Fortinet FCP - FortiAnalyzer 7.4 Analyst FCP_FAZ_AN-7.4 Exam Practice Test
Which two statement regarding the outbreak detection service are true? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
You created a playbook on FortiAnalyzer that uses a FortiOS connector.
When configuring the FortiGate side, which type of trigger must be used so that the actions in an automation stich are available in the FortiOS connector?
Answer : D
When using FortiAnalyzer to create playbooks that interact with FortiOS devices, an Incoming Webhook trigger is required on the FortiGate side to make the actions in an automation stitch accessible through the FortiOS connector. The incoming webhook trigger allows FortiAnalyzer to initiate actions on FortiGate by sending HTTP POST requests to specified endpoints, which in turn trigger automation stitches defined on the FortiGate.
Here's an analysis of each option:
Option A: FortiAnalyzer Event Handler
This is incorrect. The FortiAnalyzer Event Handler is used within FortiAnalyzer itself for handling log events and alerts, but it does not trigger automation stitches on FortiGate.
Option B: Fabric Connector event
This is incorrect. Fabric Connector events are related to Fortinet's Security Fabric integrations but are not specifically used to trigger FortiGate automation stitches from FortiAnalyzer.
Option C: FortiOS Event Log
This is incorrect. While FortiOS event logs can be used for monitoring, they are not designed to trigger automation stitches directly from FortiAnalyzer.
Option D: Incoming webhook
This is correct. The Incoming Webhook trigger on FortiGate enables it to receive requests from FortiAnalyzer, allowing playbooks to activate automation stitches defined on the FortiGate device. This method is commonly used to integrate actions from FortiAnalyzer to FortiGate via the FortiOS connector.
Refer to Exhibit:
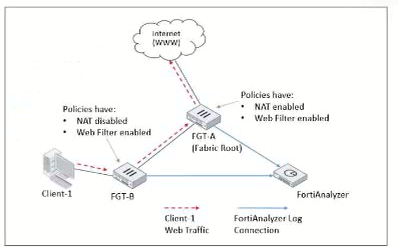
Client-1 is trying to access the internet for web browsing.
All FortiGate devices in the topology are part of a Security Fabric with logging to FortiAnalyzer configured. All firewall policies have logging enabled. All web filter profiles are configured to log only violations.
Which statement about the logging behavior for this specific traffic flow is true?
Answer : C
The topology shows a Security Fabric setup involving FortiGate devices (FGT-A and FGT-B) and a FortiAnalyzer for centralized logging. Let's break down the logging and traffic flow behavior:
Traffic Flow Analysis:
Client-1 initiates web traffic directed to the internet, which is routed through FGT-B and then FGT-A before reaching the internet. This is indicated by the direction of the red-dashed arrow from Client-1 through FGT-B to FGT-A.
Policy and NAT Settings:
On FGT-B, NAT is disabled, meaning it will pass the traffic through without altering the source IP. This device has a Web Filter enabled with a policy to log violations only.
On FGT-A, NAT is enabled, and a Web Filter profile is also applied. Like FGT-B, it logs only violations for web filtering.
Logging Behavior:
Since both FortiGate devices have logging enabled for traffic and web filtering, they can create logs if conditions are met.
FGT-B will log all traffic, as per its configuration, and will also create web filter logs if it detects a violation, as the web filter profile is applied. Because NAT is disabled on FGT-B, it processes the traffic but doesn't perform any address translation, allowing it to see the original source IP of Client-1.
FGT-A, as the Security Fabric root, will handle NAT and forward the traffic to the internet. However, in this case, the question is focused on where the traffic and web filter logs would be generated first, particularly by FGT-B.
Option Analysis:
Option A - Only FGT-B will create traffic logs: This is incorrect because FGT-B can create both traffic logs and web filter logs if it detects a violation.
Option B - FGT-B will see the MAC address of FGT-A and notify FGT-A to log: This is not how logging works in this setup. Each FortiGate logs independently based on configured policies.
Option C - FGT-B will create traffic logs and will create web filter logs if it detects a violation: This is correct, as FGT-B has logging enabled and will log traffic and web filter violations.
Option D - Only FGT-A will create web filter logs if it detects a violation: This is incorrect, as FGT-B can also log web filter violations independently.
Conclusion:
Correct Answe r : C. FGT-B will create traffic logs and will create web filter logs if it detects a violation.
FGT-B is responsible for logging the traffic from Client-1 and will generate web filter logs if there is a policy violation, as configured.
FortiOS 7.4.1 documentation on Security Fabric logging behavior and FortiAnalyzer log integration.
Which FortiAnalyzer feature allows you to use a proactive approach when managing your network security?
Answer : D
FortiAnalyzer offers several features for monitoring, alerting, and incident management, each serving different purposes. Let's examine each option to determine which one best supports a proactive security approach.
Option A - FortiView Monitor:
FortiView is a visualization tool that provides real-time and historical insights into network traffic, threats, and logs. While it gives visibility into network activity, it is generally more reactive than proactive, as it relies on existing log data and incidents.
Conclusion: Incorrect.
Option B - Outbreak Alert Services:
Outbreak Alert Services in FortiAnalyzer notify administrators of emerging threats and outbreaks based on FortiGuard intelligence. This is beneficial for awareness of potential threats but does not offer a hands-on, investigative approach. It's more of a notification service rather than an active, proactive investigation tool.
Conclusion: Incorrect.
Option C - Incidents Dashboard:
The Incidents Dashboard provides a summary of incidents and current security statuses within the network. While it assists with ongoing incident response, it is used to manage and track existing incidents rather than proactively identifying new threats.
Conclusion: Incorrect.
Option D - Threat Hunting:
Threat Hunting in FortiAnalyzer enables security analysts to actively search for hidden threats or malicious activities within the network by leveraging historical data, analytics, and intelligence. This is a proactive approach as it allows analysts to seek out threats before they escalate into incidents.
Conclusion: Correct.
Conclusion:
Correct Answe r : D. Threat hunting
Threat hunting is the most proactive feature among the options, as it involves actively searching for threats within the network rather than reacting to already detected incidents.
FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 documentation on Threat Hunting and proactive security measures.
Which statement about the FortiSIEM management extension is correct?
Answer : B
What happens when the indicator of compromise (IOC) engine on FortiAnalyzer finds web logs that match blacklisted IP addresses?
Answer : B
As part of your analysis, you discover that a Medium severity level incident is fully remediated.
You change the incident status to Closed:Remediated.
Which statement about your update is true?
Answer : C