CFA Institute CFA Level II Chartered Financial Analyst CFA-Level-II Exam Questions
Jonathan Weil, CFA, is the managing director of Weil Capital Management (WCM). Weil has decided to reevaluate the asset backed security (ABS) positions in his investors' portfolios since a recent, and severe, credit problem in the subprime lending industry has had ripple effects on other fixed-income markets. Weil expects the interest rate term structure to remain flat, but shift upward as credit terms tighten. Weil has asked one of his analysts, Vanessa Ordon, to assist him in analyzing potential ABS investments, including some products he is unfamiliar with.
Ordon provides an assessment of ABS backed by auto loans, credit card receivables, and closed end home equity loans. Ordon has assembled the following information on the collateral, credit enhancements, and prepayment risk associated with each type of ABS.
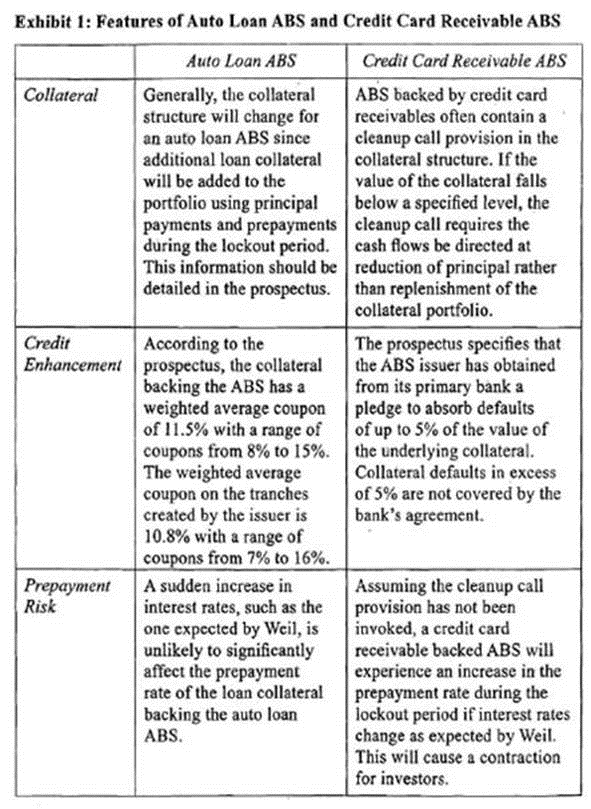
Ordon has also assembled the following information on the structure of a closed end home equity loan (HEL) asset backed security. Ordon has presented the security to Weil as a potential investment opportunity, but Weil is concerned about its default and prepayment risks. The HEL ABS does not have a shifting interest mechanism.
Ordon has also developed an assessment of mortgage backed securities (MBS). Ordon has assembled the following information related to a mortgage backed security.
Which of the following best describes the initial reaction of the home equity loan backed ABS Ordon presented to Weil if there is a collateral default of $30 million?
Answer : A
The home equity loan ABS has an internal credit enhancement known as over-collateralization. The principal of the collateral equals $475 million. The principal of the tranches, however, totals only $450 million (180 + 112.5 + 67.5 + 36 + 54). The over-collatcralization feature is included in ABS to protect the tranches from collateral defaults. Thus $25 million of the $30 million default stated in the question would first be absorbed by the extra collateral. This leaves a $5 million default that must be absorbed by one of the tranches. Tranche E has been subordinated to Tranches A - D, a structure known as credit tranching. Losses resulting from defaults (a credit event) are absorbed by Tranche E first until the principal backing the tranche is exhausted. The remaining $5 million default gets absorbed by Tranche E, reducing the principal to $49 million (54 - 5). (Study Session 15, LOS 56.b,e)
Robert Williams is a junior analyst at Anderson Brothers, a large Wall Street brokerage firm. He reports to Will McDonald, the chief economist for Anderson Brothers. McDonald provides economic research, forecasts, and interpretation of economic data to all of Anderson's investment departments, as well as the firm's clients. McDonald has asked Williams to analyze economic trends in the country of Bundovia. The currency of Bundovia is the Bunco (BU).
Williams first analyzes the effect of rising nominal Bundovian interest rates relative to U.S interest rates on the supply and demand for BU. He determines that the increase in Bundovian nominal interest rates would increase the demand for BU and, because the BU supply curve is upward sloping, the BU will appreciate and the equilibrium quantity of BU will increase proportionately.
