Juniper Enterprise Routing and Switching, Specialist JN0-351 Exam Practice Test
Exhibit
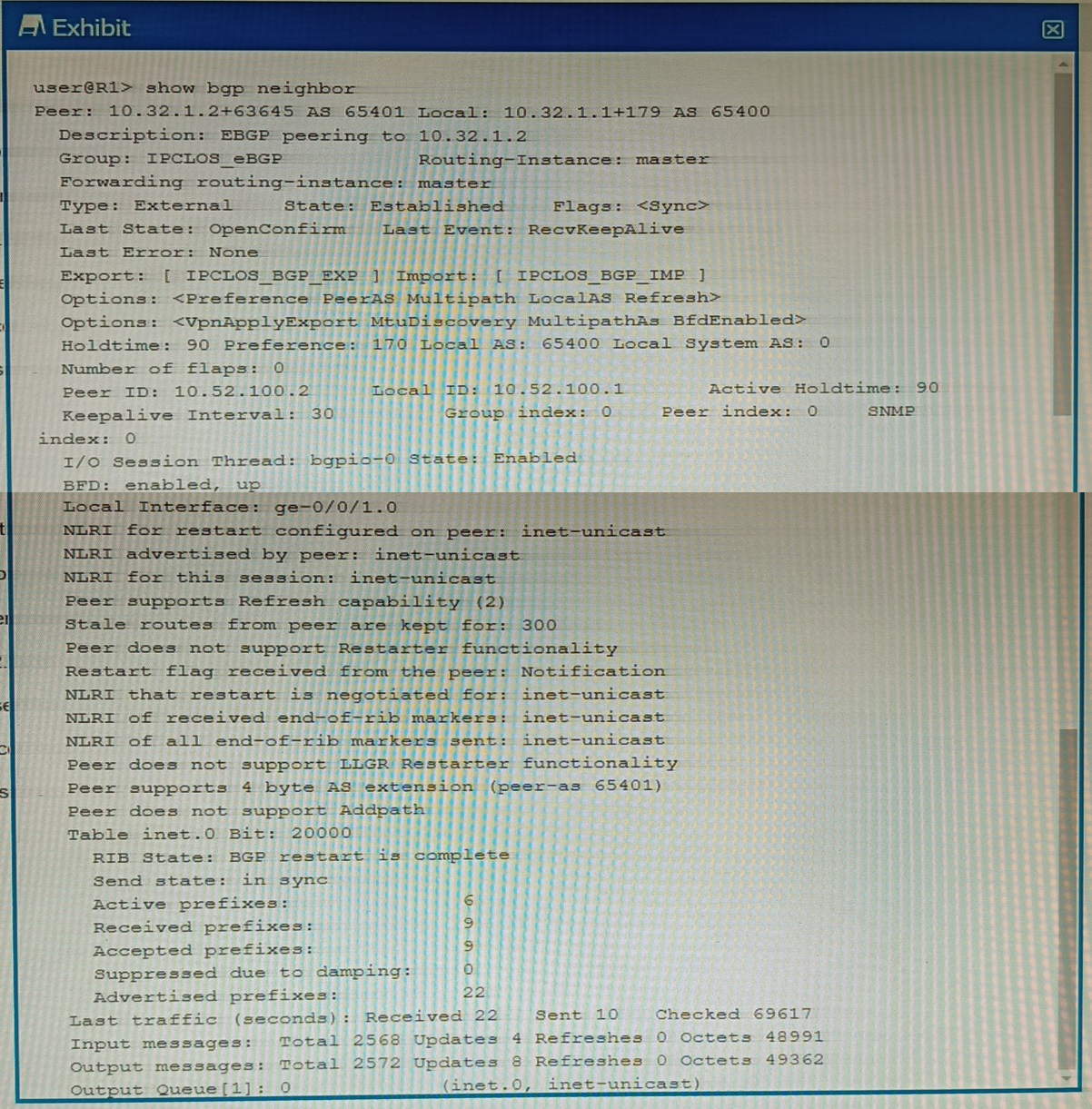
You are a network operator troubleshooting BGP connectivity.
Which two statements are correct about the output shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
Which statement is correct about the storm control feature?
Answer : A
Option C is incorrect. There's no information available that suggests the storm control feature is not supported on aggregate Ethernet interfaces.
Which two statements correctly describe RSTP port roles? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, D
Therefore, options A and D are correct.
