HP Aruba Certified Campus Access Architect HPE7-A03 Exam Practice Test
A large multinational financial institution has contracted you to design a new full-stack wired and wireless network for their new 6-story regional office building. The bottom two floors of this facility will be retail space for a large banking branch. The upper floors will be carpeted office space for corporate users, each floor being approximately 100.000 sq ft (9290 sqm). Data centers are all off site and will be out of scope for this project. The customer is underserved by its existing L2-based network infrastructure and would like to take advantage of modern best practices in the new design. The network should be fully resilient and fault-tolerant, with dynamic segmentation at the edge.
The retail space will include public guest Wi-Fi access. Retail associates will have corporate tablets for customer service, and there will be a mix of wired and wireless devices throughout the retail floors. The corporate users will primarily use wireless for connectivity, but several wired clients, printers, and hard VoIP phones will be in use.
The customer is also planning on renovating the corporate office space in order to take advantage of "smart office' technology. These improvements will drive blue-dot wayfinding. presence analytics, and other location-based services
The client has provided floorplans. wall density, and ceiling heights tor the wireless deployment in the carpeted office space
What else will be needed to write an accurate bill of material? (Select two)
Answer : B, C
Ceiling construction details are essential for a wireless deployment because the material and structure of the ceiling can affect the propagation of wireless signals. Different materials can absorb or reflect RF signals differently, impacting coverage and signal strength. Understanding ceiling construction helps in planning the placement of access points for optimal coverage and performance. PoE (Power over Ethernet) port details are necessary to ensure that the wired network infrastructure can provide power to the access points and other PoE-enabled devices like VoIP phones and cameras. This information is critical for planning the power budget and ensuring that the network can support the power requirements of all connected devices, ensuring a stable and reliable network infrastructure.
'Don't Buy at Us' is a US-based retail company that is expanding Into Europe. They are expanding into EMEA with a regional headquarters called HQ2 inside The Netherlands.
Their US-based headquarters HQ1 was refreshed last year based on the Aruba ESP architecture. You have treated the design for HQ? based on the same design as HQ1. a two-tier architecture. The high level is shown below.
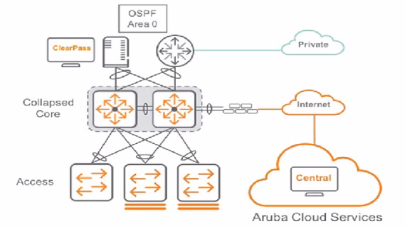
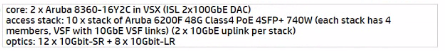
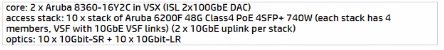
Switch BOM for this project based on Two Tier:
Collapsed Core: 2 x Aruba 8360-16Y2C in VSX (ISL 2 ICOG0E DAC)
Access Slack: 10 x Slack of Aruba 6200F 48G Class4 PoE 4SFP- 740W each stack has A members. VSF
with 10GbE VSF links) 12 x 10GbE uplink pet stack)
During the presentation of your design to the CTO of 'Don't Buy at Us' you were informed about the updated fiber infrastructure that Don't Buy at Us' has installed in HQ2.
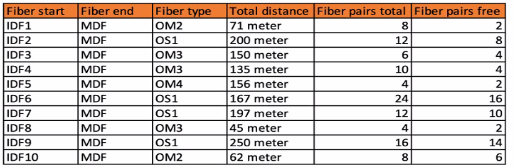
The core stack is Installed in the MDF and per IOF there is one access stack installed. Based on best practice, what is the most cost-effective update to the switch BOM?
A)
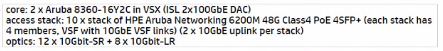
B)
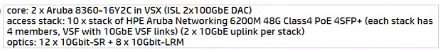
C)
D)
Answer : B
Option B is the most cost-effective solution, as it does not include long-range optics, which are unnecessary given the distances and fiber types specified. The 10GbE-SR optics are suitable for short-range connections up to 300 meters over OM3 fiber and would cover the needs of the longest fiber run mentioned, which is 250 meters. The 10GbE-LRM optics, while capable of reaching up to 220 meters over OM2 fiber, would not be necessary as the longest OM2 run is 71 meters, which is within the range of standard 10GbE-SR optics. Thus, Option B provides the required connectivity without incurring additional costs for long-range optics that are not needed given the fiber infrastructure of HQ2.
You ate presenting your network design solution to your customer. What Is important to include in your presentation?
