CIPS Commercial Negotiation L4M5 Exam Practice Test
The National Schools Purchasing Forum (NSPF) is a procurement organisation that purchases goods and services on behalf of schools on a national scale. NSPF is close to concluding negotiations in a meeting with Hygienics For All (HFA) for the supply of consumables to school washrooms. Both parties have reached an agreeable position and NSPF feels it is important that they conclude the negotiation at this point. What type of questions should NSPF ask HFA to achieve this?
Answer : D
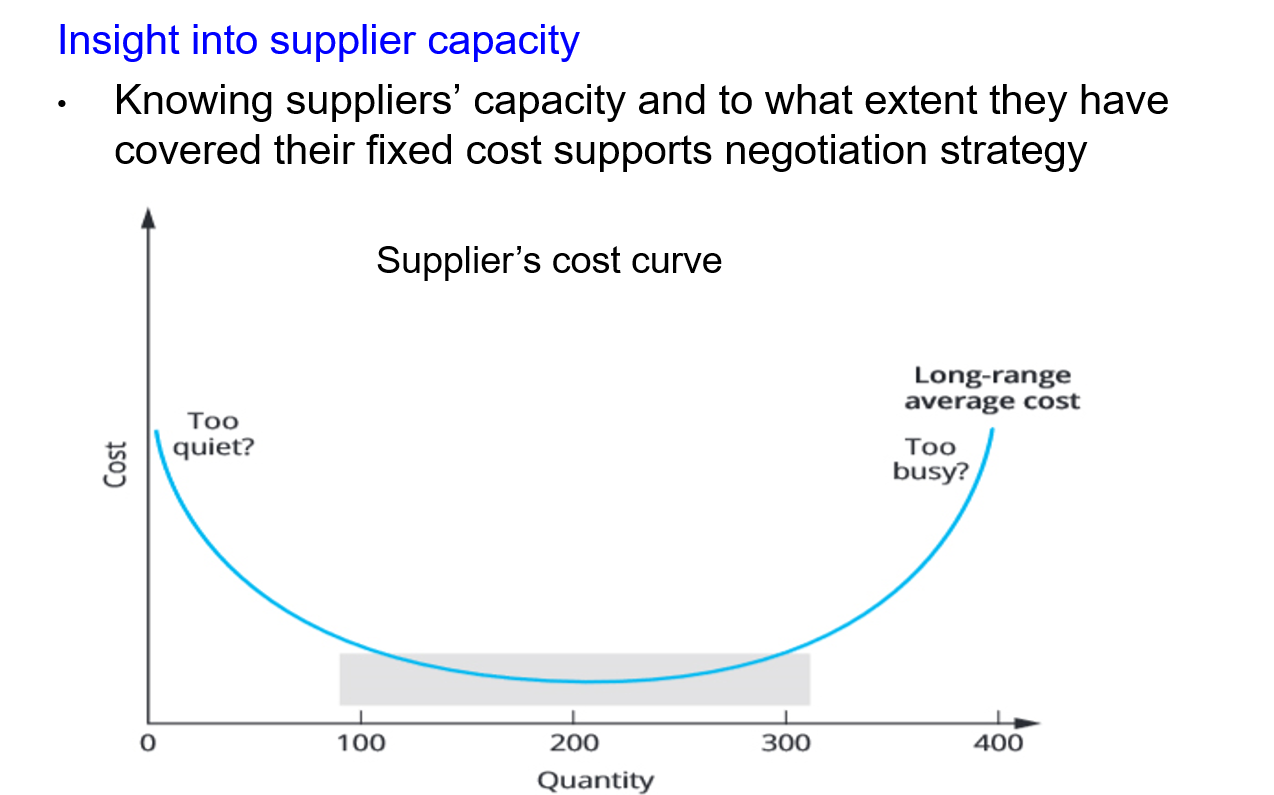
In a commercial negotiation, a procurement professional believe that the larger the order quantity from buyer, the lower the supplier's average costs. Is this assumption true?
Answer : B
:
In some markets, suppliers experience peaks and troughs in demand and so buyers can increase their leverage through developing an understanding of how busy their vendor are at particular time during the year or business cycle and targetting at quieter period. Similarly, if a buyer can develop an understanding of supplier capacity and to what extent have they covered their fixed cost, they may be able to target suppliers when their average costs are likely to be lowest. Vendor's average costs will be higher at low and high capacity utilisation.
Langham Industries is seeking to expand its operations globally. The CEO has asked the procurement department to engage in a macroeconomic analysis for its potential new supply chain to meet organisational objectives and outcomes. Which of the following would be a source of macroeconomic data?
Answer : C
Published market indices are a source of macroeconomic data, as they reflect broader economic trends and provide insights into the overall market environment, which is essential for global expansion planning. Macroeconomic analysis focuses on high-level economic indicators, as recommended in CIPS's guidelines on sourcing macroeconomic data.
Active listening in negotiation includes which of the following activities?
1. Hearing
2. Interpreting
3. Rapport
4. Influence
Answer : C
Listening is a hugely important skill in the world of work. It's a key part of effective communication [...].
Regarding active listening, there is a model called 'The SIER Hierarchy of Active Listening'. It details four key stages required for effective listening. As with all models associated with active listening, its purpose is to help the listener be a better, more effective listener who really hears what is being said, connects with the individual with whom they are communicating and builds effective relationships.
The model is a hierarchical model meaning that each stage builds on the stage before it. While the model is sometimes used for training in the sales arena, it is helpful in all walks of life. The stages of the model are: Sensing (including hearing and watching body language), Interpreting, Evaluating and Responding.
- CIPS study guide page 171-173
- The SIER Hierarchy of Active Listening: Become a Better Listener
LO 3, AC 3.3
In airline industry, suppliers prefer to adopt dynamic pricing in order to constantly monitor and change their fares in response to market conditions. Dynamics pricing is based on which costing method?
Answer : D
:
Dynamic pricing is the practice of dynamically calculating the price of a product or service in order to incorporate real-time market conditions, input costs, and/or competitive perspectives. Dynamic pricing which is based on marginal costing, is used by airlines and many other organisations.
Marginal cost is the cost of producing an additional unit of output. Marginal Costing is a costing technique wherein the marginal cost, i.e. variable cost is charged to units of cost, while the fixed cost for the period is completely written off against the contribution.
Which of the following types of relationship would possibly lead to a distributive negotiation?
Answer : D
A garden furniture supplier who is currently in negotiations for a high-value contract has offered the procurement manager a visit to their site. The supplier suggests that during this visit, they can undertake the contract negotiation. What would be an appropriate response from the procurement manager?
Answer : D
Negotiating at the supplier's site can give the supplier a psychological advantage due to their familiarity with the setting. To ensure a neutral and balanced negotiation environment, it's preferable to conduct negotiations in a neutral location or through structured channels, as recommended in CIPS's guidance on negotiation settings.