CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Exam Practice Test
[Attacks and Exploits]
A penetration tester identifies an exposed corporate directory containing first and last names and phone numbers for employees. Which of the following attack techniques would be the most effective to pursue if the penetration tester wants to compromise user accounts?
Answer : A
When a penetration tester identifies an exposed corporate directory containing first and last names and phone numbers, the most effective attack technique to pursue would be smishing. Here's why:
Understanding Smishing:
Smishing (SMS phishing) involves sending fraudulent messages via SMS to trick individuals into revealing personal information or performing actions that compromise security. Since the tester has access to phone numbers, this method is directly applicable.
Why Smishing is Effective:
Personalization: Knowing the first and last names allows the attacker to personalize the messages, making them appear more legitimate and increasing the likelihood of the target responding.
Immediate Access: People tend to trust and respond quickly to SMS messages compared to emails, especially if the messages appear urgent or important.
Alternative Attack Techniques:
Impersonation: While effective, it generally requires real-time interaction and may not scale well across many targets.
Tailgating: This physical social engineering technique involves following someone into a restricted area and is not feasible with just names and phone numbers.
Whaling: This targets high-level executives with highly personalized phishing attacks. Although effective, it is more specific and may not be suitable for the broader set of employees in the directory.
[Reporting and Communication]
A penetration tester finds it is possible to downgrade a web application's HTTPS connections to HTTP while performing on-path attacks on the local network. The tester reviews the output of the server response to:
curl -s -i https://internalapp/
HTTP/2 302
date: Thu, 11 Jan 2024 15:56:24 GMT
content-type: text/html; charset=iso-8659-1
location: /login
x-content-type-options: nosniff
server: Prod
Which of the following recommendations should the penetration tester include in the report?
Answer : A
The tester identified an HTTPS downgrade attack (e.g., SSL stripping). The best mitigation is to enforce HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security).
HSTS (Option A):
HSTS (Strict-Transport-Security) ensures that the browser always uses HTTPS, preventing downgrade attacks.
Example header:
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains
Incorrect options:
Option B (httponly flag): Protects cookies from JavaScript access but does not enforce HTTPS.
Option C (Firewall rule on port 80): Helps, but does not force browsers to use HTTPS.
Option D (Removing x-content-type-options): Unrelated; nosniff prevents MIME-type sniffing.
[Information Gathering and Vulnerability Scanning]
A penetration tester obtains the following output during an Nmap scan:
PORT STATE SERVICE
135/tcp open msrpc
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
1801/tcp open msmq
2103/tcp open msrpc
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server
Which of the following should be the next step for the tester?
Answer : B
The presence of SMB (port 445) and MSRPC (port 135) indicates potential Windows network services that could be vulnerable to misconfigurations or exploits.
Enumerate shares and search for vulnerabilities on SMB (Option B):
SMB (Server Message Block) allows file and printer sharing. Misconfigured or open shares could contain sensitive data.
Tools like enum4linux or smbclient can be used to list available shares and check for anonymous access.
SMB vulnerabilities (e.g., EternalBlue - CVE-2017-0144) can be exploited for remote code execution.
Incorrect options:
Option A (Search vulnerabilities on msrpc): MSRPC (Microsoft Remote Procedure Call) is not commonly exploited directly unless an SMB or RDP vulnerability is found.
Option C (Brute-force RDP): Brute-force attacks generate excessive failed login attempts, triggering security alerts.
Option D (Search for another port): The open ports already provide sufficient attack vectors.
[Attacks and Exploits]
A penetration tester needs to evaluate the order in which the next systems will be selected for testing. Given the following output:
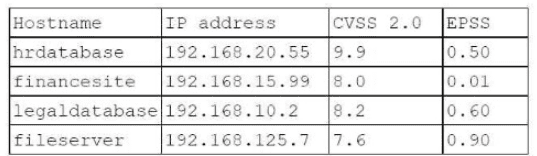
Which of the following targets should the tester select next?
Answer : A
Evaluation Criteria:
CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System): Indicates the severity of vulnerabilities, with higher scores representing more critical vulnerabilities.
EPSS (Exploit Prediction Scoring System): Estimates the likelihood of a vulnerability being exploited in the wild.
Analysis:
hrdatabase: CVSS = 9.9, EPSS = 0.50
financesite: CVSS = 8.0, EPSS = 0.01
legaldatabase: CVSS = 8.2, EPSS = 0.60
fileserver: CVSS = 7.6, EPSS = 0.90
Selection Justification:
fileserver has the highest EPSS score of 0.90, indicating a high likelihood of exploitation despite having a slightly lower CVSS score compared to other targets.
