Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiSwitch 7.2 NSE6_FSW-7.2 Exam Practice Test
Which two rules used by MSTP are similar to rules used by other STP methods? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
'MSTP is based on RSTP', so the same port role election and the same root bridge selection. Reference: FortiSwitch 7.2 Study Guide, page 187
Refer to the exhibit.
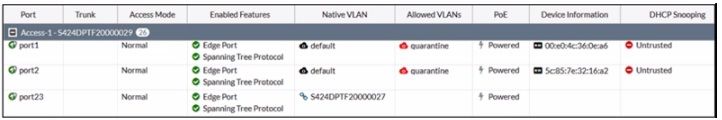
The exhibit shows the current status of the ports on the managed FortiSwitch. Access-1.
Why would FortiGate display a serial number in the Native VLAN column associated with the port23 entry?
Answer : D
The information in the 'Native VLAN' column for port23 on the FortiSwitch indicates that a standalone switch is connected to it. This is because the column displays '$424MPTF20000027,' which matches the format of a Fortinet device serial number.
Here's a breakdown of the evidence in the image:
Native VLAN: The 'Native VLAN' column typically displays the VLAN ID for untagged traffic on a trunk port. However, in this case, it shows a serial number format ('$424MPTF20000027').
No Trunk Information: The 'Trunk' column is blank for port23, indicating it's not configured as a trunk member.
Other Ports: Port1 and port2 show 'default' in the 'Native VLAN' column, which is the expected behavior for access ports.
Fortinet FortiSwitch devices typically don't display the serial number of adjacent FortiSwitch devices in the 'Native VLAN' column. This column is reserved for VLAN information on trunk ports.
Which two statements about managing a FortiSwitch stack on FortiGate are true? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
A FortiLink interface must be enabled on FortiGate (A): To manage a FortiSwitch stack, a dedicated FortiLink interface on the FortiGate is required. This interface is used to manage the communication between FortiGate and the FortiSwitch stack, enabling centralized control and configuration of the switches directly from the FortiGate.
The switch controller feature must be enabled on FortiGate (B): Enabling the switch controller feature on FortiGate allows it to manage connected FortiSwitch units. This feature provides tools and interfaces on the FortiGate for overseeing FortiSwitch configurations, monitoring switch status, and managing network policies across the stack.
Which two statements about 802.1X authentication on FortiSwitch ports are true? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, D
All hosts behind an authenticated port are allowed access after a successful authentication (A): Once a device on a port successfully authenticates using 802.1X, all other devices connected behind that port also gain network access. This is typical in scenarios where a switch is behind an authenticated port and not each device individually authenticates.
All devices connecting to FortiSwitch must support 802.1X authentication (D): For a network secured with 802.1X, all devices attempting to connect through the FortiSwitch must support and participate in 802.1X authentication to gain access. This ensures that all devices on the network are authenticated before they are allowed to communicate on the network.
What type of multimode transceiver can be used to split a 40G port?
Answer : A
QSFP+ transceiver (A): The QSFP+ (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Plus) transceiver is designed to handle 40G data rates and can be used to split a 40G port into multiple 10G connections. This type of transceiver supports such configurations, making it suitable for high-density applications where multiple 10G connections are derived from a single 40G port, thereby maximizing the utilization of the port and the fiber infrastructure.
Which two types of Layer 3 interfaces can participate in dynamic routing on FortiSwitch? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
In dynamic routing on FortiSwitch, certain types of interfaces are utilized to participate in the routing processes. The types of interfaces that can be used include:
Loopback Interfaces (B): Loopback interfaces are virtual interfaces that are always up, making them ideal for use in routing protocols where a stable interface is necessary. They are commonly used to establish router IDs and manage routing information more reliably.
Switch Virtual Interfaces (C): Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVIs) are assigned to VLANs and can have IP addresses assigned to them, making them capable of participating in Layer 3 routing. SVIs are essential for routing between different VLANs on a switch and can participate in dynamic routing protocols to advertise networks or make routing decisions.
Physical Interfaces (D) and Detected Management Interfaces (A) are not typically used directly by dynamic routing protocols for their operations in the context of FortiSwitch.
What can an administrator do to maintain a FortiGate-compatible FortiSwitch configuration when changing the management mode from standalone to FortiLinK?
Answer : C
When transitioning the management of a FortiSwitch from standalone mode to being managed by FortiGate via FortiLink, it is critical to ensure that the existing configurations are preserved. The best practice involves:
FortiGate's Role in Configuration Preservation: FortiGate has the capability to automatically preserve the existing configuration of a FortiSwitch when it is integrated into the network via FortiLink. This feature helps ensure that the transition does not disrupt the network's operational settings.
Configuration Integration: As FortiSwitch is integrated into FortiGate's management via FortiLink, FortiGate captures and integrates the existing switch configuration, enabling a seamless transition. This process involves FortiGate recognizing the FortiSwitch and its current setup, then incorporating these settings into the centralized management interface without the need for manual reconfiguration or the use of additional tools.