Bundovia has announced plans to impose either a tariff or a quota on semiconductor imports from the United States. McDonald also asks Williams to analyze the potential effect on Bundovian Semiconductors, the dominant semiconductor manufacturer located in Bundovia. Currently, Bundovian Semiconductors is not competitive in the global semiconductor market because its higher production costs make it unable to generate profits at the current world market price. Williams concludes that the imposition of either a tariff or quotas would benefit Bundovian Semiconductors. The company would become competitive with foreign producers in its domestic semiconductor market because imports would be reduced and domestic production would rise.
Exhibit 1 shows the trend in the average BU/USD exchange rate over the past three years.
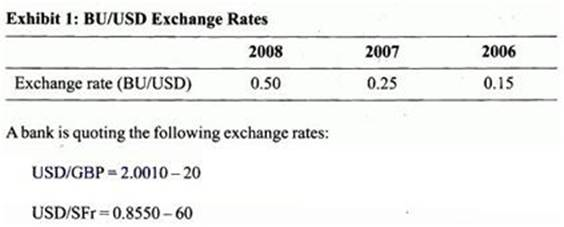
Williams asks the bank for a GBP/SFr cross rate.
From the same bank, Williams receives the following forward rate quotes in the USD/GBP market:
* 30-day forward rate: USD/GBP = USD/GBP = 2.0045 - 55
* 60-day forward rate: USD/GBP = USD/GBP = 2.0075 - 85
Williams has uncovered a potential arbitrage opportunity in the foreign exchange markets. The current spot rate is $2.00 per BU. The Bundovian risk-free interest rate is 3%, and the one-year forward rate is $2.10 per BU. The U .S . risk-free rate is 5%.
From 2006 to 2008, the Bunco has:
Answer : B
The BU/USD exchange rate is increasing over time, which means the USD has appreciated relative to the BU, and the BU has depreciated relative to the USD. Another way to see this is to recognize that it .takes more BU to buy one USD in 2008 than in 2006, which means the BU is depreciating relative to the U .S . dollar. Because the BU has depreciated, Bundovian residents will find U .S . goods more expensive. (Study Session 4, LOS 17.a)
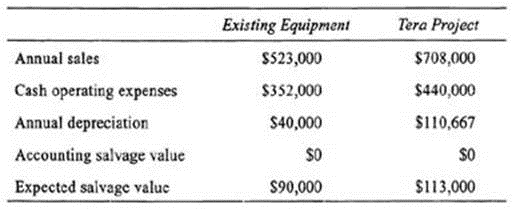
GigaTech Inc. is a large U .S .-based technology conglomerate. The firm has business units in three primary categories: hardware manufacturing, software development, and consulting services. Because of the rapid pace of technological innovation, GigaTech must make capital investments every two to four years. The company has identified several potential investment opportunities for its hardware manufacturing division. The first of these opportunities, Tera Project, would replace a portion of GigaTech's microprocessor assembly equipment with new machinery expected to last three years. The current machinery has a book value of $120,000 and a market value of $195,000. Tcra Project would require purchasing machinery for $332,000, increasing current assets by 5190,000, and increasing current liabilities by $80,000. GigaTech has a tax rate of 40%. Additional pro forma information related to the Tera Project is provided in the following table:
Analysts at GigaTech have noted that investment in the Tera Project can be delayed for up to nine months if managers at the company decide this is necessary. However, once the capital investment is made, the project will be necessary to maintain continuing operations. Tera Project can be scaled up with more equipment requiring less capital than the original investment if results are meeting expectations. In addition, the equipment used in Tera Project can be used in shift work if brief excess demand is expected.
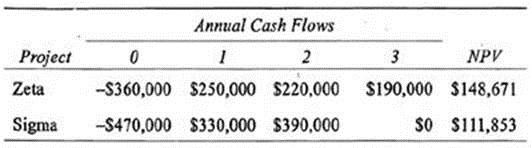
GigaTech is also considering expanding its software development operations in India. Software development equipment must be continually replaced to maintain efficiency as newer and faster technology is developed. The company has identified two mutually exclusive potential expansion projects, Zeta and Sigma. Zeta requires investing in equipment with a 3-year life, while Sigma requires investing in equipment with a 2-year life. GigaTech has estimated real capital costs for the two projects at 10.58%. GigaTech expects inflation to be approximately 4.0% for the foreseeable future. Nominal cash flows and net present values for the Zeta and Sigma projects are provided in the following table:
Recently, GigaTechs board of directors has become concerned with the firm's capital budgeting decisions and has asked management to provide a detailed explanation of the capital budgeting process. After reviewing the report from management, the board makes the following comments in a memo:
* The capital rationing system being utilized is fundamentally flawed since, in some instances, projects that do not increase earnings per share are selected over projects that do increase earnings per share.
