Fortinet NSE 7 - Network Security 7.2 Support Engineer NSE7_NST-7.2 Exam Practice Test
Consider the scenario where the server name indication (SNI) does not match either the common name (CN) or any of the subject alternative names (SAN) in the server certificate. Which action will FortiGate take when using the default settings for SSL certificate inspection?
Answer : A
SNI and Certificate Mismatch: When the Server Name Indication (SNI) does not match either the Common Name (CN) or any of the Subject Alternative Names (SAN) in the server certificate, FortiGate's default behavior is to consider this as an invalid SSL/TLS configuration.
Default Action: FortiGate, under default settings for SSL certificate inspection, will close the connection to prevent potential security risks associated with mismatched certificates.
Refer to the exhibits.
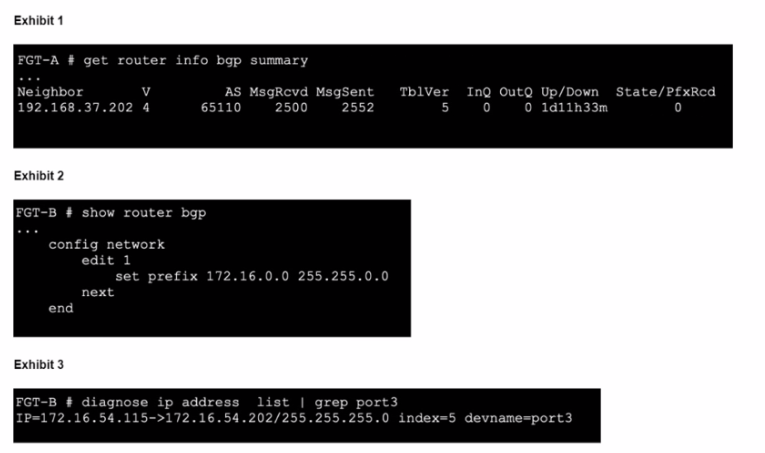
An administrator is attempting to advertise the network configured on port3. However, FGT-A is not receiving the prefix.
Which two actions can the administrator take to fix this problem'' (Choose two.)
Answer : A, D
Soft Reset of BGP:
Performing a soft reset of BGP is a common method to resolve issues where prefixes are not being received. It forces both BGP peers to resend their complete routing tables to each other.
This can be done using the command: execute router clear bgp soft in and execute router clear bgp soft out.
Network Import Check:
The network-import-check command controls whether the FortiGate should verify that the prefix exists in the routing table before advertising it.
Disabling this check can resolve issues where valid prefixes are not advertised due to stringent verification.
The command to disable this is: config router bgp set network-import-check disable end.
BGP Configuration Verification:
Ensure that the BGP configuration on FGT-B is correctly set to advertise the network 172.16.54.0/24.
Verify that the network statement is correctly configured and matches the intended prefix.
Fortinet Community: Technical Note on Configuring BGP (Welcome to the Fortinet Community!).
Fortinet Documentation: Configuring BGP on FortiGate (Fortinet Document Library).
Refer to the exhibit. which contains the output of diagnose vpn tunnel list.
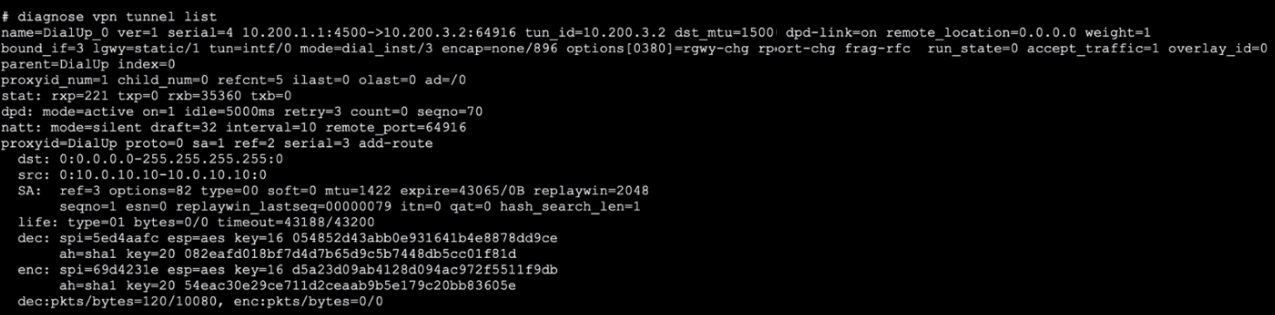
Which command will capture ESP traffic for the VPN named DialUp_0?
Answer : C
Capturing ESP Traffic:
ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) traffic is associated with IPsec and is identified by the protocol number 50. To capture ESP traffic, you need to filter packets based on this protocol.
In this specific case, you also need to filter for the host associated with the VPN tunnel, which is 10.200.3.2 as indicated in the exhibit.
Sniffer Command:
The correct command to capture ESP traffic for the VPN named DialUp_0 is:
diagnose sniffer packet any 'esp and host 10.200.3.2'
This command ensures that only ESP packets to and from the specified host are captured, providing a focused and relevant data set for troubleshooting.
What are two functions of automation stitches? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
Automation Stitches Overview:
Automation stitches in FortiOS allow administrators to automate responses to specific events, such as running diagnostic commands or taking corrective actions when certain thresholds are exceeded.
Diagnostic Commands and Alerts:
Automation stitches can be configured to run diagnostic commands and attach the results to email alerts. This is useful for monitoring and troubleshooting purposes, particularly when CPU or memory usage exceeds set thresholds.
Sequential Execution with Parameters:
When actions are executed sequentially, each action can take parameters from the previous action as input. This enables more complex workflows and automation sequences where the output of one action influences the next.
Which two statements about application-layer test commands ate true? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
Statistics and Configuration Information:
Application-layer test commands can display detailed statistics and configuration information about specific features or processes. For example, commands like diagnose vpn ipsec tunnel list provide detailed statistics about VPN tunnels.
Real-time Debugs:
These commands also facilitate real-time debugging of applications and processes. For instance, using diagnose debug application followed by the specific application, such as fssod, provides real-time debug information which is crucial for troubleshooting.
Fortinet Documentation: Application-layer Test Commands (Fortinet GURU).
Exhibit.
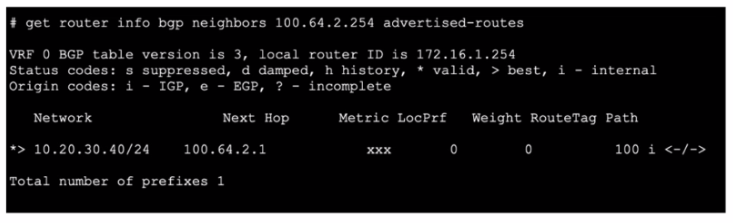
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the output of get router info bgp neighbors 100.64.2.254.
What can you conclude from the output?
Answer : D
BGP Advertisement: The output from the command get router info bgp neighbors 100.64.2.254 advertised-routes shows the routes that the local router is advertising to its BGP neighbor.
Output Analysis:
The Network column lists the networks being advertised.
The Next Hop column indicates the next-hop IP address for these routes.
The line *> 10.20.30.40/24 100.64.2.1 indicates that the 10.20.30.40/24 network is being advertised with a next-hop of 100.64.2.1.
Local Router's Role: Since the output lists the advertised routes, it means that the local router (with router ID 172.16.1.254) is advertising the 10.20.30.40/24 network to its neighbor 100.64.2.254.
This confirms that the local router is indeed advertising the specified network to its BGP neighbor.
Refer to the exhibit, which shows the omitted output of FortiOS kernel slabs.
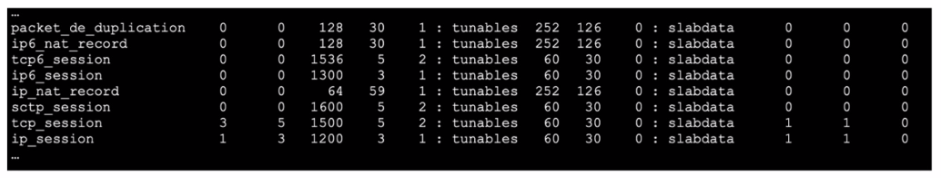
Which statement is true?
Answer : B
Kernel Slabs Overview:
The slab allocator in the Linux kernel is used for efficient memory management. It groups objects of the same type into caches, which are divided into slabs.
Each slab contains multiple objects and helps to minimize fragmentation and enhance memory allocation efficiency.
Interpreting the Exhibit:
The exhibit shows output related to various kernel slab caches.
The line for ip6_session indicates that there are 1300 kB allocated for this slab, which means the total memory size allocated for IPv6 session objects in the kernel is 1300 kB.
Linux Kernel Documentation: Slab Allocator details (Hammertux).