You are asked to create a new firewall filter to evaluate Layer 3 traffic that is being sent between VLANs. In this scenario, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
Answer : C, D
Therefore, option C is correct, because you should create a family inet firewall filter with the appropriate match criteria and actions. Option D is correct, because you should apply the firewall filter to the appropriate IRB interface.
What is a purpose of using a spanning tree protocol?
Answer : B
You have two OSPF routers forming an adjacency. R1 has a priority of 32 and a router ID of 192.168.1.2. R2 has a priority of 64 and a router ID of 192.168.1.1. The routers were started at the same time and all other OSPF settings are the default settings.
Which statement is correct in this scenario?
Answer : D
Exhibit
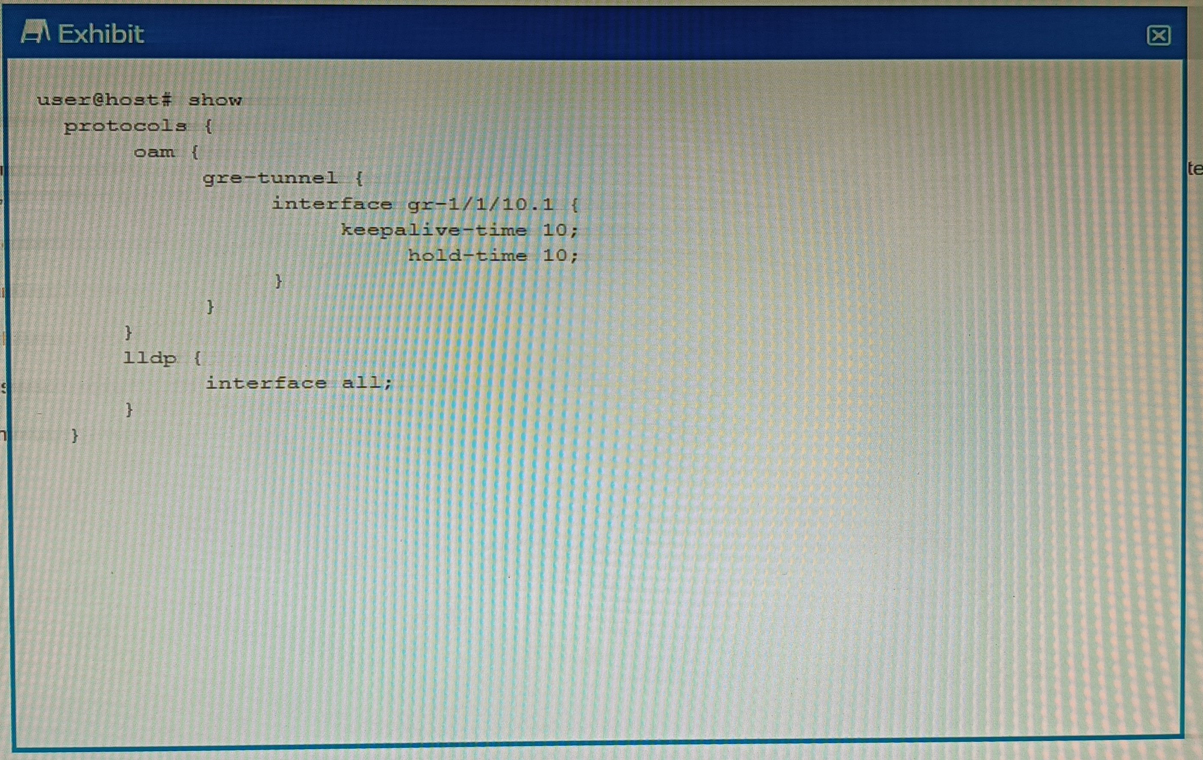
You have configured a GRE tunnel. To reduce the risk of dropping traffic, you have configured a keepalive OAM probe to monitor the state of the tunnel; however, traffic drops are still occurring.
Referring to the exhibit, what is the problem?
Answer : D
In the exhibit, the configuration shows that the keepalive-time is set to 10 seconds and the hold-time is set to 15 seconds for the gr-1/1/10.1 interface. This means that the local router will send a keepalive packet every 10 seconds and will wait for 15 seconds for a reply from the remote router. However, this hold-time value is not two times the keepalive-time value, which violates the recommended configuration. This may cause traffic drops if the remote router takes longer than 15 seconds to reply.