* The cash flow projections are flawed since they fail to include costs incurred in the search for projects or the economic consequences of increased competition resulting from highly profitable projects.
* We are making inappropriate investment decisions since the discount rate used to evaluate all potential projects is the firm's weighted average cost of capital.
Using the least common multiple of lives approach, determine whether the Zeta Project or the Sigma Project will increase the value of GigaTech by a greater amount.
Answer : B
The least common multiple of lives approach requires estimating the least common denominator between two mutually exclusive projects with unequal lives. Since the Zeta and Sigma projects have lives of 3 and 2, the least common multiple is 6. The cash flows must be stated over a 6-year period, repeating the cash flow pattern as often as necessary (twice for Zeta and three times for Sigma). The cash flows are then discounted to And rhe net present value (NPV). The project with the highest NPV is selected. The cash flows are as follows:
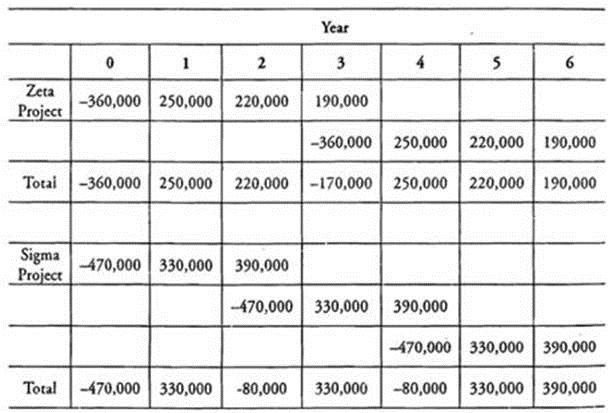
Before calculating the NPV of each project, the cost of capital must be restated in nominal terms since the cash flow projections are stated in nominal terms. The nominal cost of capital is equal to 15-0% = (1 + O.1058)(l + 0.04). The NPV of each project is calculated as follows:
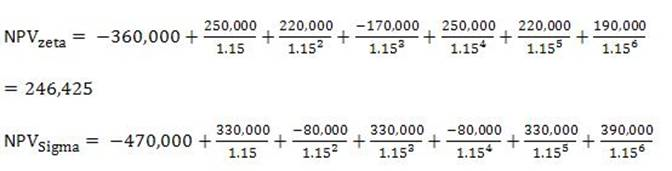
Since its NPV is greater, GigaTcch should select the Sigma project. (Study Session 8, LOS 27.c)
Jonathan Adams, CFA, is doing some scenario analysis on forward contracts. The process involves pricing the forward contracts and then estimating their values based on likely scenarios provided by the firm's forecasting and strategy departments. The forward contracts with which Adams is most concerned are those on fixed income securities, interest rates, and currencies.
The first contract he needs to price is a 270-day forward on a $1 million Treasury bond with ten years remaining to maturity. The bond has a 5% coupon rate, has just made a coupon payment, and will make its next two coupon payments in 182 days and in 365 days. It is currently selling for 98.25. The effective annual risk-free rate is 4%. Adams is also analyzing forward rate agreements (FRAs).
The LIBOR spot curve is as follows:
The LIBOR spot curve is as follows:

Finally, Adams wants to price and value a currency forward on euros. The euro spot rate is $1.1854. The dollar risk-free rate is 3%, and the euro risk-free rate is 4%.
Suppose that at maturity of the forward contract on euros the spot rate is greater than the forward rate at the initiation of the contract. Which party is exposed to credit risk, and why?