This makes it a critical target for immediate testing to mitigate potential exploitation risks.
Pentest Reference:
Risk Prioritization: Balancing between severity (CVSS) and exploitability (EPSS) is crucial for effective vulnerability management.
Risk Assessment: Evaluating both the impact and the likelihood of exploitation helps in making informed decisions about testing priorities.
By selecting the fileserver, the penetration tester focuses on a target that is highly likely to be exploited, addressing the most immediate risk based on the given scores.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
[Information Gathering and Vulnerability Scanning]
A penetration tester reviews a SAST vulnerability scan report. The following vulnerability has been reported as high severity:
Source file: components.ts
Issue 2 of 12: Command injection
Severity: High
Call: .innerHTML = response
The tester inspects the source file and finds the variable response is defined as a constant and is not referred to or used in other sections of the code. Which of the following describes how the tester should classify this reported vulnerability?
Answer : B
A false positive occurs when a vulnerability scan incorrectly flags a security issue that does not exist or is not exploitable in the context of the application. Here's the reasoning:
Definition of Command Injection:Command injection vulnerabilities occur when user-controllable data is passed to an interpreter or command execution context without proper sanitization, allowing an attacker to execute arbitrary commands.
Code Analysis:
The response variable is defined as a constant (const), which implies its value is immutable during runtime.
The response is not sourced from user input nor used elsewhere, meaning there is no attack surface or exploitation pathway for an attacker to influence the content of response.
Scanner Misclassification:Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tools may flag vulnerabilities based on patterns (e.g., .innerHTML usage) without assessing the source and flow of data, resulting in false positives.
Final Classification:Since the response variable is static and unchangeable, the flagged issue is not exploitable. This makes it a false positive.
CompTIA Pentest+ Reference:
Domain 3.0 (Attacks and Exploits)
Domain 4.0 (Penetration Testing Tools)
OWASP Static Code Analysis Guide
[Attacks and Exploits]
Which of the following is the most efficient way to infiltrate a file containing data that could be sensitive?
Answer : D
When considering efficiency and security for exfiltrating sensitive data, the chosen method must ensure data confidentiality and minimize the risk of detection. Here's an analysis of each option:
Use steganography and send the file over FTP (Option A):
Steganography hides data within other files, such as images. FTP is a protocol for transferring files.
Drawbacks: FTP is not secure as it transmits data in clear text, making it susceptible to interception. Steganography can add an extra layer of obfuscation, but the use of FTP makes this option insecure.
Compress the file and send it using TFTP (Option B):
TFTP is a simple file transfer protocol that lacks encryption.
Drawbacks: TFTP is inherently insecure because it does not support encryption, making it easy for attackers to intercept the data during transfer.
Split the file in tiny pieces and send it over dnscat (Option C):
dnscat is a tool for tunneling data over DNS.
Drawbacks: While effective at evading detection by using DNS, splitting the file and managing the reassembly adds complexity. Additionally, large data transfers over DNS can raise suspicion.
Encrypt and send the file over HTTPS (Answer: D):
Encrypting the file ensures that its contents are protected during transfer. HTTPS provides a secure, encrypted channel for communication over the internet.
Advantages: HTTPS is widely used and trusted, making it less likely to raise suspicion. Encryption ensures the data remains confidential during transit.
The use of HTTPS for secure data transfer is a standard practice in cybersecurity, providing both encryption and integrity of the data being transmitted.
Conclusion: Encrypting the file and sending it over HTTPS is the most efficient and secure method for exfiltrating sensitive data, ensuring both confidentiality and reducing the risk of detection.
[Attacks and Exploits]
A penetration tester finished a security scan and uncovered numerous vulnerabilities on several hosts. Based on the targets' EPSS and CVSS scores, which of the following targets is the most likely to get attacked?
Answer : A
EPSS and CVSS Analysis:
EPSS (Exploit Prediction Scoring System) indicates the likelihood of exploitation.
CVSS (Common Vulnerability Scoring System) represents the severity of the vulnerability.
Rationale:
Target 1 has the highest EPSS score (0.6) combined with a moderately high CVSS score (4), making it the most likely to be attacked.
Other options either have lower EPSS or CVSS scores, reducing their likelihood of being exploited.
CompTIA Pentest+ Reference:
Domain 2.0 (Information Gathering and Vulnerability Identification)