HP Advanced HPE Storage Integrator Solutions Written HPE7-J02 Exam Practice Test
You need to evaluate a customer virtual server environment to size an HPE Block storage solution according to the metrics seen on the system over a period of time. The environment consists of Lenovo servers and Pure Storage as the storage vendor for a Microsoft Hyper-V cluster managed by Microsoft SCVMM.
Which HPE tools can you utilize to gather the usage metrics of this setup?
Answer : A
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
HPE CloudPhysics provides comprehensive environment assessment and competitive sizing for virtualized environments (VMware, Hyper-V, etc.). The CloudPhysics collector (available as a .vhdx for Hyper-V) is deployed into the cluster to gather metrics on CPU, memory, storage IOPS/latency, and utilization trends. These analytics feed into the sizing of HPE storage solutions.
Distractors:
B: InfoSight sizing tools work with HPE systems, not competitive 3rd-party storage like Pure.
C: SAF is a manual assessment requiring email submission and is not the correct modern method for this case.
D: NinjaProtected applies to backup analysis, not production Hyper-V cluster sizing.
Key Concept: CloudPhysics.vhdx collector for Hyper-V sizing with 3rd-party infrastructure.
You are sizing an HPE Alletra Storage MP B10000 array (graphic provided).
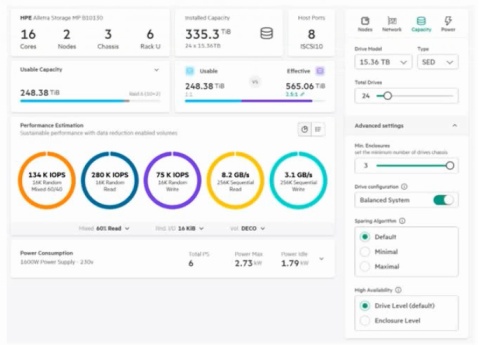
What happens when the High Availability (HA) option is switched from Drive Level to Enclosure Level?
Answer : D
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
Changing HA from Drive Level to Enclosure Level means the system must reserve additional capacity to tolerate the loss of an entire disk enclosure. This decreases usable capacity, as more parity/spare space is required. Performance remains similar, but capacity overhead increases.
Distractors:
A: Multiple enclosures exist in the config; option is valid.
B: Switched vs direct-connect is unrelated to HA settings.
C: Performance estimates are not directly reduced by HA level change; capacity is.
Key Concept: Enclosure HA = more reserve overhead less usable capacity.
Refer to the exhibit.
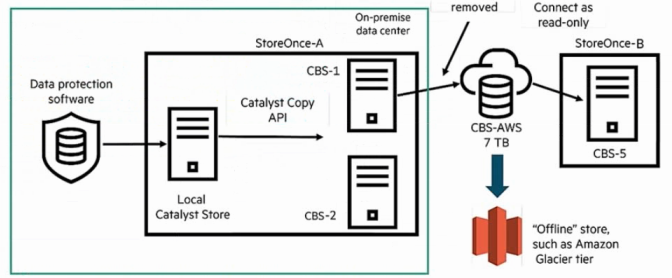
A junior engineer is expanding a StoreOnce deployment for a law firm with a hybrid environment. The customer already has Veeam backing up to StoreOnce 3660 Gen 4 at both primary and secondary sites. They want to add Cloud Bank Storage (CBS) to archive into AWS Glacier tier for compliance. The junior engineer has added Cloud Bank licenses for the 80TB onsite capacity at the primary office.
Question : What does the junior engineer need to add to enable this scenario?
Answer : D
Your customer has deployed an HPE Alletra MP B10000 array in its virtualized environment. Data protection follows 3-2-1 best practices, with snapshots on the array, Veeam v12 backups, and storage on an external HPE StoreOnce appliance. Despite this, a ransomware attack made data recovery impossible.
Your customer asks how to enhance data protection with immutability and application consistency.
What is a possible solution using HPE Virtual Lock technology?
Answer : C
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
Option C is correct because HPE StoreOnce Virtual Lock technology provides immutability at the Catalyst store level, preventing backup data from being deleted or modified for a defined retention period. This ensures ransomware or malicious actors cannot encrypt, alter, or delete the protected backups, aligning with modern data protection requirements for immutability and compliance. In integration with Veeam v12, backups stored on StoreOnce Catalyst stores can be locked, creating an additional immutability layer beyond application-consistent snapshots.
