Dell EMC Expert - PowerMax and VMAX All Flash Solutions DEE-1111 Exam Practice Test
A user can create, manage, and delete PowerMax SRDF device pairs. They can also view the array information, masking objects, device information, and the defined RBAC rules. However, they are unable to create and delete SRDF groups.
Which RBAC profile has been assigned to the user's profile?
Answer : C
Which metrics are recommended to start analyzing the overall efficiency of the array due to cache?
Answer : D
The metrics that are recommended to start analyzing the overall efficiency of the array due to cache are array-level % Hit and % Cache WP. The array-level % Hit metric shows the percentage of read requests that are satisfied from the cache memory, without accessing the physical disks. A high % Hit value indicates that the cache is effective in reducing the read latency and improving the performance. The % Cache WP metric shows the percentage of cache memory that is occupied by write pending data, which is data that has been written to the cache but not yet destaged to the physical disks. A high % Cache WP value indicates that the cache is under pressure and may not have enough space to accommodate new write requests, which can lead to performance degradation. By monitoring these two metrics, a storage administrator can evaluate the overall efficiency of the array due to cache and identify any potential issues or bottlenecks.
System efficiency overview | Dell PowerMax: Data Reduction | Dell Technologies Info Hub
Metrics (PowerMax & VMAX) - VMware Docs
Replication cache | Dell EMC PowerMax and VMAX All Flash: TimeFinder SnapVX Local Replication
An SRDF/Metro device pair was in an ActiveActive state. A link failure between arrays occurs. The application continues running on the R1 side, and the link failure is addressed.
What is the current state of the Metro device pair?
Answer : B
An SRDF/Metro device pair was in an ActiveActive state, meaning that both the R1 and R2 devices were read/write accessible to the host or hosts. A link failure between arrays occurs, causing the device pair to become Not Ready (NR) on the SRDF link. SRDF/Metro responds by making the non-biased or R2 paired device inaccessible (not ready) to the host or host cluster, while keeping the biased or R1 paired device accessible (ready). This ensures that there is no data inconsistency or split-brain scenario between the two sites. The device pair enters an Active Bias state, which indicates that only one side of the pair is active and has a bias attribute set. The bias attribute determines which side of the pair remains accessible in case of a link failure. By default, the bias is set to the R1 side of the pair, but it can be changed using the symrdf set bias command. The application continues running on the R1 side, and the link failure is addressed. Once the link is restored, the device pair resumes the ActiveActive state and both devices become accessible again.
VMware vSphere Metro Storage Cluster (vMSC) with Dell PowerMax and Dell EMC VMAX SRDF/Metro
Refer to the exhibit.
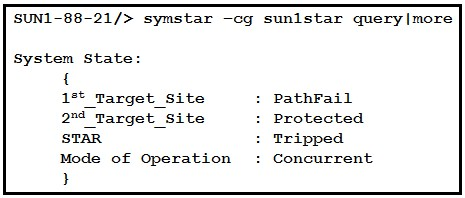
What should be done first to recover from this Concurrent SRDF/Star configuration failure?
During a Non-Disruptive Migration (NDM), what is the result of issuing the ReadyTgt SYMCLI command to the migrating Storage Group?
Which external storage can be connected to PowerMax using DX emulation?
Answer : A
B, C, and D are incorrect because they are not external storage that can be connected to PowerMax using DX emulation. Unity (B), PowerStore , and Compellent (D) are primary storage arrays that do not support ProtectPoint technology or DX emulation.
A disaster occurred at the workload site of an SRDF/Star configuration. The administrator decides to move the workload to the Synchronous site (Site B).
What symstar command should be used before the workload switch?