Answer : D
When presenting a network design solution to a customer, it is crucial to focus on the benefits that the solution will bring to their business. This includes both tangible returns, such as cost savings, increased efficiency, and improved performance, and intangible returns, such as enhanced security, scalability, and user satisfaction. Highlighting how the solution addresses the customer's specific needs and challenges, and how it aligns with their business objectives, helps in demonstrating the value of the solution and facilitates decision-making. Including tangible and intangible returns in the presentation makes it more compelling and relevant to the customer's business goals, thereby increasing the likelihood of the proposal's acceptance.
XYZ Regional Hospital is an integrated healthcare system of Hospitals, neighborhood health centers, and small doctor offices. XYZ Regional Hospital has recently merged with 1x neighborhood health centers and 1Z5 doctor branch offices. The wireless, wired access, and AAA solutions are outdated and need to be replaced.
XYZ Regional Hospital is looking to future-proof and improve efficiency across all sites by enhancing wired and wireless access and migrating to a centralized and unified wired/wireless and policy management that can provide uninterrupted availability of all systems.
Locations:
- XYZ Regional Hospital Is located In New York City
- Dila Health Center Is located in City A
- Mount Health Center is located In City B
- Rock Health Center is located in City C
- Branch clinics are located at different locations across the United States
Requirements:
- Provide, via management software, one single pane of glass to manage wired and wireless LANs, and VPNs across campus, branch, and remote via web/cloud architecture providing near real-time insight, troubleshooting tools, and service Level performance reporting.
- Seamless integration across wired, wireless. WAN, S0-8ranch. loT
* Provide secure wireless access to all the employees of (he Regional Hospital and partners, as well as provide wireless Internet access to medical citizens when they visit our facilities.
- All-access points must support the following features and specifications: 802.1 lax (WI-FI 6E Certified)
- Security options Including WPZ/WPA3. 80Z.1 X with Radius secure authentication
- Identify and authenticate every wireless and wired device
- End-to-end role-based security
- Seamless mobility across the hospital tor medical teams, patients, and visitors
- Cuts Wi-Fi deployment times from days to hours and enables Zero-Touch deployments across the site
- Establishes a resilient, future-ready network infrastructure with the intelligence, scalability, and intuitive toolsets to meet emerging needs
- Fully redundant branch solution with dynamic path selection to the hospital
XYZ Regional Hospital is looking tor an NAC solution to address its security challenges-Requirements:
- fully redundant NAC solution for management and authentication
- wireless and wired authentication for the main hospital will be handled locally
- wireless and wired authentication for the health centers will be handled locally
- wireless and wired authentication tor the clinics will be authenticated against the main hospital NAC
- staff ustrs/devices should able to visit any site and haw the same experience
- support 35k devices
Locations:
- XYZ Regional Hospital is located in City 1 - 15k devices
- Dila Health center is located in City 2 - 8k devices
- Mount Health Center is located in City 3 - 5k devices
- Rock Health Center is located in City 4 - 4k devices
-125 branch clinics are located at different locations across the US - 2k devices
Which solution meets the customer's requirements?
A)

B)

C)

D)

Answer : B
Option B in the provided selections outlines a configuration that includes an Aruba ClearPass Policy Manager as a Publisher for the main DC and as a Standby Publisher for the DR, with subscriber servers allocated to the main hospital and health centers. This setup is likely to match the requirement for a fully redundant NAC solution, with local handling of authentication for the main hospital and health centers, and centralized authentication for the clinics. The inclusion of VMs (Virtual Machines) as subscribers for health centers suggests scalability and flexibility for future expansion. The provision of 35k access licenses aligns with the support for 35k devices across all locations.
A global cruise line company needs to refresh its current fleet. They win refresh the insides' of the ship to be cost-effective and increase their sustain ability. They Mill replace the complete WLAN/LAN hardware of the ship. In this refresh, the company will not refresh Us current security requirements. The CIO also wants to limit the number of unused ports in the switches. Future expansion will always mean a refresh of hardware. They start with the smallest ship with a maximum of 800 guests
Each ship has a LAN infrastructure consisting of two core switches, up to 10 redundant distribution switches, and up to 500 access switches (400 cabins. 100 technical rooms). The Core switches are located in the MDF of the ship and the distribution switches are located in the IDFs of the ship. Each cabin and technical room gets one single access switch.
The cabling structure of the ship will not be refreshed. Each IDF is connected to the MDF by SMF. of which two pairs are available for the interconnect between the core and distribution. The length of SM fiber between MDF and IDF is less than 300 meters (930 ft) and the type used is 0S1. Each cabin is connected by a single 0M2 pair to the IDF. the maximum length is 60 meters (200 ft). Each technical room is connected by a single 0M2 pail to the IDF. with lengths between 100 and 150 meters (320 and 500 ft).
