. Amylase may normalize within 48-72 hours and may also be elevated in non-pancreatic conditions.
According to ACG (American College of Gastroenterology) Guidelines:
''Serum lipase is preferred over amylase due to its higher sensitivity, specificity, and prolonged elevation in pancreatitis.''
American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) Clinical Guideline: Management of Acute Pancreatitis, 2013.
Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, Levine D. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 5th ed. Elsevier, 2017.
---
Which pancreatic condition is commonly associated with complete or partial atresia of the duodenum?
Answer : D
Annular pancreas is a congenital anomaly in which pancreatic tissue encircles the second part of the duodenum, potentially causing partial or complete duodenal obstruction (atresia). It is due to abnormal migration of the ventral pancreatic bud.
According to Rumack's Diagnostic Ultrasound:
''Annular pancreas results from failure of the ventral pancreatic bud to rotate properly, leading to encirclement of the duodenum.''
Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, Levine D. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 5th ed. Elsevier, 2017.
Moore KL, Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 8th ed. Wolters Kluwer, 2018.
---
Which condition is demonstrated in this image?
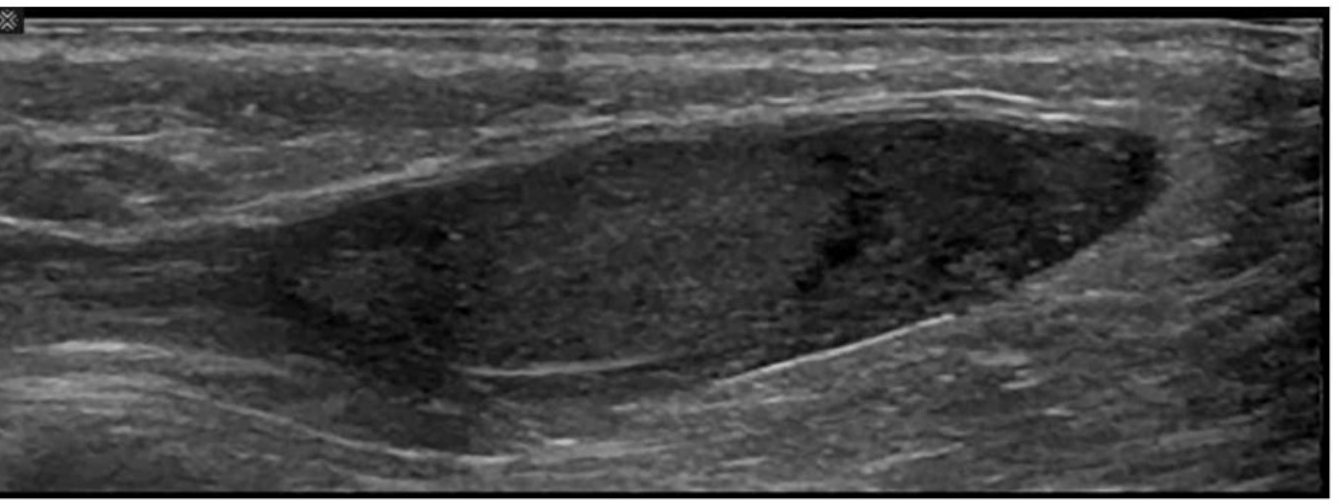
Answer : D
The ultrasound image shows an ovoid, homogeneously hypoechoic soft tissue structure located in the inguinal canal, surrounded by echogenic fat and soft tissue. This is consistent with an undescended testis, also known as cryptorchidism.
Cryptorchidism refers to the failure of one or both testes to descend into the scrotal sac. On ultrasound, the undescended testis typically appears:
Ovoid in shape
Homogeneous and hypoechoic compared to scrotal testis
Located in the inguinal canal or, less commonly, within the abdomen
Smaller in size than a normally descended testis
Comparison of answer choices:
A . Bell clapper deformity refers to an anatomic predisposition for testicular torsion where the tunica vaginalis surrounds the entire testis and epididymis---usually a clinical rather than directly sonographic diagnosis.
B . Inguinal hernia appears as bowel or omentum within the inguinal canal or scrotum with peristalsis or fat---no bowel loops are seen here.
C . Pyocele is a complex fluid collection around the testis (usually with septations and internal echoes)---not evident in this image.
D . Cryptorchidism --- Correct. The findings match those of an undescended testis in the inguinal canal.
Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, Levine D. Diagnostic Ultrasound, 5th ed. Elsevier; 2017.
Dogra VS, Gottlieb RH, Rubens DJ, Oka M. Sonography of the scrotum. Radiology. 2003;227(1):18--36.
AIUM Practice Parameter for the Performance of Scrotal Ultrasound Examinations (2021).
Which technique best differentiates a bladder mass from a hematoma?
Answer : D
Changing the patient's position allows evaluation of lesion mobility. Blood clots and hematomas are often mobile, while true bladder wall masses remain fixed. This technique helps differentiate between solid masses and non-adherent debris.
According to Rumack's Diagnostic Ultrasound:
''Changing patient position may distinguish between mobile blood clots and fixed bladder wall masses.''
Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, Levine D. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 5th ed. Elsevier, 2017.
AIUM Practice Parameter for Bladder Ultrasound, 2020.
In which position should a patient be placed when internal echoes are seen within a fluid-filled bladder?
Answer : C
Lateral decubitus positioning allows shifting of internal echoes within the bladder, helping differentiate mobile debris (such as blood clots or sediment) from adherent masses like tumors. This technique is helpful in evaluating questionable bladder filling defects.
According to Rumack's Diagnostic Ultrasound:
''Changing the patient's position, such as turning to the lateral decubitus, can help distinguish mobile debris from attached bladder wall lesions.''
Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, Levine D. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 5th ed. Elsevier, 2017.
AIUM Practice Parameter for Bladder Ultrasound, 2020.
A patient presents with ampulla of Vater obstruction, distention of the gallbladder, and painless jaundice. Which condition is most likely associated with these findings?
Answer : C
Courvoisier sign describes the clinical finding of painless jaundice combined with a palpable, distended gallbladder. This typically results from obstruction at the distal common bile duct, often due to pancreatic head carcinoma or cholangiocarcinoma, leading to bile accumulation and gallbladder distention. In contrast, Mirizzi syndrome involves compression of the common hepatic duct by an impacted stone in the cystic duct.
According to Rumack's Diagnostic Ultrasound and standard clinical references:
''Courvoisier sign refers to a palpable, enlarged gallbladder due to obstruction of the distal bile duct, often from malignancy.''
Rumack CM, Wilson SR, Charboneau JW, Levine D. Diagnostic Ultrasound. 5th ed. Elsevier, 2017.
Moore KL. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 8th ed. Wolters Kluwer, 2018.
---
What is the main purpose for performing focused abdominal sonography for trauma (FAST) exams?
Answer : A
The FAST exam is primarily used to detect free intraperitoneal or pericardial fluid in trauma patients, serving as a rapid, bedside assessment tool. While organ injuries may be suspected, the FAST exam is not primarily designed to assess for solid organ lacerations.
According to AIUM and ACEP guidelines:
''The primary goal of the FAST exam is to detect the presence of free fluid suggestive of hemorrhage in trauma patients.''
American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP) Ultrasound Guidelines, 2016.
AIUM Practice Parameter for the Performance of the FAST Examination, 2020.
---