Juniper Service Provider Routing and Switching, Professional Exam JN0-664 JNCIP-SP Exam Practice Test
Which statement is true regarding BGP FlowSpec?
Answer : C
Exhibit
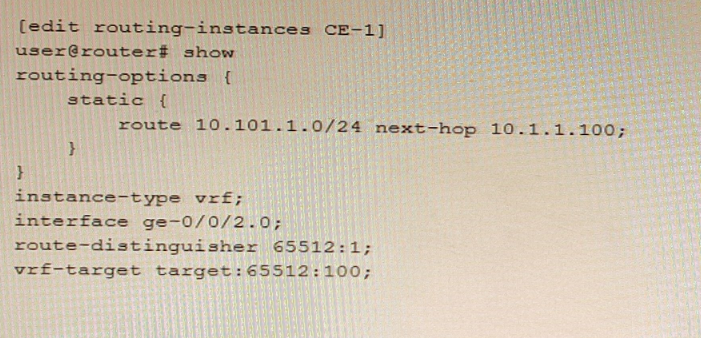
Referring to the exhibit, which statement is true?
Answer : D
The auto-export parameter is a routing option that allows a routing instance to share routes with other routing instances or the master routing table. The auto-export parameter automatically exports routes from one routing instance to another based on the route target communities attached to the routes. In this scenario, the 10.101.1.0/24 route will be shared if the auto-export parameter is configured under [edit routing-options] hierarchy level.
Which origin code is preferred by BGP?
Exhibit
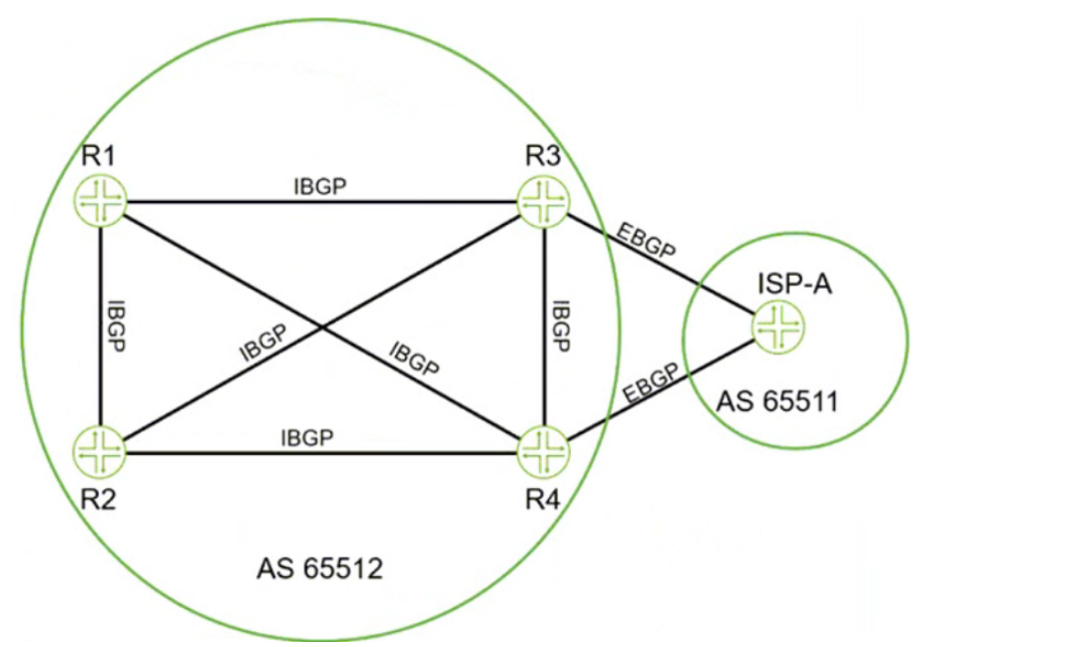
Click the Exhibit button-Referring to the exhibit, which two statements are correct about BGP routes on R3 that are learned from the ISP-A neighbor? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, D
Analyzing the Exhibit
The diagram represents BGP peering between:
AS 65512 (Enterprise Network)
AS 65511 (ISP-A)
R3 and R4 are peering with ISP-A using EBGP.
R1, R2, R3, and R4 are peering within AS 65512 using IBGP.
Understanding BGP Route Behavior
Option A: 'By default, the next-hop value for these routes is not changed by ISP-A before being sent to R3.'
Incorrect!
EBGP behavior: When a BGP route is advertised via EBGP, the next-hop IP is changed to the router's own IP by default.
Since ISP-A is advertising routes via EBGP to R3, the next-hop is changed to ISP-A's IP.
Thus, this statement is incorrect.
Option B: 'The BGP local-preference value that is used by ISP-A is not advertised to R3.'
Correct!
BGP Local Preference (LOCAL_PREF) is an IBGP-only attribute.
Local Preference is NOT shared over EBGP because it is used within an AS to influence route selection.
ISP-A will not send LOCAL_PREF to R3, as R3 is in a different AS.