Exposed to credit risk Reason
Answer : B
If the spot rate for euros at maturity is greater than the forward contract rate at initiation, the long (euros) position value is positive and the short position value is negative. Because the short owes the long, the long has credit risk. (Study Session 16, LOS 58.d)
Ivan Johnson is reviewing the investment merits of BioTLab, a fast-growing biotechnology company. BioTLab has developed several drugs, which arc being licensed to major drug companies. BioTLab also has several drugs in phase III trials (phase III trials are the last testing stage before FDA approval). Johnson notes that two drugs recently received approval which should provide BioTLab solid revenue growth and generate predictable cash flow well into the future. Based on the potential for the two drugs, BioTLab's estimated annual cash flow growth rate for the next two years is 25%, and long-term growth is expected to be 12%. Because of BioTLab's attractive investment opportunities, the company does not pay a dividend. BioTLab's current weighted average cost of capital is 15% and its stock is currently trading at $50 per share. Financial information for BioTLab for the most recent 12 months is provided below:
* Net working capita! excluding cash increased from $7,460,000 to $9,985,000;
* Book value increased from $81,250,000 to $101,250,000.
* BioTLab currently has no debt.
* Research facilities and production equipment were purchased for $8,450,000.
* BioTLab held non-operating assets in the amount of $875,000.
* Net income for the 12 months was $20,000,000.
* BioTLab has a marginal tax rate of 40%.
* Noncash charges for depreciation and restructuring for the 12 months were $1,250,000.
BioTLab's management has indicated an interest in establishing a dividend and will fund new drug research by issuing additional debt.
Johnson also reviews a competitor to BioTLab, Groh Group, which has a larger segment operating in a highly cyclical business. The Groh Group has a debt to equity ratio of 1.0 and pays no dividends. In addition, Groh Group plans to issue bonds in the coming year.
Using a two-stage, free cash flow to the firm model, determine which of the following is closest to the value of BioTLab.
Answer : C
Free cash flow to the firm (FCFF) can be calculated in many ways but in this question, you are given enough information to calculate the measure in the following way:
FCFF = net income + non-cash charges + interest (1 - t) - fixed capital investment -working capital investment
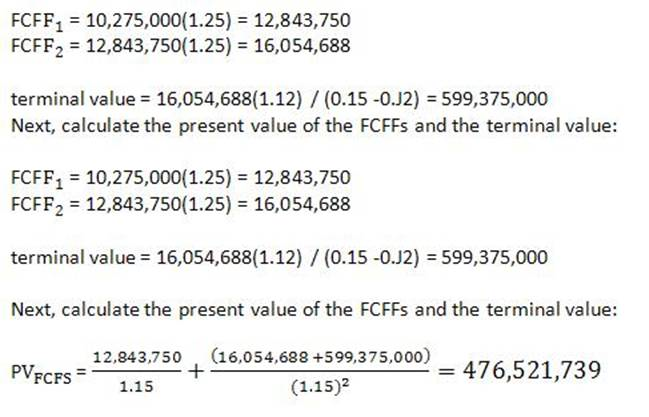
If a firm has non-operating assets (e.g., land held for investment) on its balance sheet, the value of these assets must be added to the value of the operating assets (determined using the present value of the FCFFs and terminal value) to find the total firm value.
Total firm value = value of operating assets + value of non-operating assets
Total firm value = 476,521,739 + 875,000 = 477,396,739
(Study Session 12. LOS 41.k)
Emily De Jong, CFA, works for Charles & Williams Associates, a medium-sized investment firm operating in the northeastern United States. Emily is responsible for producing financial reports to use as tools to attract new clients. It is now early in 2009, and Emily is reviewing information for O'Connor Textiles and finalizing a report that will be used for an important presentation to a potential investor at the end of the week.
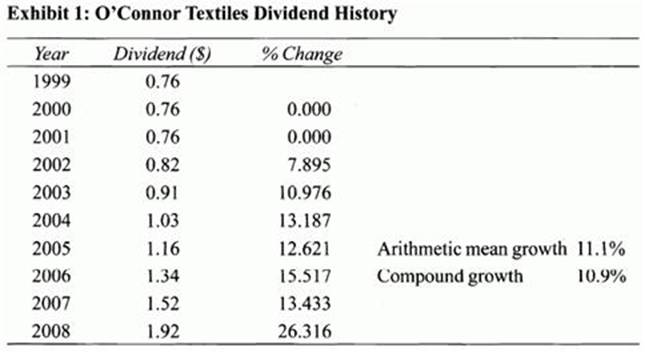
Following an acquisition of a major competitor in 1992, O'Connor went public in 1993 and paid its first dividend in 1999. Dividends are paid at the end of the year. After 2008, dividends are expected to grow for three years at 11%: $2.13 in 2009, $2.36 in 2010, and $2.63 in 2011. The average of the arithmetic and compound growth rates are given in Exhibit 1. Dividends are then expected to settle down to a long-term growth rate of 4%. O'Connor's current share price of $70 is expected to rise to $72.92 by the end of the year according to the consensus of analysts' forecasts.
