Microsoft Querying Data with Transact-SQL 70-761 Exam Practice Test
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You create a table by running the following Transact-SQL statement:

You need to develop a query that meets the following requirements:
* Output data by using a tree-like structure.
* Allow mixed content types.
* Use custom metadata attributes.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you run?

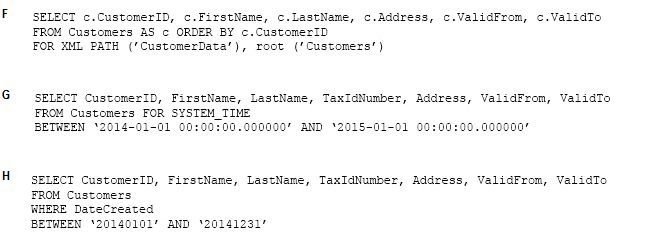
Answer : F
In a FOR XML clause, you specify one of these modes: RAW, AUTO, EXPLICIT, and PATH.
* The EXPLICIT mode allows more control over the shape of the XML. You can mix attributes and elements at will in deciding the shape of the XML. It requires a specific format for the resulting rowset that is generated because of query execution. This rowset format is then mapped into XML shape. The power of EXPLICIT mode is to mix attributes and elements at will, create wrappers and nested complex properties, create space-separated values (for example, OrderID attribute may have a list of order ID values), and mixed contents.
* The PATH mode together with the nested FOR XML query capability provides the flexibility of the EXPLICIT mode in a simpler manner.
References:
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms178107.aspx
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have a database named DB1 that contains two tables named Sales.Customers and Sales.Orders. Sales.Customers has a foreign key relationship to a column named CustomerID in SalesOrders.
You need to recommend a query that returns all the customers. The query must also return the number of orders that each customer placed in 2016.
Solution: You recommend the following query:

Does this meet the goal?
Answer : B
You run the following Transact-SQL statement:

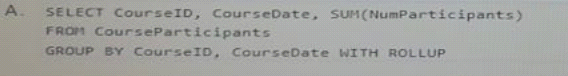
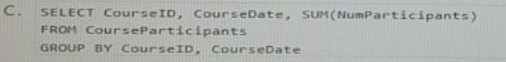
You use the table to store data about training courses: when they finished the location, and the number of participants in the courses.
You need to display a result set that shows aggregates for all possible combinations of the number of participants.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you run?
A)
B)

C)
D)

Answer : C
The WITH CUBE clause causes the query to compute all possible totals
References:
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/craigfr/2007/09/27/aggregation-with-cube/
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You have a database that is denormalized. Users make frequent changes to data in a primary table.
You need to ensure that users cannot change the tables directly, and that changes made to the primary table also update any related tables.
What should you implement?
Answer : B
Using an Indexed View would allow you to keep your base data in properly normalized tables and maintain data-integrity while giving you the denormalized 'view' of that data.
References:
You are building a stored procedure named sp1 that calls a stored procedure named SP2.
SP2 calls another stored procedure named SP3 that returns a Recordset. The Recordset is stored in a temporary table.
You need to ensure that SP2 returns a text value to sp1.
What should you do?
Answer : B
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section. You will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have a table named Products that stores information about products your company sells. The table has a column named ListPrice that stores retail pricing information for products.
Some products are used only internally by the company. Records for these products are maintained in the Products table for inventory purposes. The price for each of these products is $0.00. Customers are not permitted to order these products.
You need to increase the list price for products that cost less than $100 by 10 percent. You must only increase pricing for products that customers are permitted to order.
Solution: You run the following Transact-SQL statement:

Does the solution meet the goal?
Answer : A
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that use the same or similar answer choices. An answer choice may be correct for more than one question in the series. Each question is independent of the other questions in this series. Information and details provided in a question apply only to that question.
You create a table by running the following Transact-SQL statement:

You need to develop a query that meets the following requirements:
* Output data by using a tree-like structure.
* Allow mixed content types.
* Use custom metadata attributes.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you run?


Answer : F