Dell EMC Dell PowerMax Operate v.2 D-PVM-OE-01 Exam Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
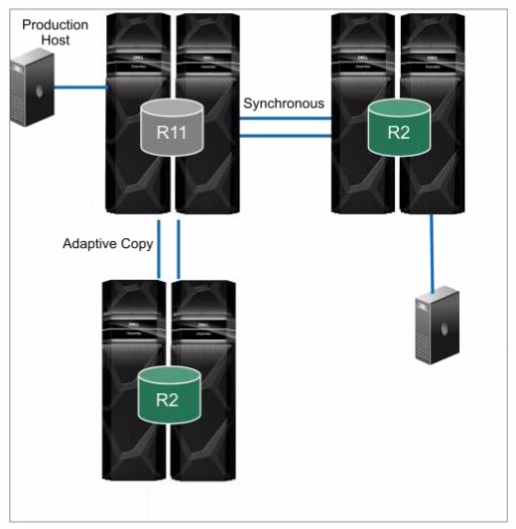
What is the topology shown1?
Answer : A
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
The topology shown in the exhibit depicts Cascaded SRDF. This SRDF configuration involves three storage arrays (or sites) connected in a chained or cascaded manner.
Here's how it works:
Primary Site (R1): The production host is connected to the primary storage array (R1).
Intermediate Site (R2): The primary array (R1) synchronously replicates data to an intermediate array (R2).
Remote Site (R2): The intermediate array (R2) then asynchronously replicates data to a remote array (also labeled R2 in the diagram).
This cascading setup provides a multi-hop disaster recovery solution, where data is first replicated synchronously to a nearby site for high availability and then asynchronously replicated to a further remote site for disaster recovery.
Why other options are incorrect:
B . SRDF/Star: SRDF/Star involves a central array replicating to multiple remote arrays in a star-like pattern.
C . SRDF/Metro: SRDF/Metro is designed for synchronous replication over short distances, typically within a metropolitan area.
D . Concurrent SRDF: Concurrent SRDF allows multiple SRDF relationships to exist simultaneously for the same device.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Solutions Enabler 10.0.0 SRDF Family CLI User Guide: This guide provides detailed information about different SRDF configurations, including Cascaded SRDF. You can find this document on the Dell Support website by searching for 'Solutions Enabler SRDF Family CLI User Guide.'
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide offers a comprehensive overview of SRDF and its functionalities, including various topologies and use cases.
SIMULATION
A customer has an existing host with two 100 GB volumes that are assigned from existing PowerMax storage. They would like to add three additional volumes of 100 GB each and change the service level that is assigned to the storage group from Gold to Platinum to support the current application SLO requirements.
Answer : A
You want a detailed, step-by-step guide on how to add three 100 GB volumes to an existing host and change the service level of the associated storage group from Gold to Platinum on a PowerMax array, using the Unisphere for PowerMax interface shown in the image.
Here's a comprehensive guide, broken down into manageable steps:
Phase 1: Provisioning the New Volumes
Step 1: Log in to Unisphere for PowerMax
Open your web browser and enter the URL for your Unisphere for PowerMax management interface.
Log in with your administrator credentials.
Step 2: Navigate to Storage Groups
In the left-hand navigation pane, click on Storage to expand the storage management section.
Click on Storage Groups under the Storage section. This will display a list of existing storage groups on your PowerMax array.
Step 3: Locate the Target Storage Group
Identify the storage group that currently contains the host's existing two 100 GB volumes.
Tip: You can find this by:
Looking at the 'Hosts' tab within each storage group's details. It will list the hosts connected to that storage group.
If you know the host's name, you might be able to search for it using the Unisphere search bar (if available).
Step 4: Initiate Adding Volumes
Once you've found the correct storage group, select it by clicking on its name.
Look for a button or option related to adding volumes. The exact wording might vary slightly depending on your Unisphere version, but it could be:
'Add to Storage Group'
'+' (a plus icon, which often signifies adding something)
'Add Volumes'
Click this button to start the process of adding new volumes to the storage group.
Step 5: Configure Volume Details
A new window or panel will appear, allowing you to specify the characteristics of the new volumes.
Select 'Create new volumes'
Number of Volumes: Enter 3 in the field for the number of volumes.
