Juniper Enterprise Routing and Switching, Professional JN0-650 JNCIP-ENT Exam Questions
You have two multicast receivers connected to the same VLAN. You notice that the switch that they are connected to is forwarding multicast traffic out of all the ports in the same VLAN, instead of just the two ports for the connected multicast receivers
In this scenario, what would you configure to optimize multicast forwarding?
Answer : C
You run a multivendor switching environment where you have configured VSTP. You have 450 VLANs and notice that some of your VLANs do not function properly. How should you change the configuration to get all 450 VLANs working?
Answer : B
Exhibit.
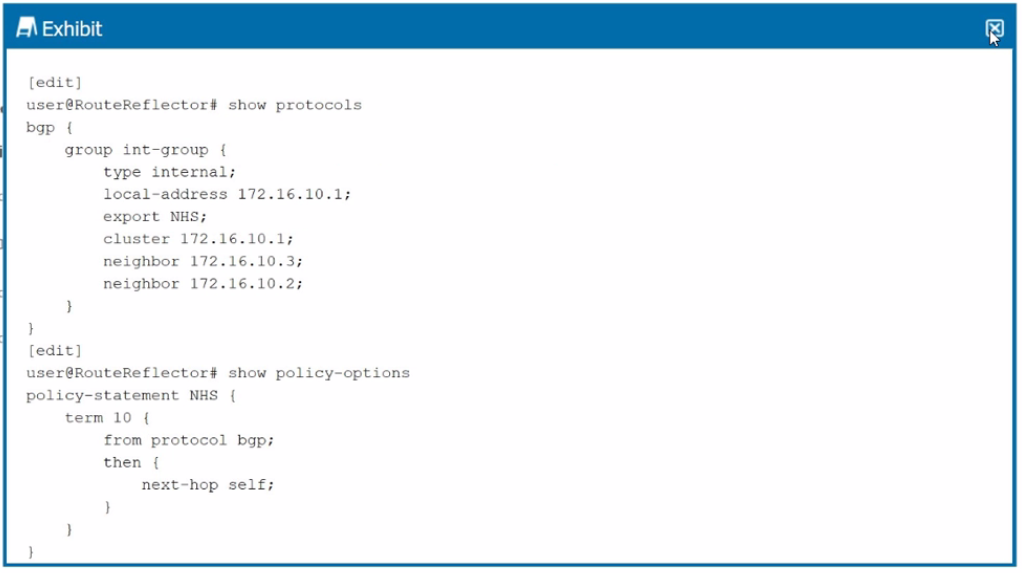
You have determined that traffic in your network is being routed through your route reflector instead of using the optimal path. Referring to the exhibit, what are two configuration changes on the route reflector that would solve the problem? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
You have created a private community VLAN called RND The private community VLAN works fine within switch S1, but traffic in the private RND community VLAN does not reach VLAN members connected to switch S2.
Which statement is correct in this scenario?
Answer : B
Exhibit
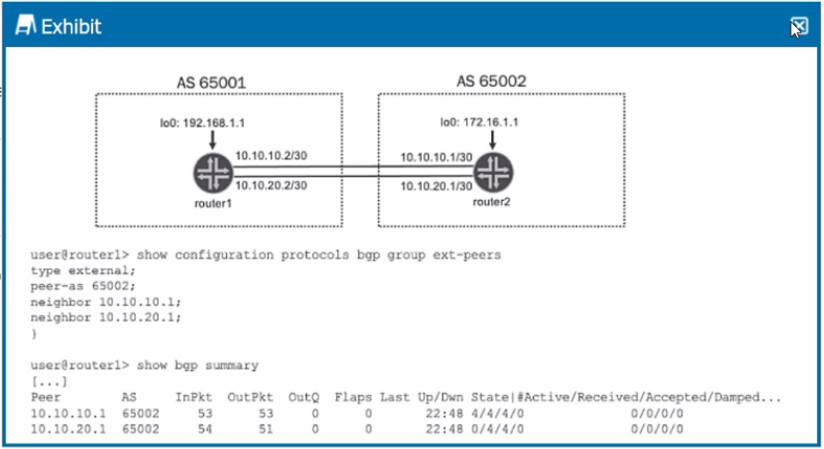
Referring to the exhibit, what will enable active routes from both peers?
Answer : A
You are deploying IP phones in your enterprise networks. When plugged in. the IP phones must automatically be provided with their geographic location details by the EX Series switches.
In this scenario, which protocol should be used to enable this behavior?
Answer : B
You are troubleshooting a multicast deployment in a network. Some multicast groups operate in PIM-ASM mode and others operate in PIM-SSM mode. While troubleshooting, you note the following:
- The network uses IGMPv2 for some segments and IGMPv3 for others.
- For group 232.1.1.1, receivers know the exact source IP of the multicast sender
- For group 239.10.10.10. receivers do not know the source address in advance.
Which two statements correctly describe the operational differences between these two modes in Junos OS? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, D