ISTQB Certified Tester Foundation Level CTFL-Foundation Exam Questions
Which of the following is not decided in the test-planning phase..?
Answer : D
The test-planning phase involves deciding on schedules and deliverables, hardware and software requirements, and entry and exit criteria. However, the specific types of test cases to be used are typically defined during the test design phase, not during the test planning phase. Test planning focuses on the overall approach and resources needed for testing. Reference: ISTQB CTFL Syllabus V4.0, Section 5.1.1.
Which of the following test cases will ensure that the statement 'Print 'Hold'' is exercised? [K3]
Refer to the exhibit
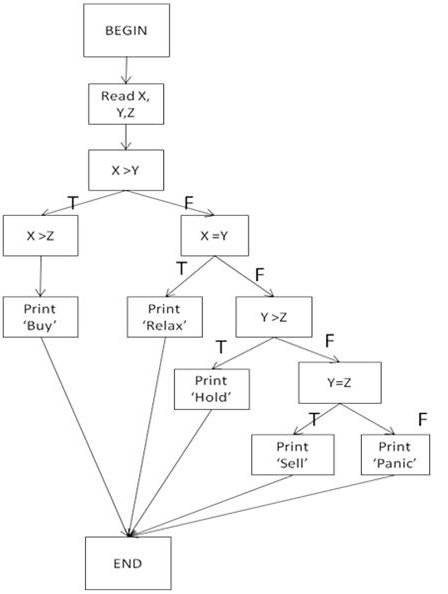
Answer : C
To ensure that the statement 'Print 'Hold'' is exercised:
X=2, Y=4, Z=3 This test case will follow the path where X Y (False), Y > Z (True), leading to the 'Print 'Hold'' statement.
What is the main reason for using a pilot project to introduce a testing tool into an organization? [K1]
Answer : C
The main reason for using a pilot project to introduce a testing tool into an organization is to assess whether the tool will be cost-effective. A pilot project allows the organization to evaluate the tool's benefits, identify any potential issues, and determine whether the investment in the tool is justified based on its performance and the value it adds.
What factors should be considered to determine whether enough testing has been performed?
(i) The exit criteria.
(ii) The budget.
(iii) How big the test team is.
(iv) The product's risk profile.
(v) How good the testing tools are.
(vi) Sufficient details of the system status to allow decisions
Answer : A
Determining whether enough testing has been performed involves considering several factors. These include:
(i) The exit criteria, which define the conditions that must be met to conclude testing. (ii) The budget, which affects the extent of testing that can be conducted. (iv) The product's risk profile, which helps prioritize testing efforts on high-risk areas. (vi) Sufficient details of the system status to allow decisions, ensuring that stakeholders have the necessary information to make informed decisions about the software's readiness.
These factors together ensure a balanced and informed decision-making process regarding the sufficiency of testing.
What is the value of static code analysis?
Answer : B
The value of static code analysis lies in its ability to detect defects early in the development process. By analyzing the code without executing it, static analysis can identify potential issues, such as coding errors or violations of coding standards, which can be addressed before they lead to more significant problems.
Which of the following defects is most likely to be found by a test harness?
Answer : B
Variance from programming standards defects (option (A)) are found during the review or static testing process. Therefore a test harness is unlikely to find a defect in programming standards.
Memory leak defects (option (C)) could potentially be found by a test harness designed to run many test cases.
Regression defects (option (D)) could be found using many types of test tool.
Defects in middleware (option (B)) are generally more likely to be found by a test harness or a dynamic analysis tool than by any other type of tool.
Which is not a major task of test implementation and execution?
Answer : C
Checking test logs against the exit criteria specified in test planning is part of the exit criteria evaluation phase, not the test implementation and execution phase. Test implementation and execution tasks include developing and prioritizing test cases, creating test data, writing test procedures, preparing test harnesses, writing automated test scripts, logging the outcome of test execution, and verifying the test environment setup. The ISTQB CTFL Syllabus delineates these tasks to ensure proper test preparation and execution.