For each cabin/technical room the customer is looking to replace their current fan-less 2530/2540 without changing the requirements, except they need to upgrade the uplink to distribution switch to 10GbEto handle the increased network traffic, and the technical rooms need redundant power.
The WLAN infrastructure will be 1:1 refreshed without new cabling or new AP locations. Their WLAN Infrastructure is based on the 200/300 series Indoor and outdoor APs running instantOS (less than 300 APs). the customer has no change in WLAN requirements.
The cruise line company will replace its current Internet connection before the LAN/WLAN refresh. The new Internet connection will provide a 99.8% uptime, which is needed to ensure the paid guest Wi-Fi is always operational. With this new internet connection, the CIO of the cruise line wants to base the design on the ESP architecture from Aruba because Internet connection is guaranteed.
Based on the best practices, what should you recommend as the most cost-effective switch model for the cabins?
Answer : A
For the cabin switches in the global cruise line's fleet refresh project, the most cost-effective switch model that meets the requirement for fan-less operation, 10GbE uplink capability, and PoE support is the HPE Aruba Networking 6200F 12G Class4 PoE 2G/2SFP+. This switch model offers a compact form factor with sufficient port density for cabin connectivity, Power over Ethernet for powering devices directly through the network cable, and SFP+ ports for high-speed uplink connections to the distribution switches. This choice is in line with the company's aim to upgrade the network infrastructure to handle increased traffic while maintaining a focus on cost-effectiveness and sustainability. The 6200F series is designed for exactly such environments, providing reliable performance and energy efficiency, which is crucial for the limited space and power availability in a ship setting.
A large multinational financial institution has contracted you to design a new full-stack wired and wireless network for their new 6-story regional office building. The bottom two floors of this facility will be retail space for a large banking branch. The upper floors will be carpeted office space for corporate users, each floor being approximately 100.000 sq ft (9290 sqm). Data centers are all off site and will be out of scope for this project. The customer is underserved by its existing L2-based network infrastructure and would like to take advantage of modern best practices in the new design. The network should be fully resilient and fault-tolerant, with dynamic segmentation at the edge.
The retail space will include public guest Wi-Fi access. Retail associates will have corporate tablets for customer service, and there will be a mix of wired and wireless devices throughout the retail floors. The corporate users will primarily use wireless for connectivity, but several wired clients, printers, and hard VoIP phones will be in use.
The customer is also planning on renovating the corporate office space in order to take advantage of "smart office' technology. These improvements will drive blue-dot wayfinding. presence analytics, and other location-based services
The client is looking to utilize lower-cost Aruba OS-CX switches in their wiring closets. They calculate that each closet will need a stack or qty 6 POE (AT) and qty 0 Gigabit Ethernet switches stacked with low-cost OACs.
Which series switch should you recommend?
Answer : C
The Aruba CX 6300F series is a suitable recommendation for the described scenario due to its performance, PoE capabilities, and cost-effectiveness for wiring closet deployments. The CX 6300F series offers the flexibility and scalability needed for modern network environments, supporting both wired and wireless connectivity demands. It provides advanced features such as stackability, high-density PoE options, and the capability to support dynamic segmentation, which is essential for separating and securing different types of network traffic, such as corporate data and guest Wi-Fi access. This series is designed to meet the needs of a full-stack wired and wireless network in a large, multi-story office building, providing the necessary infrastructure for both current and future network requirements.
You are delivering a replacement collapsed core network proposal to the customer where the core switches will have the switched virtual interlaces (SVl) configured. The customer is not sure that a USX pair of switches will Be able to act as I tie spanning tree root in their environment.
Which options are true about spanning tiee and VSX that will help assure the customer that a VSX pair of switches are appropriate for a collapsed core? (Select two.)
Answer : D, E
According to Aruba Campus Access documents and learning resources, Aruba VSX (Virtual Switching Extension) technology is designed to provide advanced high availability and redundancy features for campus networks. Specifically, answer D is correct because Aruba VSX supports both Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) and Rapid Per VLAN Spanning Tree (RPVST), ensuring efficient tree structures for VLANs and rapid convergence in case of topology changes. Answer E is also true as the Inter-Switch Link (ISL) used for the VSX pair is not part of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) domain, meaning it does not send or receive Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs). This design prevents the ISL from influencing STP calculations, ensuring that the operational roles of the primary and secondary switches in the VSX pair are clear and predictable to the rest of the network. This separation helps maintain deterministic behavior and failover capabilities in the network, aligning with the goals of a collapsed core network design.