Fortinet FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.4 Administrator FCSS_EFW_AD-7.4 Exam Practice Test
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a corporate network and a new remote office network.
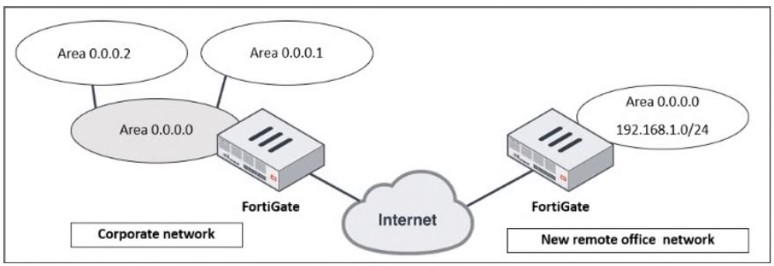
An administrator must integrate the new remote office network with the corporate enterprise network.
What must the administrator do to allow routing between the two networks?
Answer : D
In this scenario, the corporate network and the new remote office network need to communicate over the Internet, which requires a secure and dynamic routing method. Since both networks are using OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) as the routing protocol, the best approach is to establish an OSPF over IPsec VPN to ensure secure and dynamic route propagation.
OSPF is already running on the corporate network, and extending it over an IPsec tunnel allows dynamic route exchange between the corporate FortiGate and the remote office FortiGate. IPsec provides encryption for traffic over the Internet, ensuring secure communication. OSPF over IPsec eliminates the need for manual static routes, allowing automatic route updates if networks change.
The new remote office's 192.168.1.0/24 subnet will be advertised dynamically to the corporate network without additional configuration.
Refer to the exhibit, which contains the partial output of an OSPF command.
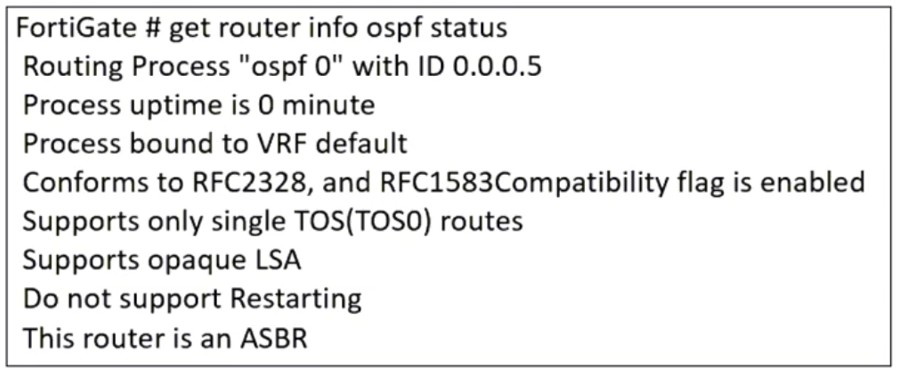
An administrator is checking the OSPF status of a FortiGate device and receives the output shown in the exhibit.
Which statement on this FortiGate device is correct?
Answer : A
From the OSPF status output, the key information is:
'This router is an ASBR' This means the FortiGate is acting as an Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR).
An ASBR is responsible for injecting external routing information into OSPF from another routing protocol (such as BGP, static routes, or connected networks).
A user reports that their computer was infected with malware after accessing a secured HTTPS website. However, when the administrator checks the FortiGate logs, they do not see that the website was detected as insecure despite having an SSL certificate and correct profiles applied on the policy.
How can an administrator ensure that FortiGate can analyze encrypted HTTPS traffic on a website?
Answer : D
FortiGate, like other security appliances, cannot analyze encrypted HTTPS traffic unless it decrypts it first. If only certificate inspection is enabled, FortiGate can see the certificate details (such as the domain and issuer) but cannot inspect the actual web content.
To fully analyze the traffic and detect potential malware threats:
Full SSL inspection (Deep Packet Inspection) must be enabled in the SSL/SSH Inspection Profile.
This allows FortiGate to decrypt the HTTPS traffic, inspect the content, and then re-encrypt it before forwarding it to the user.