Capacity: Enter 100 in the field for the capacity of each volume. Make sure the unit is set to GB.
Volume Name (Optional): You can give the volumes a specific name or prefix, or you can let Unisphere auto-generate names.
Service Level: Since the final goal is to move the entire Storage Group to platinum, you can either set this to platinum now or change it for the whole group later.
Other Settings: Review any other available settings (e.g., thin provisioning, data reduction). In most cases, the default settings should be fine, but adjust them if needed based on your environment's best practices.
Step 6: Execute Volume Creation
After you've configured all the volume settings, review them carefully to make sure they are correct.
Click the button to execute the operation. This button might be labeled:
'Run Now'
'OK'
'Finish'
'Apply'
Unisphere will start creating the new volumes. This might take a few moments.
Phase 2: Changing the Storage Group's Service Level
Step 7: Navigate Back to Storage Groups
Once the volume creation is complete, go back to the list of storage groups. You can usually do this by clicking 'Storage Groups' in the left-hand navigation pane again.
Step 8: Select the Target Storage Group
Find the same storage group you worked with in Phase 1 (the one containing the host's volumes).
Click on the storage group's name to open its properties.
Step 9: Modify the Service Level
Look for a setting related to the 'Service Level.' It might be a dropdown menu, a field you can edit, or a link to a separate settings page.
Change the Service Level from Gold to Platinum.
Step 10: Save the Changes
Click the button to save the changes to the storage group's service level. This button might be labeled:
'Apply'
'Save'
'OK'
Phase 3: Host-Side Configuration
Step 11: Rescan for New Storage on the Host
The host needs to be made aware of the newly provisioned storage. The exact process for this depends on the host's operating system:
Windows:
Open Disk Management (diskmgmt.msc).
Go to Action > Rescan Disks.
Linux:
Identify the SCSI host bus numbers (e.g., ls /sys/class/scsi_host).
Use the command echo '- - -' > /sys/class/scsi_host/hostX/scan, replacing hostX with the appropriate host bus number.
You might also be able to use tools like rescan-scsi-bus.sh.
VMware ESXi:
In the vSphere Client, select the host.
Go to Configure > Storage Adapters.
Select the relevant storage adapter (e.g., your HBA).
Click Rescan Storage.
Step 12: Initialize, Partition and Mount (if needed):
Once the host detects the new volumes, you'll need to initialize them, create partitions, format them with a filesystem, and mount them, depending on your operating system and how you intend to use the storage. This is done using the host's operating system tools.
Phase 4: Verification and Monitoring
Step 13: Verify in Unisphere
Go back to the storage group in Unisphere and check the 'Volumes' tab. You should see the three new 100 GB volumes listed along with the original two, and they should all have the 'Platinum' service level.
Step 14: Verify on the Host
Confirm that the host can see and access the new volumes.
Step 15: Monitor Performance
After making these changes, monitor the performance of the storage group and the application using Unisphere's performance monitoring tools. Ensure that the Platinum service level is meeting your application's requirements
What function can a storage administrator enable on the Port Attributes page?
Answer : B
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
The Port Attributes page in Unisphere for PowerMax allows storage administrators to configure various settings related to the front-end ports on the storage array. One of the functions available on this page is Select Mgt Option.
This option allows you to specify how the port is used for management purposes:
Dedicated Management Port: You can designate a port as a dedicated management port, which is used exclusively for communication with management tools like Unisphere and Solutions Enabler.
Shared Management Port: You can configure a port to be shared for both management traffic and host I/O traffic.
This flexibility allows you to optimize port usage and segregate management traffic if needed.
Why other options are incorrect:
A . Manage Protocol: Protocol settings (like FC or iSCSI) are typically configured elsewhere in Unisphere, not on the Port Attributes page.
C . Volume Set Addressing: Volume Set Addressing is a feature related to mainframe connectivity and is not directly managed through the Port Attributes page.
D . ORS Ceiling: ORS (Open Replicator Solutions) settings are managed separately and not through the Port Attributes page.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Unisphere for PowerMax 10.0.0 Online Help: The online help for Unisphere provides detailed information about the Port Attributes page and the available configuration options, including the 'Select Mgt Option' function. You can access this help within Unisphere itself or on the Dell Support website.
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide may offer general information about port management and configuration in PowerMax.
