Juniper Service Provider Routing and Switching, Specialist JN0-363 JNCIS-SP Exam Practice Test
Which statement describes integrated routing and bridging (IRB) interfaces?
Answer : A
An Integrated Routing and Bridging (IRB) interface is used to provide Layer 3 routing services to hosts within a bridge domain. The IRB acts as a default gateway for hosts in that domain, enabling communication with other networks.
Juniper Networks Technical Documentation on IRB Interfaces
Exhibit
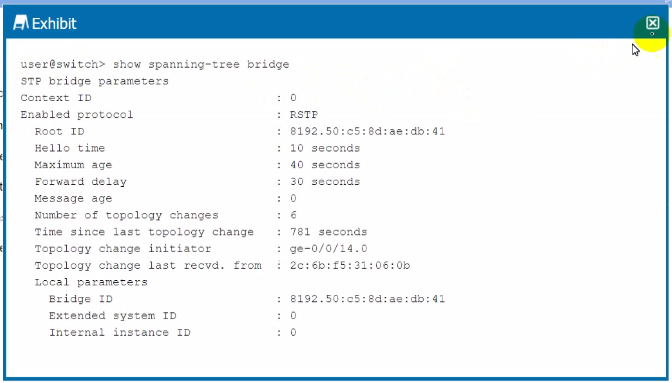
Which two statements are correct about the information shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
The exhibit shows the output of the command show spanning-tree bridge, which provides information about the spanning tree status of the switch. From the output, we can see that the switch has a bridge ID different from the root ID, which implies that this switch is not the root bridge. The 'Topology change initiator' field shows ge-0/0/14, which indicates that the last topology change occurred on this interface, and this is also the interface used to reach the root bridge.
Juniper Networks documentation on Spanning Tree Protocol: Understanding Spanning Tree Protocols
The segment touting SRGB start label Is 10,000 and the SRGB index range is 500.
In this scenario, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
The Segment Routing Global Block (SRGB) defines a range of MPLS labels reserved for segment routing. With an SRGB starting label of 10,000 and an index range of 500, the first usable label is indeed 10,001 because label 10,000 is typically reserved and not used for forwarding. The last usable label would be 10,499 because the range includes 500 labels starting from 10,001.
Juniper Networks documentation on Segment Routing: Segment Routing Overview
Exhibit
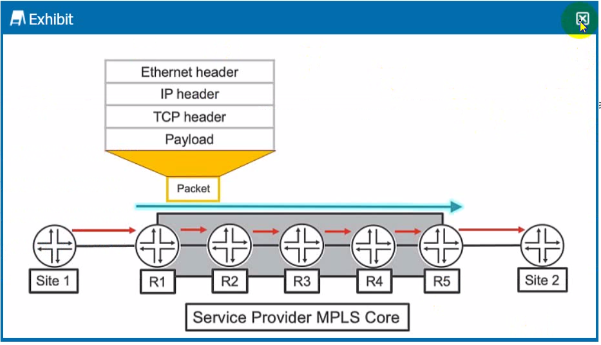
Which two statements ate correct about the actions taken as the packet traverses the service provider MPLS network from Site 1 to Site 2 as shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
In MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) networks, routers use label switching to forward packets. The first router at the edge of the MPLS network (R1) will perform a lookup in the mpls.0 table to determine the label to attach to the packet as it enters the MPLS network. This label informs the next routers in the MPLS network (like R2) on how to forward the packet. Internal MPLS routers, like R2, also perform lookups in their mpls.0 table to determine how to switch the packet toward its destination (label swapping). The inet.3 table is used for resolving next-hop information for labeled routes, but it's the mpls.0 table that is used for label switching decisions.
Juniper Networks documentation on MPLS: MPLS Applications User Guide for Routing Devices
Click the Exhibit button.
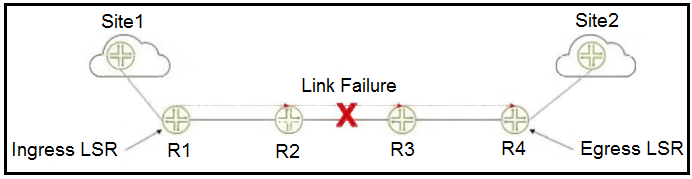
Referring to the exhibit, you have an established RSVP LSP between R1 and R4 when you experience a link failure between R2 and R3.
Which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, D
Upon a link failure in an RSVP-signaled LSP, the router upstream of the failure (R2) sends a PathTear message upstream to the ingress router (R1), and the router downstream of the failure (R3) sends a ResvTear message downstream to the egress router (R4). These messages signal the failure and initiate tear down of the LSP state in the respective directions. Reference::
RSVP-TE Overview, Juniper Networks Documentation
Understanding RSVP Signal Failures, Juniper Networks Documentation
Exhibit
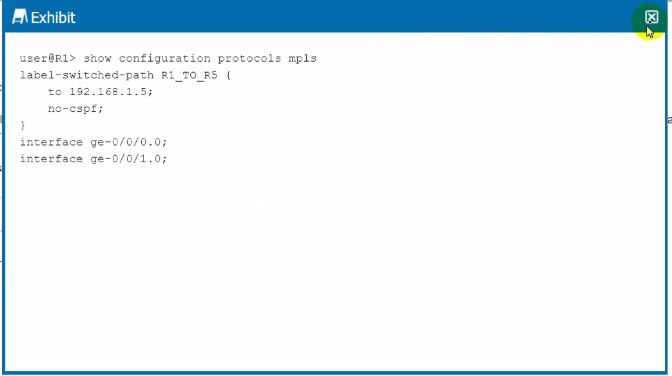
You have an established LSP between your R1 and R5 devices using the configuration shown in the exhibit. You are asked to ensure that MPLS labels are used to forward traffic by all devices within the LSP.
Which action will accomplish this behavior?
Answer : B
The 'ultimate-hop-popping' term refers to the action taken by the penultimate router in an LSP to remove the MPLS label before delivering the packet to the ultimate router, which is not desired here. Configuring the 'explicit-null' statement causes the penultimate router to replace the top label with a label that has a value of 0, which instructs the ultimate router to perform a label lookup and preserve the label switching for the entire LSP.
Juniper Networks documentation on MPLS: MPLS Applications User Guide for Routing Devices
You want to share routes between two routing instances that you have configured?
What are two ways to accomplish this task? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, D
static route with a next-hop of next-table pointing to the appropriate routing table which contains more accurate information rib-groups to mirror routing information from one route-table to another. However, in many cases, in order to make this work, interface-routes also need to be mirrored. RIB Group policy can be used to constrain the routing information instance-import and instance-export statements configured within the individual routing-instances to leak routes from one table to another. Again, policy can be used here to constrain the routing information. This method is more straightforward than the rib-group method A final approach is to use physical interfaces or logical-tunnels to stitch routing-instances and use a routing protocol or static routes across this connection between the two routing-instances.
To share routes between two routing instances on a Junos device, you can configure an instance import policy in one or both instances to import routes from the other instance. Alternatively, a RIB (Routing Information Base) group can be used to share routes between instances. Reference::
Routing Instances Overview, Juniper Networks Documentation
RIB Groups Configuration Guide, Juniper Networks Documentation