Without full SSL inspection, threats embedded in encrypted traffic may go undetected.
Refer to the exhibit.
A pre-run CLI template that is used in zero-touch provisioning (ZTP) and low-touch provisioning (LTP) with FortiManager is shown.
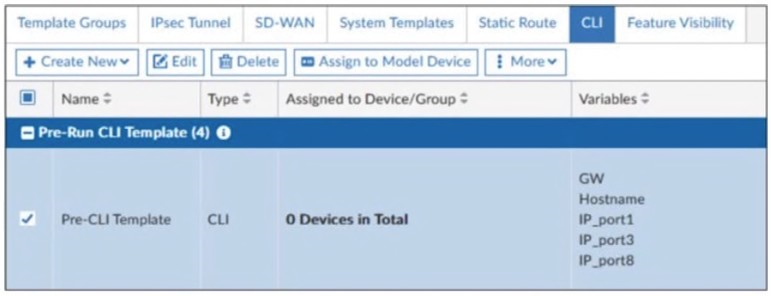
The template is not assigned even though the configuration has already been installed on FortiGate.
What is true about this scenario?
Answer : B
In FortiManager, pre-run CLI templates are used in Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP) and Low-Touch Provisioning (LTP) to configure a FortiGate device before it is fully managed by FortiManager.
These templates apply configurations when a device is initially provisioned. Once the pre-run CLI template is executed, FortiManager automatically unassigns it from the device because it is not meant to persist like other policy configurations. This prevents conflicts and ensures that the FortiGate configuration is not repeatedly applied after the initial setup.
A company's users on an IPsec VPN between FortiGate A and B have experienced intermittent issues since implementing VXLAN. The administrator suspects that packets exceeding the 1500-byte default MTU are causing the problems.
In which situation would adjusting the interface's maximum MTU value help resolve issues caused by protocols that add extra headers to IP packets?
Answer : C
When using IPsec VPNs and VXLAN, additional headers are added to packets, which can exceed the default 1500-byte MTU. This can lead to fragmentation issues, dropped packets, or degraded performance.
To resolve this, the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) should be adjusted only if all devices in the network path support it. Otherwise, some devices may still drop or fragment packets, leading to continued issues.
Why adjusting MTU helps:
VXLAN adds a 50-byte overhead to packets.
IPsec adds additional encapsulation (ESP, GRE, etc.), increasing the packet size.
If packets exceed the MTU, they may be fragmented or dropped, causing intermittent connectivity issues.
Lowering the MTU on interfaces ensures packets stay within the supported size limit across all network devices.
An administrator applied a block-all IPS profile for client and server targets to secure the server, but the database team reported the application stopped working immediately after.
How can an administrator apply IPS in a way that ensures it does not disrupt existing applications in the network?
Answer : A
Applying an aggressive IPS profile without prior testing can disrupt legitimate applications by incorrectly identifying normal traffic as malicious. To prevent disruptions while still monitoring for threats:
Enable IPS in 'Monitor Mode' first:
This allows FortiGate to log and analyze potential threats without actively blocking traffic.
Administrators can review logs and fine-tune IPS signatures to minimize false positives before switching to blocking mode.
Verify and adjust signature patterns:
Some signatures might trigger unnecessary blocks for legitimate application traffic.
By analyzing logs, administrators can disable or modify specific rules causing false positives.
An administrator is extensively using VXLAN on FortiGate.
Which specialized acceleration hardware does FortiGate need to improve its performance?
Answer : A
VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) is an overlay network technology that extends Layer 2 networks over Layer 3 infrastructure. When VXLAN is used extensively on FortiGate, hardware acceleration is crucial for maintaining performance.
NP7 (Network Processor 7) is Fortinet's latest network processor designed to accelerate high-performance networking features, including:
VXLAN encapsulation/decapsulation
IPsec VPN offloading
Firewall policy enforcement
Advanced threat protection at wire speed
NP7 significantly reduces latency and improves throughput when handling VXLAN traffic, making it the best choice for large-scale VXLAN deployments.