SIMULATION
A customer has a clone session for the storage group DATA that is no longer needed.
Using the simulator, terminate the clone session for the storage group.
Answer : A
We need to terminate a clone session for the storage group named 'DATA' in the Unisphere for PowerMax simulator.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do this, based on typical Unisphere functionality and the context of the question:
Steps:
1. Launch the Simulator and Navigate to the TimeFinder/Clone Section
Open Unisphere for PowerMax in your web browser.
Log in to the simulator (you should already be logged in with the array SID 1762 selected, based on the provided image).
In the left-hand navigation pane, locate the section related to TimeFinder operations. This is usually found under:
Data Protection
Local Protection
TimeFinder
Expand the relevant sections and click on TimeFinder SnapVX or TimeFinder Clone (the exact wording might vary slightly in the simulator). The goal is to get to the view where you can manage clone sessions.
2. Locate the Clone Session for the 'DATA' Storage Group
The TimeFinder/Clone view will display a list of existing clone sessions.
You need to find the session associated with the 'DATA' storage group. Look for the following:
Storage Group Name: The 'DATA' storage group should be listed as the source of the clone session.
Session Type/Mode: Verify that it's a Clone session (not a SnapVX snapshot or another type of session).
3. Select the Clone Session
Once you've found the correct clone session for the 'DATA' storage group, select it.
You can usually do this by:
Clicking a checkbox next to the session.
Clicking on the session itself (if the interface allows it).
4. Terminate the Clone Session
After selecting the clone session, look for an action button or menu option to terminate it. This might be labeled:
'Terminate'
'Delete'
'Remove'
'Fracture' (in some older versions)
'Stop'
Click the appropriate button to initiate the termination process.
Confirmation: You will likely be prompted with a confirmation message to ensure you want to terminate the selected clone session. Verify that you have selected the correct session (the one for the 'DATA' storage group) and confirm the termination.
Which three device types can be managed using Solutions Enabler and Unisphere?
Answer : A, C, E
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
Dell PowerMax storage arrays utilize different device types for various purposes. Solutions Enabler (SYMCLI) and Unisphere for PowerMax are management tools that can interact with these device types. Here's a breakdown:
SRDF Thin Devices (RDF1 or RDF2): These devices are specifically used for SRDF (Symmetrix Remote Data Facility) replication. RDF1 devices represent the local copy of data in an SRDF relationship, while RDF2 devices represent the remote copy. Both Solutions Enabler and Unisphere can manage these devices to configure and monitor SRDF replication.
Internal Thin Devices (Int+TDEV): These are thin provisioned devices that reside within the PowerMax storage array. They are used for general storage purposes and can be managed by both Solutions Enabler and Unisphere for tasks like provisioning, allocating capacity, and monitoring performance.
Thin Devices (TDEV): This is a general term for thin provisioned devices in PowerMax. Thin provisioning allows for efficient storage utilization by allocating capacity on demand. 1 Both Solutions Enabler and Unisphere can manage these devices.
https://www.n-able.com/blog/thin-provision-vs-thick-provision
https://www.n-able.com/blog/thin-provision-vs-thick-provision
Why other options are incorrect:
B . Thin BCV Devices (BCV+TDEV): BCV (Business Continuance Volume) devices are used for creating point-in-time copies for disaster recovery. While Solutions Enabler can manage BCV devices, Unisphere for PowerMax has limited functionality for managing them directly.
D . Data Devices (TDATs): TDATs are physical devices within the PowerMax array. While Solutions Enabler can interact with TDATs at a lower level, Unisphere for PowerMax primarily focuses on managing logical devices and storage groups.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide provides an overview of PowerMax devices and their management. It mentions the different device types and how they are used in the PowerMax environment.
Dell Solutions Enabler 10.0.0 CLI User Guide: This guide provides detailed information about Solutions Enabler commands for managing various device types, including SRDF devices, thin devices, and internal devices.
Dell Unisphere for PowerMax 10.0.0 Online Help: The online help documentation for Unisphere for PowerMax explains how to manage different device types through the graphical user interface, including provisioning, monitoring, and configuring storage.
Refer to the exhibit.
