CompTIA SecurityX Certification Exam CAS-005 Practice Questions
A security analyst is reviewing a SIEM and generates the following report:
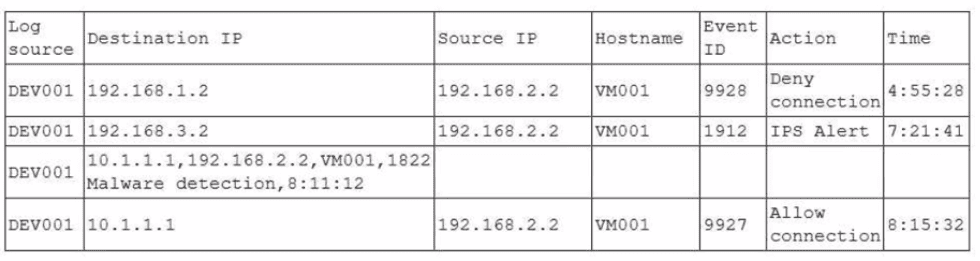
Later, the incident response team notices an attack was executed on the VM001 host. Which of the following should the security analyst do to enhance the alerting process on the SIEM platform?
Answer : B, B
The SIEM already contains multiple events that, if correlated, would have indicated an active attack sequence on VM001---such as denied connections, IPS alerts, malware detection, and then an allowed connection. CAS-005 Security Operations objectives emphasize log correlation as a way to enhance detection by linking related events across different time stamps and data sources into a single, higher-confidence alert.
Option A (adding EDR logs) could add visibility but does not address the need to connect existing events for earlier detection.
Option C (improving parsing) ensures readability but does not create actionable alerts.
Option D (creating a new malware detection rule) is redundant since malware detection already appeared in logs; the issue was the lack of correlation to act on it in time.
By correlating IDS, IPS, firewall, and malware detection logs, the SIEM can raise a higher-priority alert before the attack is completed.
Anorganization has noticed an increase in phishing campaigns utilizingtyposquatting. A security analyst needs to enrich the data for commonly used domains against the domains used in phishing campaigns. The analyst uses a log forwarder to forward network logs to the SIEM. Which of the following would allow the security analyst to perform this analysis?
Answer : D, D
Enriching data to compare domains requires actionable visibility. Let's analyze:
A . Cron job:Automates updates but doesn't analyze in the SIEM.
B . Parser:Processes logs but doesn't provide comparison insights.
C . Filter query:Excludes matches, opposite of enrichment.
A company implemented a NIDS and a NIPS on the most critical environments. Since this implementation, the company has been experiencing network connectivity issues. Which of the following should the security architect recommend for a new NIDS/NIPS implementation?
Answer : A, A
Best practice in CAS-005 network security design is to deploy:
NIDS passively via a port mirror (SPAN port) to avoid introducing latency or failure points.
NIPS inline in a strategic point, such as integrated with the main firewall, to actively block threats.This combination provides both visibility and active protection without overloading network paths.
An organization is prioritizing efforts to remediate or mitigate risks identified during the latest assessment. For one of the risks, a full remediation was not possible, but the organization was able to successfully apply mitigations to reduce the likelihood of the impact. Which of the following should the organization perform next?
Answer : A, A
After applying mitigations that reduce the likelihood of a risk's impact, the next step is toassess the residual risk---the risk that remains after controls are implemented. This ensures the organization understands if the mitigation is sufficient or if further action is needed, aligning with risk management best practices.
Option A:Correct---residual risk assessment is the logical next step to evaluate the effectiveness of mitigations.
Option B:Updating the threat model might follow but isn't immediate; residual risk comes first.
Option C:Moving to the next risk skips evaluating the current mitigation's success.
Option D:Recalculating impact magnitude is part of residual risk assessment but isn't the full process.
Which of the following best describes a common use case for homomorphic encryption?
Answer : C, C
Homomorphic encryptionallows computations to be performed directly on encrypted data without decrypting it first. This technology is particularly useful for securely transmitting confidential data to a cloud service provider (CSP) and allowing the CSP to process the data without having any visibility into its content. This maintains data confidentiality even during processing. It is not about securing data at rest and in transit or simply storing data across nodes.
An organization decides to move to a distributed workforce model. Several legacy systems exist on premises and cannot be migrated because of existing compliance requirements. However, all new systems are required to be cloud-based. Which of the following would best ensure network access security?
Answer : A, A
For a distributed workforce needing access to compliance-bound on-premises systems, VPN access ensures encrypted, authenticated connectivity while limiting exposure. SecurityX CAS-005 emphasizes using VPNs for secure remote access when direct migration to cloud is not possible.
Moving legacy systems to cloud (B) violates the compliance constraints.
SDN security controls (C) are beneficial but do not inherently provide secure remote connectivity.
Microsegmentation (D) is useful for internal lateral movement control but does not solve remote access needs.
An organization recently experienced a security incident due to an exterior door in a busy area getting stuck open. The organization launches a security campaign focused on the motto, "See Something, Say Something." Which of the following best describes what the organization wants to educate employees about?
Answer : A, A