Analysis of Incorrect Options (Distractors):
A: Virtual Lock is not a Veeam feature. While Veeam v12 supports immutability on certain storage backends (object lock-enabled S3, hardened Linux repositories), HPE Virtual Lock is specific to StoreOnce Catalyst stores, not Veeam job settings.
B: VMware vCenter datastores do not have a native immutability feature. Snapshots in vCenter can be deleted or corrupted during ransomware events, making this option incorrect.
D: HPE Alletra arrays support application-consistent snapshots and replication, but they do not provide the immutability guarantee that StoreOnce Virtual Lock enforces. Array-level snapshots can still be deleted if admin credentials are compromised.
Key Concept:
This question targets knowledge of HPE StoreOnce Virtual Lock --- a feature designed to enforce immutability on Catalyst backup stores, making backup data resistant to deletion or alteration during ransomware or insider attacks.
HPE StoreOnce Systems Technical White Paper
HPE StoreOnce and Veeam Integration Best Practices
HPE Data Protection Solutions for Ransomware Resilience Guide
The storage solution based on the exhibit is deployed at a customer site.
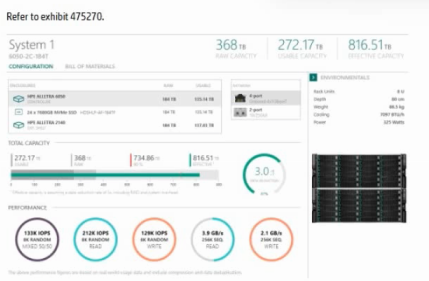
How can the sequential read performance values be enhanced for this configuration?
Answer : B
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
The exhibit shows a system delivering ~2.3 GB/s sequential read. For large-block sequential workloads, aggregate host link bandwidth (number speed of front-end ports) is the primary limiter. Increasing the count of 10/25 Gb iSCSI NICs adds parallel lanes, raising sustained read GB/s to the hosts. This is a recommended first step in HPE sizing before changing protocols.
Analysis of Incorrect Options (Distractors):
A: Adding an expansion shelf increases capacity, not front-end bandwidth.
C: Moving to 32 Gb FC can help, but simply adding more existing 10/25 Gb ports achieves the same goal without a protocol/adapter change and is the straightforward, supported scale-out path.
D: SCM (Storage Class Memory) targets latency/IOPS; it doesn't materially lift sequential GB/s if the link budget is the bottleneck.
Key Concept: Scale front-end connectivity to increase sequential throughput; capacity or media class changes won't fix a link-limited system.
Your customer has just gone through a merger and is consolidating datacenters. They are currently using a mix of manufacturers. They are evaluating whether to consolidate on HPE as their new standard. You are helping them size their new virtualized environment.
What additional information do you need to decide on an assessment tool?
Answer : B
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
The choice of assessment tool (e.g., HPE CloudPhysics for VMware vs. CloudPhysics.vhdx collector for Hyper-V) depends primarily on the virtualization platform in use. VMware and Hyper-V require different collectors, and this is the deciding factor for tool selection.
Distractors:
A: Public cloud use matters for hybrid sizing but not for tool selection.
C: Expired contracts are unrelated to tool choice.
D: Procurement model (CapEx vs. GreenLake) is separate from sizing assessment.
Key Concept: Assessment tool choice = based on hypervisor platform (VMware vs Hyper-V).
Your new customer asks about HPE storage networking capabilities for multisite implementations.
Which statement about HPE's FCIP capabilities is correct?
Answer : A
Detailed Explanatio n:
Rationale for Correct Answe r:
In Brocade (HPE B-Series) SAN switches, FCIP trunking allows multiple IP circuits to be aggregated. This increases bandwidth and provides resiliency (if one link fails, traffic continues over remaining paths). It is the correct statement regarding HPE's FCIP feature set.
Distractors:
B: High availability still requires redundant fabrics; FCIP trunking alone doesn't replace fabric design best practices.
C: FCIP can run over shared IP WANs; no need for dedicated links.
D: Encryption adds overhead; performance impact exists (although minimal with hardware offload).
Key Concept: FCIP trunking = bandwidth + availability for multisite SAN.