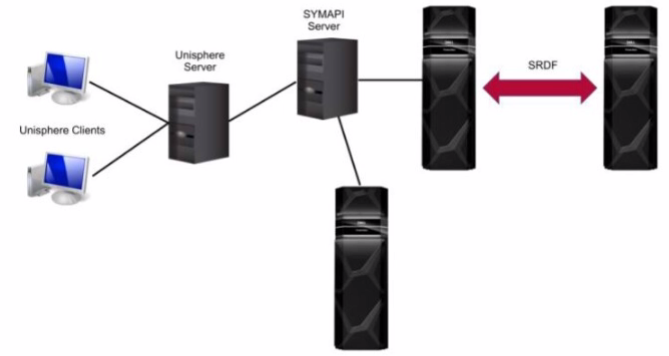
What is the Unisphere for PowerMax deployment option pictured?
Answer : C
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
Unisphere for PowerMax offers different deployment options to manage PowerMax storage arrays. Based on the exhibit, we can identify the following:
Separate SYMAPI Server: The diagram shows a dedicated SYMAPI server. SYMAPI (Symmetrix Application Programming Interface) is a command-line interface used to manage PowerMax and VMAX storage arrays. This indicates that the Unisphere server is not directly connected to the storage arrays.
Unisphere Server Connected to SYMAPI Server: The Unisphere server is shown to be connected to the SYMAPI server. This means that the Unisphere server relies on the SYMAPI server to communicate with the PowerMax arrays.
No Direct Connection to Arrays: The Unisphere server does not have a direct connection to the PowerMax arrays.
Considering these points, the deployment option depicted in the exhibit is a remote deployment. In a remote deployment, the Unisphere server is installed on a separate host and communicates with the PowerMax arrays through a SYMAPI server. This allows for centralized management of multiple arrays from a single Unisphere instance.
Why other options are incorrect:
A . Embedded: In an embedded deployment, the Unisphere software runs directly on the PowerMax array itself. This eliminates the need for a separate Unisphere server.
B . Either remote or local: While the diagram could technically represent a local deployment with a dedicated SYMAPI server, the presence of the separate SYMAPI server and the lack of direct connection to the arrays strongly suggest a remote deployment.
D . Local: In a local deployment, the Unisphere server is typically installed on the same host as Solutions Enabler, which has direct connectivity to the storage arrays.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Unisphere for PowerMax 10.0.0 Installation Guide: This guide provides detailed information about the different Unisphere deployment options, including local, remote, and embedded. It also includes diagrams and explanations of each deployment scenario. You can find this document on the Dell Support website by searching for 'Unisphere for PowerMax Installation Guide.'
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide offers a general overview of PowerMax systems and their management using Unisphere. It may provide context for understanding the different deployment options.
What are two characteristics of a SnapVX Clone?
Answer : B, E
Step by Step Comprehensive Detailed
SnapVX Clones: SnapVX clones are full, writable copies of a source volume created using the SnapVX snapshot technology. They are independent volumes that can be used for various purposes, such as testing, development, or data analysis.
Secure Snapshots: SnapVX offers the capability to create 'secure snapshots.' When a clone is derived from a secure snapshot, it inherits the same protection, making it immutable and preventing any modifications or deletion. This ensures data integrity and protection against accidental or malicious changes.
Crash Consistent: SnapVX clones can be made crash consistent. This means that the clone captures a point-in-time copy of the source volume that is consistent with a database or application crash. This is important for ensuring data integrity and recoverability in situations where the source volume experiences an unexpected outage.
Why other options are incorrect:
A . Maximum 1024 snaps per volume: This limit applies to the source volume, not the clones themselves. Each clone is an independent volume.
C . Restores directly to the source volume: Clones are independent copies and do not directly restore to the source volume. Data can be copied or moved from the clone to the source if needed.
D . Is Read-only: SnapVX clones are fully writable copies, not read-only.
Reference and documents of Dell's public documentation for PowerMax Operate v.2:
Dell Solutions Enabler 10.0.0 TimeFinder SnapVX CLI User Guide: This guide provides detailed information about SnapVX features and commands, including how to create and manage clones. It confirms the ability to create secure clones and the option to make them crash consistent.
Dell PowerMax Family: Essentials and Best Practices Guide: This guide offers a comprehensive overview of PowerMax technologies, including SnapVX. It highlights the benefits of SnapVX clones for various use cases.