Fortinet FCSS - Enterprise Firewall 7.6 Administrator FCSS_EFW_AD-7.6 Exam Practice Test
Refer to the exhibit, which shows an enterprise network connected to an internet service provider.
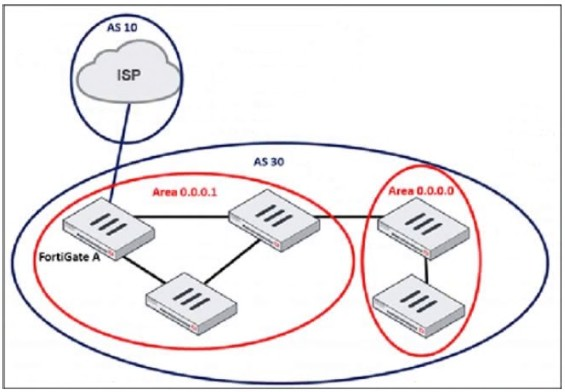
The administrator must configure the BGP section of FortiGate A to give internet access to the enterprise network.
Which command must the administrator use to establish a connection with the internet service provider?
Answer : A
In BGP (Border Gateway Protocol), a neighbor (peer) configuration is required to establish a connection between two BGP routers. Since FortiGate A is connecting to the ISP (Autonomous System 10) from AS 30, the administrator must define the ISP's BGP router as a neighbor.
The config neighbor command is used to:
Define the ISP's IP address as a BGP peer
Specify the remote AS (AS 10 in this case)
Allow BGP route exchanges between FortiGate A and the ISP
Refer to the exhibit, which shows an OSPF network.
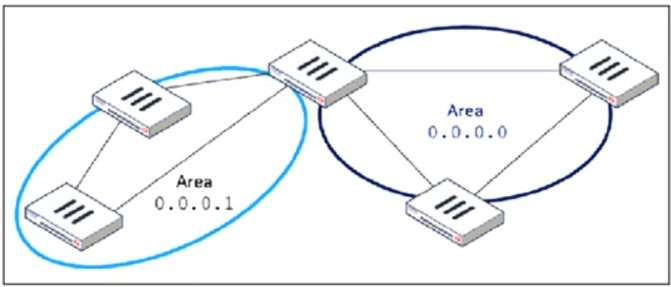
Which configuration must the administrator apply to optimize the OSPF database?
Answer : B
The OSPF database optimization is necessary to reduce unnecessary routing information and improve network performance. In the given topology, Area 0.0.0.1 is a non-backbone area connected to Area 0.0.0.0 (the backbone area) through an Area Border Router (ABR).
To optimize OSPF in this scenario, configuring Area 0.0.0.1 as a Stub Area will:
Reduce the size of the OSPF database by preventing external routes (from outside OSPF) from being injected into Area 0.0.0.1.
Allow only intra-area and inter-area routes, meaning routers in Area 0.0.0.1 will rely on a default route for external destinations.
Improve convergence time and reduce router processing load since fewer LSAs (Link-State Advertisements) are exchanged.
Refer to the exhibit, which contains the partial output of an OSPF command.
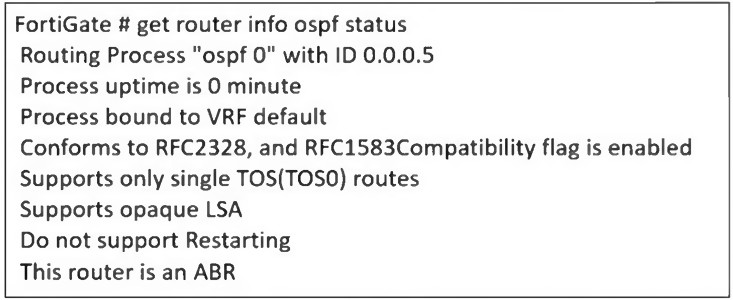
An administrator is checking the OSPF status of a FortiGate device and receives the output shown in the exhibit.
What two conclusions can the administrator draw? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
The output of the get router info ospf status command provides key information about the OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) configuration on the FortiGate device.
The FortiGate device is connected to multiple areas
The output states: 'This router is an ABR'
ABR (Area Border Router) means the device is connected to multiple OSPF areas and maintains routing information between them.
This confirms that the FortiGate is not just in one area, but at least one backbone area (Area 0) and another OSPF area.
The FortiGate device injects external routing information
The output states: 'Supports opaque LSA'
Opaque LSAs (Type 9, 10, and 11) are used in OSPF extensions, including those that support external route injection.
Typically, ABRs or ASBRs (Autonomous System Boundary Routers) inject external routes, allowing routes from other routing protocols (such as BGP or static routes) to be advertised into OSPF.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a command output.

FortiGate_A and FortiGate_B are members of an FGSP cluster in an enterprise network.
While testing the cluster using the ping command, the administrator monitors packet loss and found that the session output on FortiGate_B is as shown in the exhibit.
What could be the cause of this output on FortiGate_B?
