HP Aruba Certified Switching Associate HPE6-A72 Exam Questions
What is true about VSX? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, E
Refer to the exhibit.
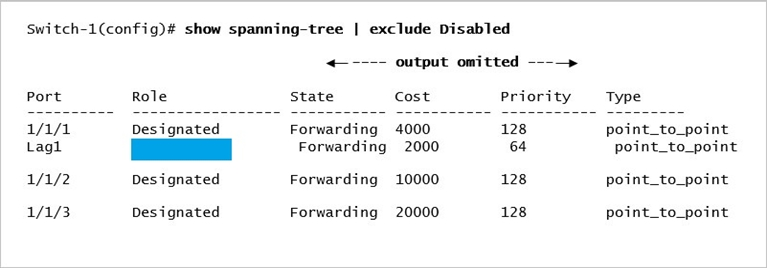
Switch-1 is not the root bridge. The ports shown are all the connected pointtopoint interfaces. What Role (hidden by the blue rectangle) will be assigned to the Lag 1 interface?
Answer : C
Refer to the exhibits.
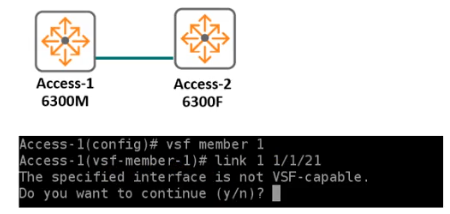
The AOS-CX 6300M switch is attempting to configure VSF with a peer CX 6300F switch. What is one reason you are receiving the above error when attempting to configure VSF on the AOS-CX 6300M switch?
Answer : C
Your customer has 349 users in a two-story building.
What are two benefits of a 2-Tier design? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, E
What command displays information regarding the secondary image installed on an AOS-CX switch?
Answer : D
Which Ethernet port combination does the Aruba 5400R ZL2 switch series support?
Answer : D
Refer to the exhibit.
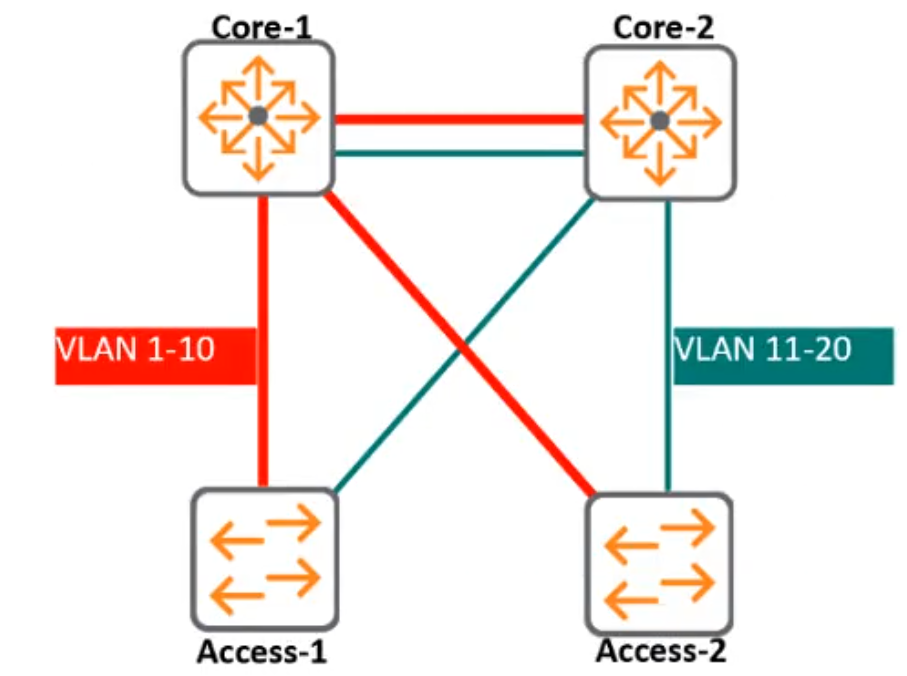
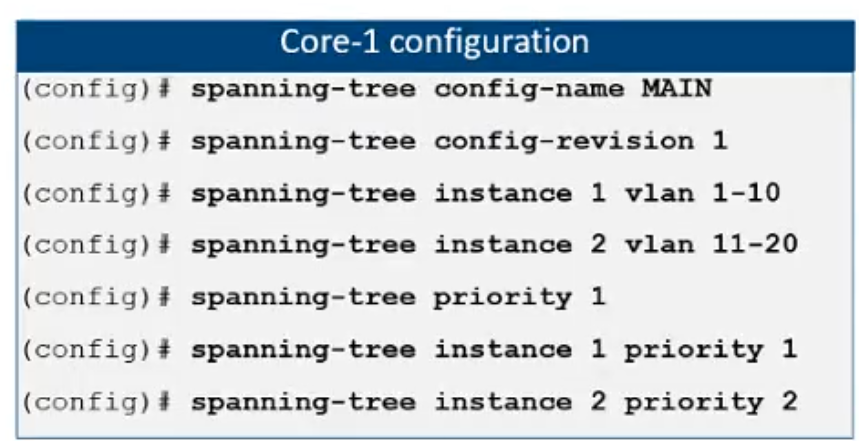
Refer to the diagram where all switches are CX 6300Ms. Which MSTP configuration should be applied to Core-2 in order for Core-2 to join the domain as the primary for Instance 2 and secondary for Instance 1?
A)

B)

C)

D)

Answer : C