Fortinet FCSS - FortiSASE 25 Administrator FCSS_SASE_AD-25 Exam Practice Test
Refer to the exhibits.
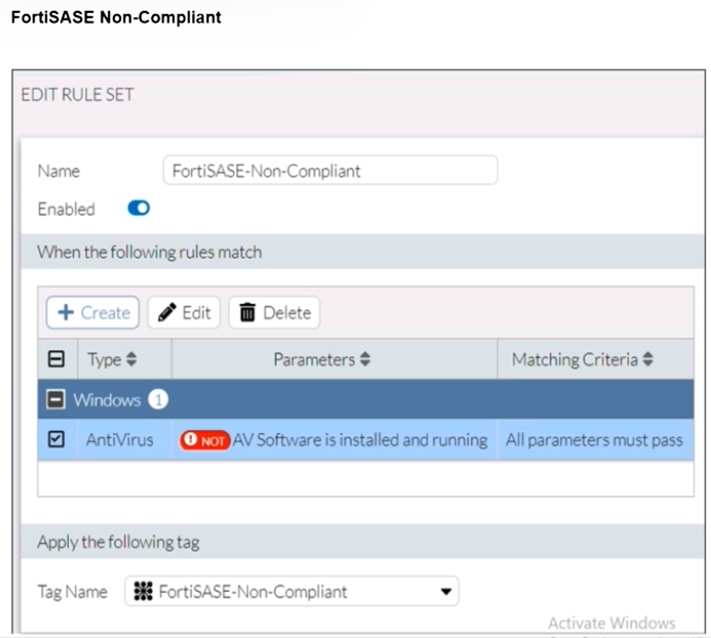

Antivirus is installed on a Windows 10 endpoint, but the windows application firewall is stopping it from running.
What will the endpoint security posture check be?
Answer : A
Although the antivirus is installed, it is not running due to the Windows application firewall blocking it. According to the FortiSASE-Non-Compliant rule, antivirus software must be both installed and running. Since this condition fails, FortiClient assigns the FortiSASE-Non-Compliant tag to the endpoint.
Which two of the following can release the network lockdown on the endpoint applied by FortiSASE? (Choose two.)\
Answer : A, D
FortiSASE releases network lockdown when the endpoint re-establishes the tunnel connection or when it is verified as compliant through ZTNA tag evaluation, ensuring it meets security posture requirements.
How do security profile group objects behave when central management is enabled on FortiSASE?
Answer : D
When central management is enabled, security profile group objects are managed exclusively through FortiManager, making them read-only on the FortiSASE portal to ensure centralized policy control.
A customer wants to upgrade their legacy on-premises proxy to a cloud-based proxy for a hybrid network.
Which two FortiSASE features would help the customer achieve this outcome? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, D
The secure web gateway (SWG) serves as the cloud-based proxy that inspects and controls web traffic, replacing the on-premises proxy. The inline-CASB provides additional visibility and control over cloud application usage, enhancing security in hybrid environments.
What are two benefits of deploying secure private access with SD-WAN? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
Deploying secure private access with SD-WAN enables the hub FortiGate to perform ZTNA posture checks, and supports both TCP and UDP applications over the tunnel, allowing for flexible and secure access to internal resources.
A company must provide access to a web server through FortiSASE secure private access for contractors.
What is the recommended method to provide access?
Answer : C
The bookmark portal is the recommended method for providing contractors access to private web applications through FortiSASE Secure Private Access, as it offers a user-friendly, secure, and controlled access mechanism without requiring full network connectivity.
Refer to the exhibits.
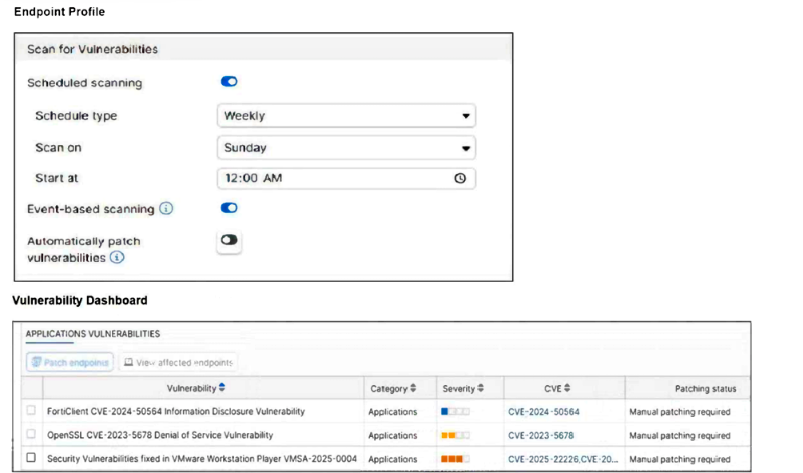
How will the application vulnerabilities be patched, based on the exhibits provided?
Answer : B