Answer : B
The Fortinet FGSP (FortiGate Session Life Support Protocol) cluster allows session synchronization between two FortiGate devices to provide seamless failover. However, ICMP (ping) is a connectionless protocol, and by default, FortiGate does not synchronize connectionless sessions unless explicitly enabled.
In the exhibit:
The command get system session list | grep icmp on FortiGate_B returns no output, meaning that ICMP sessions are not being synchronized from FortiGate_A.
If session-pickup-connectionless is disabled, FortiGate_B will not receive ICMP sessions, causing packet loss during failover.
A company's users on an IPsec VPN between FortiGate A and B have experienced intermittent issues since implementing VXLAN. The administrator suspects that packets exceeding the 1500-byte default MTU are causing the problems.
In which situation would adjusting the interface's maximum MTU value help resolve issues caused by protocols that add extra headers to IP packets?
Answer : C
When using IPsec VPNs and VXLAN, additional headers are added to packets, which can exceed the default 1500-byte MTU. This can lead to fragmentation issues, dropped packets, or degraded performance.
To resolve this, the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) should be adjusted only if all devices in the network path support it. Otherwise, some devices may still drop or fragment packets, leading to continued issues.
Why adjusting MTU helps:
VXLAN adds a 50-byte overhead to packets.
IPsec adds additional encapsulation (ESP, GRE, etc.), increasing the packet size.
If packets exceed the MTU, they may be fragmented or dropped, causing intermittent connectivity issues.
Lowering the MTU on interfaces ensures packets stay within the supported size limit across all network devices.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows a partial troubleshooting command output.

An administrator is extensively using IPsec on FortiGate. Many tunnels show information similar to the output shown in the exhibit.
What can the administrator conclude?
Answer : B
The diagnose vpn tunnel list name Hub2Spoke1 command output provides key information about the offloading status of an IPsec VPN tunnel to the Network Processing Unit (NPU).
npu_flag=20:
This flag indicates that both inbound and outbound IPsec Security Associations (SAs) have been offloaded to the NPU, meaning the VPN traffic is processed in hardware instead of the CPU.
npu_rgwy=10.10.2.2 and npu_lgwy=10.10.1.1:
These IPs represent the remote gateway (rgwy) and local gateway (lgwy), confirming that the tunnel is successfully offloaded.
npu_selid=1:
This value means the session selector for the NPU offloaded SA is active.
Since both inbound and outbound SAs are offloaded, the administrator can conclude that the FortiGate NPU is handling IPsec encryption and decryption efficiently, reducing CPU load and improving VPN performance.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows an enterprise network connected to an internet service provider.
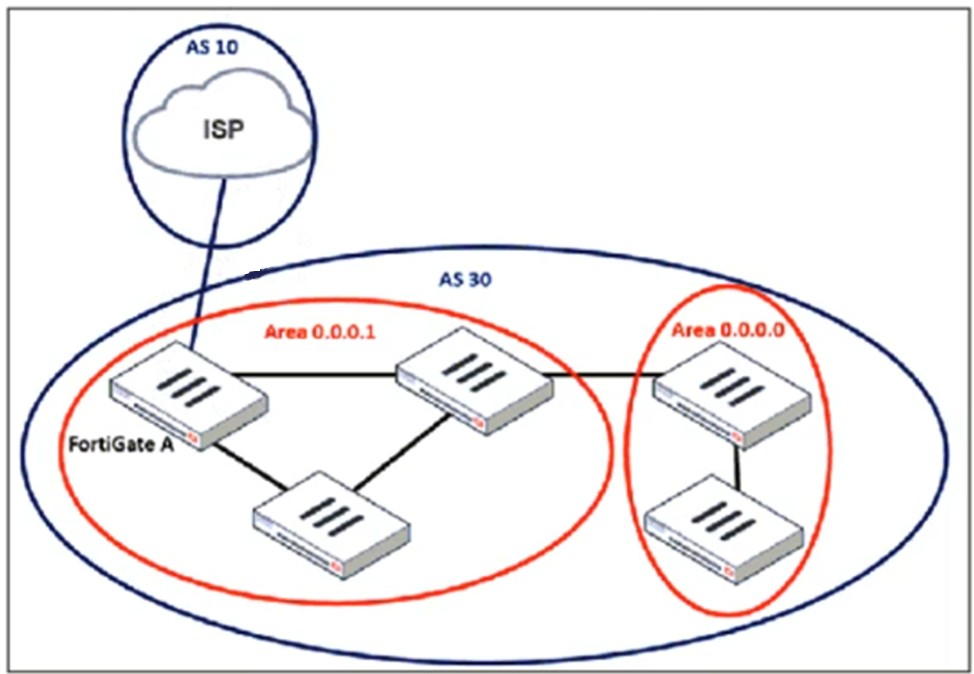
An administrator must configure a loopback as a BGP source to connect to the ISP.
Which two commands are required to establish the connection? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
When configuring a loopback interface as the BGP source for connecting to an ISP, two important settings must be applied:
1. Enable EBGP Multihop (ebgp-enforce-multihop)
2. Set the Update Source (update-source)