ASQ Quality Engineer CQE Exam Practice Test
The effectiveness of corrective action can best be assessed by
Answer : D
The effectiveness of corrective action can best be assessed by measuring the results of the corrective action. This involves evaluating whether the action taken has successfully addressed the root cause of the problem and has led to a measurable improvement in the quality metrics or process performance. Reference:
ASQ Quality Press: The Certified Quality Engineer Handbook.
Total Quality Management by Dale H. Besterfield.
Temperature measured in degrees centigrade is an example of what type of measurement scale?
Answer : D
Temperature measured in degrees centigrade is an example of an interval measurement scale. The interval scale is characterized by having equal intervals between measurements, but it does not have a true zero point. This means that while the difference between temperatures can be measured, there is no absolute zero where the absence of temperature is defined. Reference:
Fundamentals of Quality Control and Improvement by Amitava Mitra.
Measurement and Data Analysis for Engineering and Science by Patrick F. Dunn.
Refer to the exhibit.
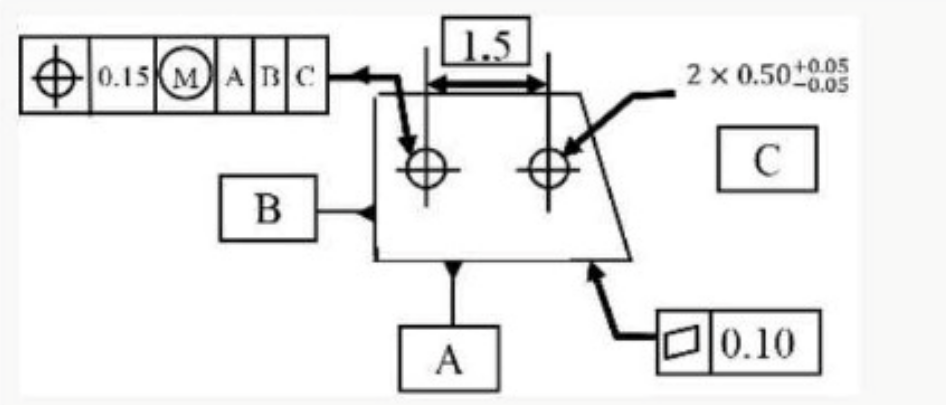
A in this drawing, the symbol is being used to indicate the
Answer : C
In the provided drawing, the symbol marked 'A' is being used to indicate a datum. A datum is a reference point, line, or surface used as a basis for measurement and to establish the location or orientation of other features. It serves as a starting point for dimensional control and ensures consistency in the manufacturing process.
'Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing' by Alex Krulikowski
ASME Y14.5 - 2009 (Dimensioning and Tolerancing)
Failure mode, effect, and criticality analysis, (FMECA) is primarily for the purpose of
Answer : B
If the probability of two cars starting on a cold morning is 0.6 for each car. what is the probability of at least one of the cars starting?
Answer : D
To find the probability of at least one car starting on a cold morning, we can use the complement rule.
Determine the probability of one car not starting:
Probability of a car starting: P(start)=0.6P(\text{start}) = 0.6P(start)=0.6
Probability of a car not starting: P(notstart)=10.6=0.4P(\text{not start}) = 1 - 0.6 = 0.4P(notstart)=10.6=0.4
Determine the probability of neither car starting:
Since the cars are independent, the probability of both cars not starting is: P(bothnotstart)=0.40.4=0.16P(\text{both not start}) = 0.4 \times 0.4 = 0.16P(bothnotstart)=0.40.4=0.16
Determine the probability of at least one car starting:
P(atleastonestarts)=1P(bothnotstart)=10.16=0.84P(\text{at least one starts}) = 1 - P(\text{both not start}) = 1 - 0.16 = 0.84P(atleastonestarts)=1P(bothnotstart)=10.16=0.84
After attempting to prevent or control risk, which of the following types of risk will remain?
Answer : B
In risk management, after measures have been taken to prevent or control risks, some risks will still remain. These are known as residual risks.
Inherent Risk:
The risk present before any control measures are applied.
Residual Risk:
The risk that remains after preventive and control measures have been implemented.
It is the risk that the organization decides to accept and manage, rather than eliminating entirely.
Control Risk:
The risk that controls will fail to prevent or detect a risk.
Credit Risk:
The risk of a financial loss due to a borrower's failure to repay a loan.
Residual risk is the remaining risk after all control measures are applied.
The number of runs required by a full-factorial design with three factors each at two levels is equal to
Answer : B
In a full-factorial design with three factors, each at two levels, the total number of runs required is calculated by 2n2^n2n, where nnn is the number of factors. For three factors, 23=82^3 = 823=8. Thus, 8 runs are required to cover all possible combinations of factor levels.
'Design and Analysis of Experiments' by Douglas C. Montgomery
ASQ Quality Glossary