Thus, this statement is correct.
Option C: 'All BGP attribute values must be removed before receiving the routes.'
Incorrect!
BGP does not remove all attributes when advertising routes. Some attributes are modified (e.g., next-hop, AS-PATH), but others (like MED, community) may be preserved.
Thus, this statement is incorrect.
Option D: 'The next-hop value for these routes is changed by ISP-A before being sent to R3.'
Correct!
As per default EBGP behavior, the next-hop is changed when a route is advertised to an EBGP peer.
This means ISP-A changes the next-hop to its own IP before sending it to R3.
Thus, this statement is correct.
Final Answer:
B. The BGP local-preference value that is used by ISP-A is not advertised to R3. D. The next-hop value for these routes is changed by ISP-A before being sent to R3.
Verification from Juniper Documentation:
Juniper BGP Configuration Guide confirms that LOCAL_PREF is not advertised over EBGP.
RFC 4271 (BGP-4) specifies that next-hop is changed by default when advertising routes via EBGP.
Exhibit
user@Rl show configuration interpolated-profile { interpolate {
fill-level [ 50 75 drop---probability [ > }
class-of-service drop-profiles
];
20 60 ];
Which two statements are correct about the class-of-service configuration shown in the exhibit? (Choose two.)
Answer : B, C
class-of-service (CoS) is a feature that allows you to prioritize and manage network traffic based on various criteria, such as application type, user group, or packet loss priority. CoS uses different components to classify, mark, queue, schedule, shape, and drop traffic according to the configured policies.
One of the components of CoS is drop profiles, which define how packets are dropped when a queue is congested. Drop profiles use random early detection (RED) algorithm to drop packets randomly before the queue is full, which helps to avoid global synchronization and improve network performance. Drop profiles can be discrete or interpolated. A discrete drop profile maps a specific fill level of a queue to a specific drop probability. An interpolated drop profile maps a range of fill levels of a queue to a range of drop probabilities and interpolates the values in between.
In the exhibit, we can see that the class-of-service configuration shows an interpolated drop profile with two fill levels (50 and 75) and two drop probabilities (20 and 60). Based on this configuration, we can infer the following statements:
The drop probability jumps immediately from 20% to 60% when the queue level reaches 75% full. This is not correct because the drop profile is interpolated, not discrete. This means that the drop probability gradually increases from 20% to 60% as the queue level increases from 50% full to 75% full. The drop probability for any fill level between 50% and 75% can be calculated by using linear interpolation formula.
The drop probability gradually increases from 20% to 60% as the queue level increases from 50% full to 75% full. This is correct because the drop profile is interpolated and uses linear interpolation formula to calculate the drop probability for any fill level between 50% and 75%. For example, if the fill level is 60%, the drop probability is 28%, which is calculated by using the formula: (60 - 50) / (75 - 50) * (60 - 20) + 20 = 28.
To use this drop profile, you reference it in a scheduler. This is correct because a scheduler is a component of CoS that determines how packets are dequeued from different queues and transmitted on an interface. A scheduler can reference a drop profile by using the random-detect statement under the [edit class-of-service schedulers] hierarchy level. For example: scheduler test { transmit-rate percent 10; buffer-size percent 10; random-detect test-profile; }
To use this drop profile, you apply it directly to an interface. This is not correct because a drop profile cannot be applied directly to an interface. A drop profile can only be referenced by a scheduler, which can be applied to an interface by using the scheduler-map statement under the [edit class-of-service interfaces] hierarchy level. For example: interfaces ge-0/0/0 { unit 0 { scheduler-map test-map; } }
Exhibit
Referring to the exhibit, what do the brackets [ ] in the AS path identify?
Which two statements about IS-IS are correct? (Choose two.)
Answer : A, C
Option A (Correct):
Complete Sequence Number PDUs (CSNPs)are periodically flooded by theDesignated Intermediate System (DIS)on multi-access networks (e.g., Ethernet).
This ensures all routers on the segment synchronize theirLink-State Databases (LSDBs).
Option C (Correct):
Partial Sequence Number PDUs (PSNPs)containonly the headers (descriptions)of LSPs (e.g., LSP ID, sequence number, checksum).
PSNPs are used to:
Request missing LSPs(when a router detects discrepancies via CSNPs).
Acknowledge LSP receipt(in point-to-point networks).
They donotinclude the full LSP data.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
Option B:Incorrect. PSNPs arenot flooded periodically---they are senton-demandfor specific LSP synchronization.
Option D:Incorrect. While CSNPsdocontain LSP descriptions (headers), the term 'only' is misleading. CSNPssummarize all LSPsin the LSDB, but they are not limited to 'only' descriptions---they serve as a complete database overview.
Key Takeaways:
CSNPsareperiodic,broadcastby the DIS, and ensure LSDB consistency.
PSNPsaretriggered, containspecific LSP headers, and handle requests/acknowledgments.
IS-IS usesCSNPs and PSNPsto maintain efficient LSDB synchronization without flooding full LSPs unnecessarily.