Huawei HCIA-Datacom V1.0 H12-811_V1.0 Exam Practice Test
In the following figure, after the OSPF routers converge, in which state is the OSPF neighbor relationship between Router B and Router C?
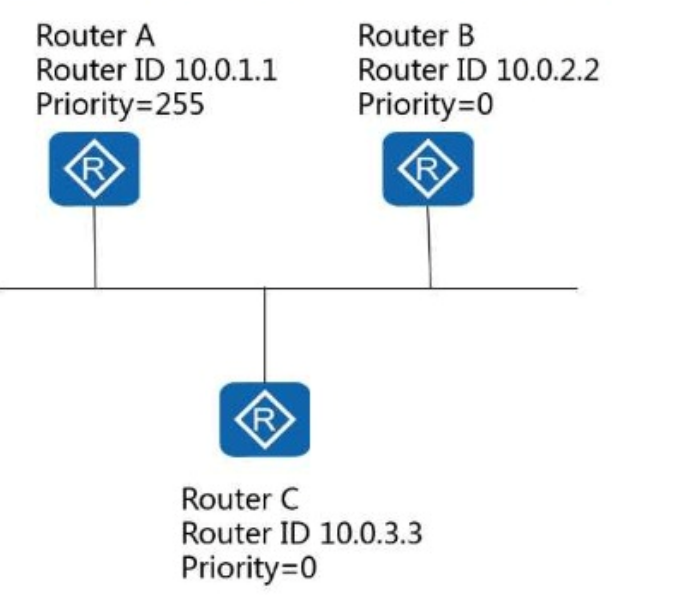
Answer : C
The following figure shows the configuration of a sub-interface on a router. For which VLAN does the sub-interface receive tagged data frames?
Answer : D
Comprehensive Explanation= The command dot1q termination vid 100 in the configuration specifies that the sub-interface is configured to receive tagged data frames for VLAN 100. VLAN tagging ensures that frames are properly identified and routed through the correct VLAN, and the sub-interface is associated with a specific VLAN ID to handle the tagged traffic.
Which of the following is not included in the routing table?
Answer : A
Comprehensive Explanation= A routing table contains information necessary for the router to determine the best path to forward packets. This includes the destination network or subnet (Destination/Mask), the next-hop address (the IP address of the next device in the path), and the cost (metric) associated with the route. MAC addresses are used at the Data Link layer (Layer 2) for local network communication and are not part of the routing table, which operates at the Network layer (Layer 3).
For STP, the Message Age in the configuration BPDUs sent by the root bridge is 0.
Answer : A
Comprehensive Explanation= In Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), the Message Age in the BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Unit) sent by the root bridge is set to 0. As BPDUs are forwarded by non-root switches, the Message Age is incremented. This timer is used to ensure that outdated information is not propagated indefinitely through the network. If the Message Age reaches a configured maximum value, the BPDU is discarded, and the network topology is recalculated.
If the value of the "Type/Length" field of an Ethernet data frame is 0x0800, the length range of the upper-layer packet header carried by the data frame is from 20B to 60B.
Answer : B
The Type/Length field value of 0x0800 indicates that the upper-layer protocol is IPv4. However, the length of the IPv4 header can range from 20 to 60 bytes, not the length of the entire upper-layer packet. The field refers to the type of the encapsulated protocol, and the length is not constrained to the header alone.
On Huawei routers, which of the following is the default preference of static routing?
Answer : A
The default preference of static routes on Huawei routers is 0. This means that if a static route is present, it will always take precedence over routes with higher preferences, such as dynamically learned routes, unless a lower preference is manually assigned.
(The IP addresses of VLANIF interfaces on the same switch must be different.)
Answer : A
IP Address Uniqueness on VLANIF Interfaces:
Each VLANIF interface represents a different logical interface, often tied to distinct subnets. IP addresses for VLANIF interfaces must be unique on the same switch to prevent address conflicts and routing issues.
Correct Answer:
TRUE. The IP addresses of VLANIF interfaces on the same switch must be different.