Fortinet FCSS - FortiSASE 24 Administrator FCSS_SASE_AD-24 Exam Practice Test
To complete their day-to-day operations, remote users require access to a TCP-based application that is hosted on a private web server. Which FortiSASE deployment use case provides the most efficient and secure method for meeting the remote users' requirements?
Answer : C
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) private access provides the most efficient and secure method for remote users to access a TCP-based application hosted on a private web server. ZTNA ensures that only authenticated and authorized users can access specific applications based on predefined policies, enhancing security and access control.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA):
ZTNA operates on the principle of 'never trust, always verify,' continuously verifying user identity and device security posture before granting access.
It provides secure and granular access to specific applications, ensuring that remote users can securely access the TCP-based application hosted on the private web server.
Secure and Efficient Access:
ZTNA private access allows remote users to connect directly to the application without needing a full VPN tunnel, reducing latency and improving performance.
It ensures that only authorized users can access the application, providing robust security controls.
FortiOS 7.2 Administration Guide: Provides detailed information on ZTNA and its deployment use cases.
FortiSASE 23.2 Documentation: Explains how ZTNA can be used to provide secure access to private applications for remote users.
In a FortiSASE secure web gateway (SWG) deployment, which three features protect against web-based threats? (Choose three J
Answer : A, B, D
Refer to the exhibits.
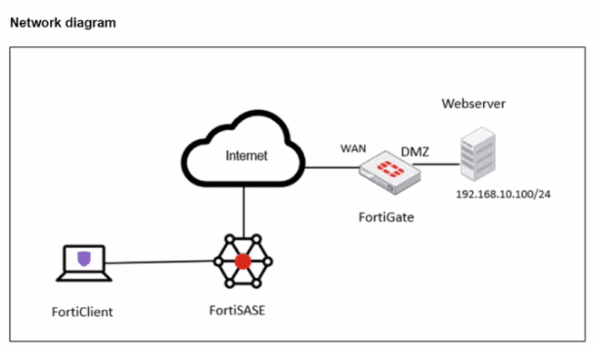
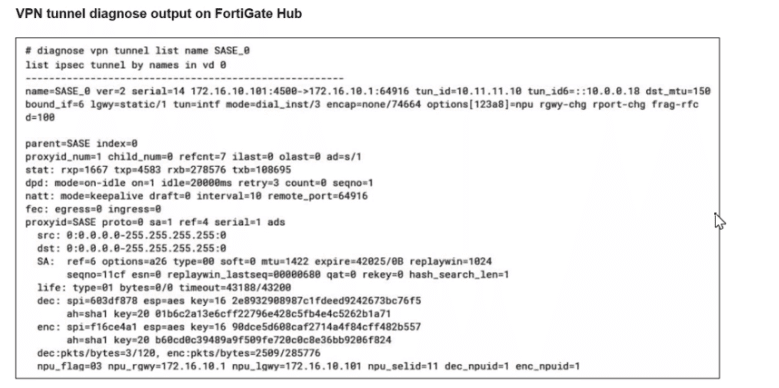
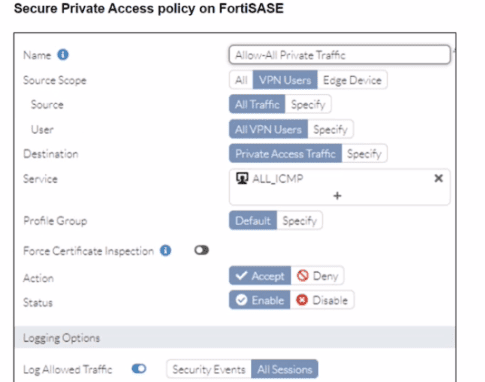
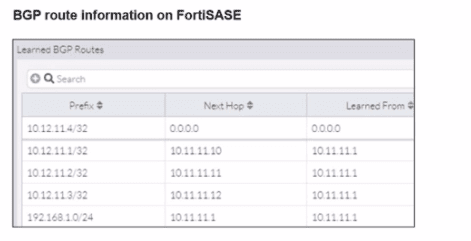

A FortiSASE administrator is trying to configure FortiSASE as a spoke to a FortiGate hub. The tunnel is up to the FortiGale hub. However, the administrator is not able to ping the webserver hosted behind the FortiGate hub.
Based on the output, what is the reason for the ping failures?
Answer : C
Which three configurations must you perform to set up FortiGate as a FortiSASE LAN extension? (Choose three.)
Answer : B, D, E
Which FortiSASE feature ensures least-privileged user access to corporate applications that are protected by an on-premises FortiGate?
Answer : D
The correct answer is D. zero trust network access (ZTNA).
Explanation
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is the FortiSASE feature specifically designed to provide secure, least-privileged access to applications. It operates on the core principle of 'never trust, always verify.'
Instead of granting broad network access like a traditional VPN, ZTNA grants access to specific applications on a per-session basis, only after verifying the user's identity and the security posture of their device. This ensures a user can only access the corporate applications they are explicitly authorized for, and nothing else on the network, perfectly embodying the principle of least-privileged access.
The FortiSASE solution achieves this by creating a secure, encrypted tunnel from the remote user directly to the application protected by the on-premises FortiGate, which acts as a ZTNA access proxy.
Which two settings are automatically pushed from FortiSASE to FortiClient in a FortiSASE deployment with default settings? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
Which secure internet access (SIA) use case minimizes individual workstation or device setup, because you do not need to install FortiClient on endpoints or configure explicit web proxy settings on web browser-based end points?
Answer : B
The Secure Internet Access (SIA) use case that minimizes individual workstation or device setup is SIA for agentless remote users. This use case does not require installing FortiClient on endpoints or configuring explicit web proxy settings on web browser-based endpoints, making it the simplest and most efficient deployment.
SIA for Agentless Remote Users:
Agentless deployment allows remote users to connect to the SIA service without needing to install any client software or configure browser settings.
This approach reduces the setup and maintenance overhead for both users and administrators.
Minimized Setup:
Without the need for FortiClient installation or explicit proxy configuration, the deployment is straightforward and quick.
Users can securely access the internet with minimal disruption and administrative effort.
FortiOS 7.2 Administration Guide: Details on different SIA deployment use cases and configurations.
FortiSASE 23.2 Documentation: Explains how SIA for agentless remote users is implemented and the benefits it provides.