O'Connor's annual dividend history is shown in Exhibit 1.
De Jong is also considering whether or not she should value O'Connor using a free cash flow model instead of the dividend discount model.

The output from the regression appears in Exhibit 2.
De Jong determines that employing the CAPM to estimate the required return on equity suffers from the following sources of error:
* Estimation of the model's inputs (e.g., the market risk premium). The company's dividend payment schedule.
* The accuracy of the beta estimate.
* Whether or not the model is the appropriate one to use.
De Jong observes that two reputable statistical analysis firms estimate betas for O'Connor stock at 0.85 and 1.10. She concludes that the differences between her beta estimate and the published estimates resulted from her use of standard errors in her regression to correct for serial correlation; the other firms did not make a similar adjustment.
De Jong considers using adjusted beta in her analysis. Typically, her company uses 1/3 for the value of .

She determines that her adjusted beta forecast will be closer to the mean reverting level using this value than it would be using a value of 1/3.
The required return on equity (according to the CAPM) for O'Connor is closest to:
Answer : B
The beta of 1.04 is estimated from the slope coefficient on the independent variable (the return on the market) from the regression.
Factor Analytics Capital Management makes portfolio recommendations using various factor models. Mauricio Rodriguez, a Factor Analytics research analyst, is examining the prospects of two portfolios, the FACM Century Fund (CF) and the FACM Esquire Fund (EF).
The variance of returns are identical for the two funds. The estimates in Exhibit 1 were derived for CF and EF using monthly data for the past five years.
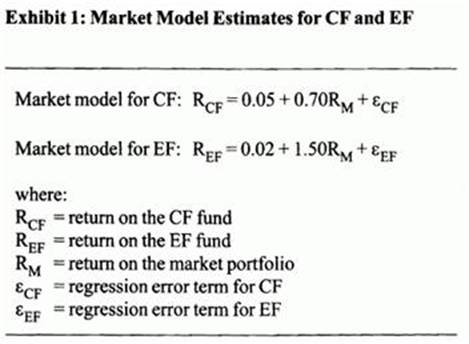
Supervisor Barbara Woodson asks Rodriguez to use the Capita! Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and a multifactor model (APT) to make a decision to continue or discontinue the EF fund. The two factors in the multifactor model are not identified. To help with the decision, Woodson provides Rodriguez with the capital market forecasts in Exhibit 2.

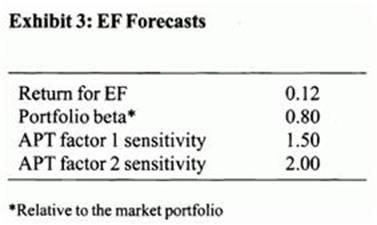
After examining the prospects for the EF portfolio, Rodriguez derives the forecasts in Exhibit 3.
Rodriguez also develops a 2-factor macroeconomic factor model for the EF portfolio. The two factors used in the model are the surprise in GDP growth and the surprise in Investor Sentiment. The equation for the macro factor model is:

During an investment committee meeting, Woodson makes the following statements related to the 2-factor macroeconomic factor model.
Statement 1: An investment combination in CF and EF that provides a GDP growth factor beta equal to one and an Investor Sentiment factor beta equal to zero will have lower active factor risk than a tracking portfolio consisting of CF and EF.
Statement 2: When markets are in equilibrium, no combination of CF and EF will produce an arbitrage opportunity
In their final meeting, Rodriguez informs Woodson that the CF portfolio consistently outperformed its benchmark over the past five years. Rodriguez makes the following comments to Woodson: "The consistency with which CF outperformed its benchmark is amazing. The difference between the CF monthly return and its benchmark return was nearly always positive and varied little over time."
Using data provided in Exhibit 2, the intercept and slope of the Security Market Line (SML) are closest to: Intercept Slope
Answer : C
The SML is the graph of the CAPM:
