Fortinet NSE 7 - Zero Trust Access 7.2 NSE7_ZTA-7.2 Exam Practice Test
Which method is used to install passive agent on an endpoint?
Answer : D
The method used to install a passive agent on an endpoint is:
D) Installed by user or deployment tools: Passive agents are typically installed on endpoints either manually by users or automatically through deployment tools used by the organization.
The other options do not accurately describe the installation of passive agents:
A) Deployed by using a login/logout script: This is not the standard method for deploying passive agents.
B) Agent is downloaded from Playstore: This is more relevant for mobile devices and does not represent the general method for passive agent installation.
C) Agent is downloaded and run from captive portal: This method is not typically used for installing passive agents.
FortiNAC Agent Deployment Guide.
Installation Methods for Passive Agents in FortiNAC.
Exhibit.
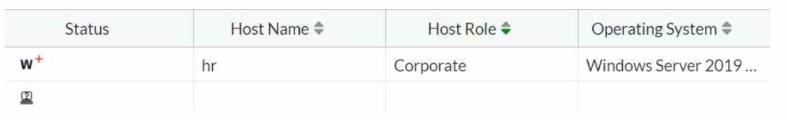
Which two statements are true about the hr endpoint? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
Based on the exhibit, the true statements about the hr endpoint are:
B) The endpoint is marked as a rogue device: The 'w' symbol typically indicates a warning or an at-risk status, which can be associated with an endpoint being marked as rogue due to failing to meet the security compliance requirements or other reasons.
C) The endpoint has failed the compliance scan: The 'w' symbol can also signify that the endpoint has failed a compliance scan, which is a common reason for an endpoint to be marked as at risk.
Which statement is true about disabled hosts on FortiNAC?
Answer : A
They are quarantined and placed in the remediation VLAN. This is a standard practice in network access control systems where non-compliant or disabled hosts are isolated in a VLAN where they can be remediated or reviewed.
Exhibit.
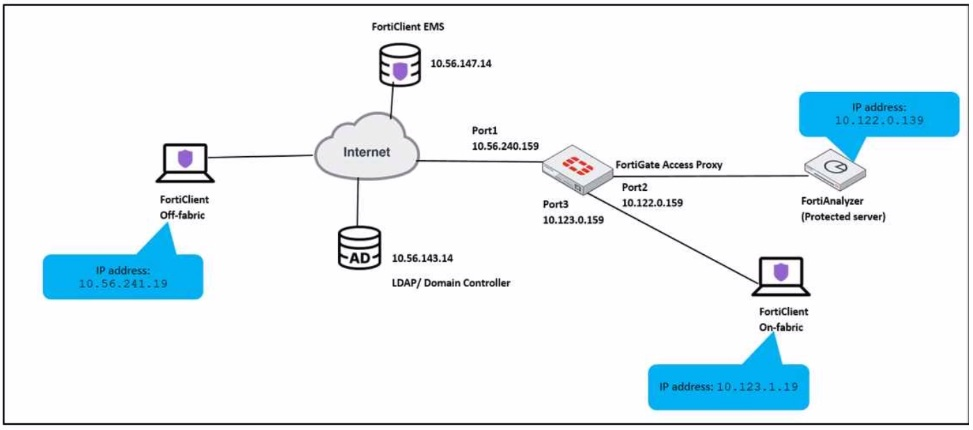
An administrator has to provide on-fabric clients with access to FortiAnalyzer using ZTNA tags
Which two conditions must be met to achieve this task? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, B
For on-fabric clients to access FortiAnalyzer using ZTNA tags, the following conditions must be met:
A) The on-fabric client should have FortiGate as its default gateway: This is essential to ensure that all client traffic is routed through FortiGate, where ZTNA policies can be enforced.
B) The ZTNA server must be configured on FortiGate: For ZTNA tags to be effectively used, the ZTNA server, which processes and enforces these tags, must be configured on the FortiGate appliance.
Configuring ZTNA tags and tagging rules
Synchronizing FortiClient ZTNA tags
Technical Tip: ZTNA Tags fail to synchronize between FortiClient and FortiGate
Exhibit.
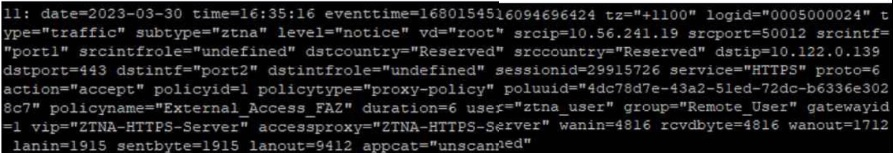
Based on the ZTNA logs provided, which statement is true?
Answer : A
Based on the ZTNA logs provided, the true statement is:
A) The Remote_user ZTNA tag has matched the ZTNA rule: The log includes a user tag 'ztna_user' and a policy name 'External_Access_FAZ', which suggests that the ZTNA tag for 'Remote_User' has successfully matched the ZTNA rule defined in the policy to allow access.
The other options are not supported by the information in the log:
B) An authentication scheme is configured: The log does not provide details about an authentication scheme.
C) The external IP for ZTNA server is 10.122.0.139: The log entry indicates 'dstip=10.122.0.139' which suggests that this is the destination IP address for the traffic, not necessarily the external IP of the ZTNA server.
D) Traffic is allowed by firewall policy 1: The log entry 'policyid=1' indicates that the traffic is matched to firewall policy ID 1, but it does not explicitly state that the traffic is allowed; although the term 'action=accept' suggests that the action taken by the policy is to allow the traffic, the answer option D could be considered correct as well.
Interpretation of FortiGate ZTNA Log Files.
Analyzing Traffic Logs for Zero Trust Network Access.
Exhibit.
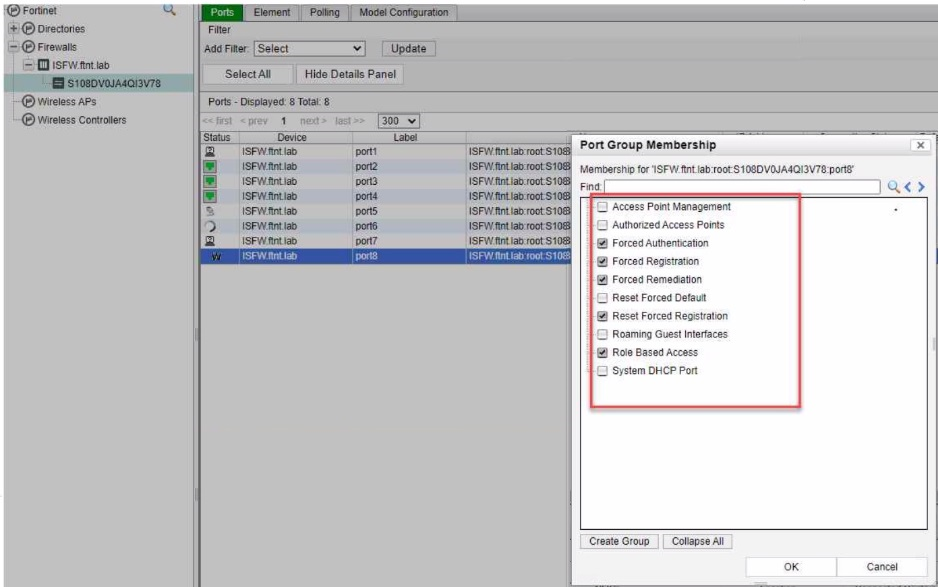
Which port group membership should you enable on FortiNAC to isolate rogue hosts'?
Answer : C
In FortiNAC, to isolate rogue hosts, you should enable the:
C) Forced Remediation: This port group membership is used to isolate hosts that have been determined to be non-compliant or potentially harmful. It enforces a remediation process on the devices in this group, often by placing them in a separate VLAN or network segment where they have limited or no access to the rest of the network until they are remediated.
The other options are not specifically designed for isolating rogue hosts:
A) Forced Authentication: This is used to require devices to authenticate before gaining network access.
B) Forced Registration: This group is used to ensure that all devices are registered before they are allowed on the network.
D) Reset Forced Registration: This is used to reset the registration status of devices, not to isolate them.