Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiAnalyzer 7.2 Administrator NSE6_FAZ-7.2 Exam Practice Test
An administrator, fortinet, can view logs and perform device management tasks, such as adding and removing registered devices. However, administrator fortinet is not able to create a mail server that can be used to send alert emails.
What can be the problem?
Answer : B
If the administrator 'fortinet' can view logs and perform device management tasks but cannot create a mail server for alert emails, it is likely due to the administrative profile assigned to them. The Standard_User administrative profile may restrict certain administrative functions, such as creating mail servers. To perform all administrative tasks, including creating mail servers, a higher privilege profile, such as Super_Admin, might be required. Reference: FortiAnalyzer 7.2 Administrator Guide, 'Mail Server' section.
Which two of the available registration methods place the device automatically in its assigned ADOM? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
The registration methods that automatically place a device in its assigned ADOM are using the serial number and fabric authorization. When devices are added to FortiAnalyzer using these methods, they are automatically placed in the appropriate ADOM, which could be a default ADOM based on the device type or a predefined ADOM based on the serial number or fabric authorization. This simplifies the management of devices and their logs by organizing them into their respective ADOMs from the moment they are registered. Reference: FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 Administration Guide, 'Default device type ADOMs' and 'Assigning devices to an ADOM' sections.
Which two statements are true regarding the log synchronization states for HA on FortiAnalyzer? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
For HA on FortiAnalyzer, Log Data Sync ensures real-time log synchronization among all cluster members, including backup devices. This feature is enabled by default. The Initial Logs Sync state is triggered when a new unit is added to an HA cluster, where the primary unit synchronizes its logs with the newly added unit. After the initial synchronization, the secondary unit reboots and rebuilds its log database with the synchronized logs. Reference: FortiAnalyzer 7.2 Administrator Guide, 'Log synchronization' section.
You finished registering a FortiGate device. After traffic starts to flow through FortiGate. you notice that only some of the logs expected are being received on FortiAnalyzer.
What could be the reason for the logs not arriving on FortiAnalyzer?
Answer : A
When only some of the expected logs from a FortiGate device are being received on FortiAnalyzer, it often indicates a configuration issue on the FortiGate side. Proper logging configuration on FortiGate involves specifying what types of logs to generate (e.g., traffic, event, security logs) and ensuring that these logs are directed to the FortiAnalyzer unit for storage and analysis. If the logging settings on FortiGate are not correctly configured, it could result in incomplete log data being sent to FortiAnalyzer. This might include missing logs for certain types of traffic or events that are not enabled for logging on the FortiGate device. Ensuring comprehensive logging is enabled and correctly directed to FortiAnalyzer is crucial for full visibility into network activities and for the effective analysis and reporting of security incidents and network performance.
An administrator has configured the following settings:

What is the purpose of executing these commands?
Answer : C
The purpose of executing the provided CLI commands, which include setting the log-checksum to md5-auth, is to ensure the integrity of the log files. This setting is used to record the MD5 hash value of log files, which is a widely used cryptographic hash function that produces a 128-bit (16-byte) hash value. By using MD5 authentication, FortiAnalyzer ensures that the log files have not been altered or tampered with during transit, thereby verifying their integrity upon receipt. This is not related to encrypting log transfers, scheduling reports, or creating secure channels for OFTP (Over-the-FortiGate Protocol) processes.
Refer to the exhibit.
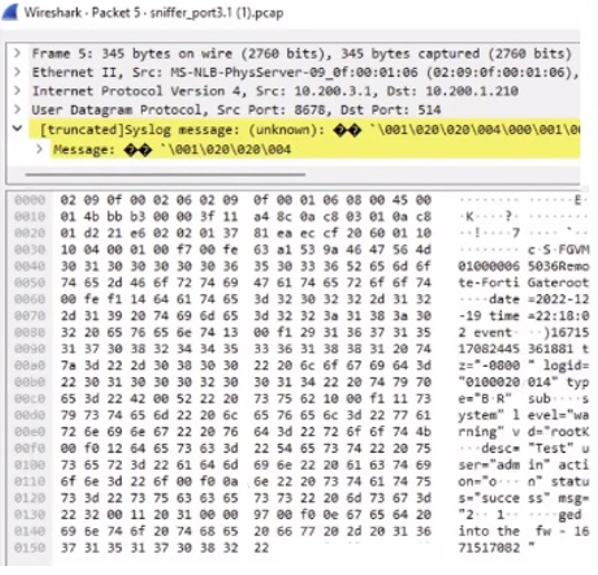
Which image corresponds to the packet capture shown in the exhibit?
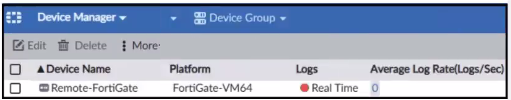
A)
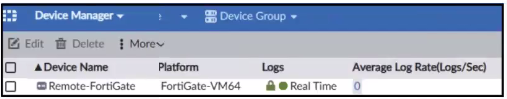
B)
C)
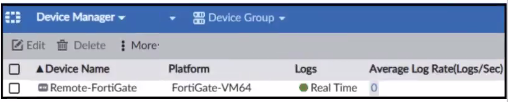
Answer : A
The exhibit shows a packet capture with a syslog message containing a log event from a FortiGate device. This log event includes several details such as the date, time, and event message. The corresponding image that matches this packet capture would be the one which shows that the FortiGate device has logs being received in real-time, as indicated by the highlighted section in the packet capture where it mentions 'real-time'. Therefore, Option A is the correct answer because it shows logs with 'Real Time' status for the FortiGate-VM64 device, indicating that this FortiAnalyzer is currently receiving real-time logs from the device, matching the activity in the packet capture. Reference: Based on the provided exhibits and the real-time logging information, correlated with the knowledge from the FortiAnalyzer 7.2 Administrator documentation regarding log reception and device management.
Which two statements are true regarding FortiAnalyzer system backups? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, D
FortiAnalyzer allows for the inclusion of existing reports in the backup files, providing a comprehensive backup of configurations and data. Additionally, the backup files can be configured to be uploaded to SCP and SFTP servers, ensuring secure transfer and offsite storage of backup data. This can be configured both in the GUI and the CLI, providing flexibility in how backups are scheduled and managed. Reference: FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 Administration Guide, 'Scheduling automatic backups' section.