Fortinet FCP - FortiWeb 7.4 Administrator FCP_FWB_AD-7.4 Exam Practice Test
Which two statements about running a vulnerability scan are true? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
You should run the vulnerability scan during a maintenance window: Running a vulnerability scan during a maintenance window minimizes the risk of affecting normal operations. Scans can be resource-intensive and may cause disruptions if run during peak hours or when the system is in use.
You should run the vulnerability scan in a test environment: It is important to run the vulnerability scan in a test environment first to avoid unintended disruptions on the live system. This helps to identify potential issues or false positives without impacting production systems.
Refer to the exhibits.

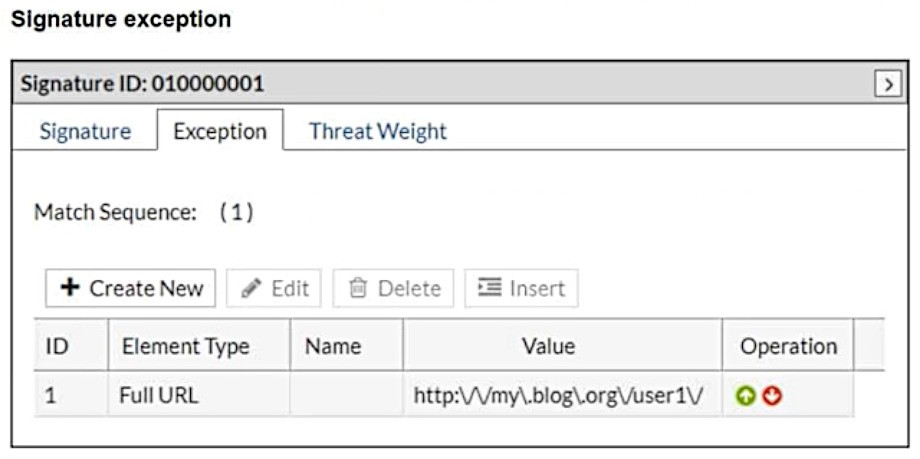
What will happen when a client attempts a mousedown cross-site scripting (XSS) attack against the site http://my.blog.org/userl1/blog.php and FortiWeb is enforcing the highlighted signature?
Answer : D
In the provided configuration, the signature exception has been set for the URL http://my.blog.org/user1V. This means that any request to this specific URL will bypass the signature ID 01000001, which is designed to block cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks using the mousedown event. As the request comes from the URL http://my.blog.org/userl1/blog.php, which does not match the exception rule for http://my.blog.org/user1V, the attack will be allowed through.
Therefore, the connection will be allowed because the exception rule bypasses protection for the specified URL.
Refer to the exhibit.
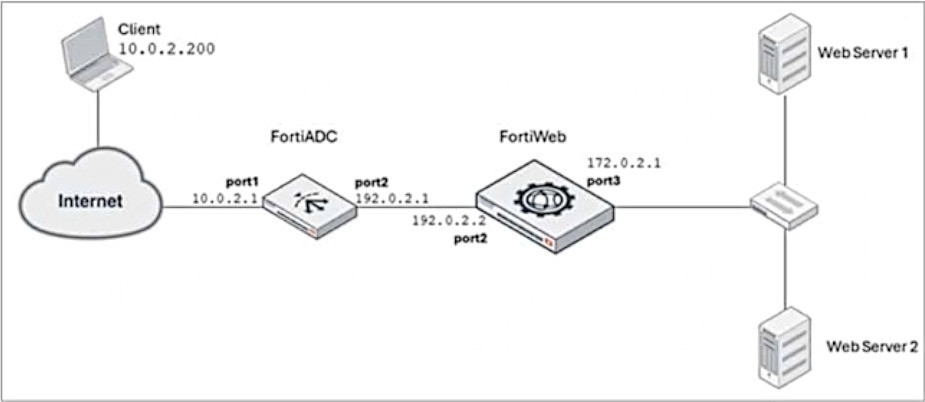
FortiADC is applying SNAT to all inbound traffic going to the servers.
When an attack occurs, FortiWeb blocks traffic based on the 192.0.2.1 source IP address, which belongs to FortiADC. This setup is breaking all connectivity and genuine clients are not able to access the servers.
What can the administrator do to avoid this problem? (Choose two.)
Answer : C, D
Place FortiWeb in front of FortiADC: This configuration change places FortiWeb between the client and FortiADC, so that FortiWeb can directly inspect and protect the incoming traffic before FortiADC applies SNAT (Source Network Address Translation). By placing FortiWeb in front, it will have access to the real client IP addresses, and it will be able to properly identify and handle attack traffic without blocking legitimate client traffic.
Enable and configure the Use X-Forwarded-For setting on FortiWeb: This setting allows FortiWeb to extract the original client IP address from the X-Forwarded-For header in the HTTP request, which is inserted by FortiADC when performing SNAT. With this setting enabled, FortiWeb will be able to block traffic based on the original client IP address rather than the SNATed IP address (192.0.2.1), preserving the accuracy of the security measures.
What are two results of enabling monitor mode on FortiWeb? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, D
It does not affect denial-of-service (DoS) protection profile actions to rate limit traffic: Monitor mode allows FortiWeb to monitor traffic without impacting the protection profile actions, including rate limiting in the DoS protection profiles. Traffic will still be subjected to DoS protection actions like rate limiting, but FortiWeb will not block traffic unless a violation occurs.
It overrides all usual profile actions. FortiWeb accepts all requests and generates alert email or log messages only for violations: In monitor mode, FortiWeb will allow all traffic through and generate logs or alerts for any violations, but it will not take active actions like blocking requests or redirecting traffic. This allows you to observe the traffic patterns and potential threats without disrupting normal operations.
Which high availability (HA) mode uses gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to advertise a failover event to neighboring network devices?
Answer : B
In Active-Passive high availability (HA) mode, the active unit is responsible for handling traffic while the passive unit remains idle, ready to take over in case of a failure. When a failover occurs, the active unit sends out gratuitous ARP messages to notify neighboring devices about the change in the active unit's IP address. This ensures that the network devices update their ARP tables and can forward traffic to the new active unit.
In which two operating modes can FortiWeb modify HTTP packets? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, D
Virtual proxy: In virtual proxy mode, FortiWeb acts as an intermediary between clients and the server, and it can modify HTTP packets. It performs various security checks, such as inspecting and filtering HTTP traffic before forwarding it to the web server.
Reverse proxy: In reverse proxy mode, FortiWeb sits between the client and the server, handling incoming requests from clients, modifying or inspecting HTTP packets as needed, and forwarding them to the backend servers.
What is the difference between an API gateway protection schema and a machine learning (ML) API protection schema?
Answer : C
In FortiWeb's API protection mechanisms, there are distinctions between the traditional API gateway protection schema and the machine learning (ML) based API protection schema:
Data Type Support: The API gateway protection schema has the capability to support various data types beyond just strings, allowing for more comprehensive validation and enforcement of API schemas.
Schema Adaptability: The ML-based API protection schema is designed to automatically learn and adapt to changes in the API structure without requiring manual intervention from administrators. This dynamic learning process enables FortiWeb to identify and protect against anomalies and potential threats in real-time.