NCARB ARE 5.0 Project Planning & Design (PPD) Project-Planning-Design Exam Practice Test
Which of the following need to be considered to enhance the acoustic design of an office building? Check the four that apply.
Answer : A, B, D, E
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
Enhancing acoustic design requires:
(A) Careful location of noise-sensitive spaces away from noise sources.
(B) Choosing structural floor systems with good sound isolation between floors.
(D) Using exterior barriers (natural or built) to reduce external noise.
(E) Selecting interior finishes with favorable acoustical absorption properties.
Minimizing steel stud framing (C) is not always required; proper detailing can address acoustic issues.
Treatments that decrease sound absorption (F) worsen acoustics.
ARE 5.0 PPD -- Building Systems and Assemblies, Acoustics
The Architect's Handbook of Professional Practice, 15th Edition -- Acoustic Design
For a government-owned project, architects can reduce consumption and waste by including which of the following requirements in their design and specifications? Check the four that apply.
Answer : A, B, D, F
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
To reduce consumption and waste, especially for government projects emphasizing sustainability:
Construction waste recycling (A): Diverts materials from landfill.
Use of local materials (B): Reduces transportation energy and emissions.
Reuse of existing structures (D): Minimizes new material use and demolition waste.
Use of low flow fixtures (F): Conserves water and reduces operational consumption.
Means of construction (C) and limiting bidding (E) affect cost and process but less directly impact waste reduction.
ARE 5.0 PPD -- Environmental Conditions and Context, Sustainable Design
The Architect's Handbook of Professional Practice, 15th Edition -- Green Building
________________________________________
A recital hall requires a clear span of 75 feet. Special consideration must also be given to the prevention of airplane noise that would interfere with performances.
Which of the following wall-bearing structural solutions will provide the most reasonable and economical roof-framing system to meet these needs?
Answer : B
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
For a recital hall needing noise reduction and a 75-foot clear span:
Cast-in-place reinforced concrete slabs (B) provide mass and stiffness, reducing noise transmission (including airplane noise) and offering sound isolation.
Steel joists and wood beams (A, D) are lighter, less dense, and less effective acoustically.
Precast concrete tees (C) may provide structural support but less acoustic mass.
Therefore, cast-in-place concrete best balances span, acoustics, and cost.
ARE 5.0 PPD -- Building Systems and Assemblies, Acoustic and Structural Design
Refer to the exhibit.
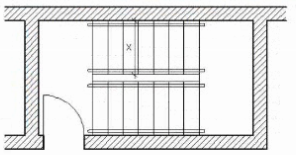
Refer to the exhibit (stair connecting four stories, occupant load 100, not accessible exit).
Not including the permitted projection for handrails and stringers, what is the minimum clear width of the stair at dimension X?
Answer : B
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
For stairs serving 100 occupants, building codes such as IBC require a minimum clear width of 44 inches to accommodate occupant egress.
36 inches is typical minimum for stairs serving smaller occupant loads.
Wider widths like 48 or 60 inches are required for higher occupant loads.
Handrails and projections may reduce nominal width but are not included in minimum clear width measurements.
ARE 5.0 PPD -- Codes and Regulations, Egress Requirements
IBC 2018 Chapter 10 -- Means of Egress
Refer to the exhibit.
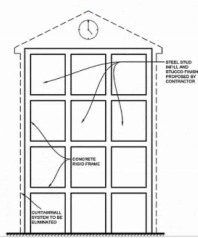
Refer to the exhibit (concrete rigid frame building with aluminum curtain wall system).
The drawing shows a proposed concrete rigid frame building enclosed in an aluminum curtain wall system. To save money, the contractor proposed to eliminate the curtain wall system and substitute steel stud framing, which is anchored between the columns and beams and covered with a stucco finish.
What is the most likely result of this substitution?
Answer : C
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
Curtain wall systems are designed to accommodate building movement, including deflections from wind and seismic loads, and provide an air and moisture barrier without carrying structural loads.
Replacing the curtain wall with a steel stud framing covered with stucco, which is rigid and brittle, will not accommodate differential movement between the frame and cladding. This is likely to cause stucco cracking as the steel framing and concrete frame move differently under lateral loads.
The wind load will not necessarily overload the concrete frame (A), as loads are transferred properly in both systems.
The substitution may save initial cost but will cause durability and maintenance problems (B).
Dead load increase (D) is minimal compared to structural effects of cracking.
NCARB guidelines stress proper cladding systems that can accommodate structural deflections to prevent damage.
ARE 5.0 PPD -- Building Systems and Assemblies, Curtain Wall Systems
The Architect's Handbook of Professional Practice, 15th Edition -- Building Envelope
An architect has just received client approval of the Schematic Design documents for a three-story, outpatient medical clinic. The clinic is located within a mixed-use development governed by
a City-approved Planned Development (PD) document. The medical clinic design utilizes standardized departmental layouts and includes outpatient clinics, as well as treatment spaces,
administrative spaces and public/lobby spaces.
The site needs to accommodate four different vehicular traffic flows: patient traffic, staff traffic, service and delivery traffic, and emergency services traffic. In addition, a pedestrian plaza
must connect to the mixed-use development sidewalks. The plaza must provide space for bicycle parking and will serve as the future bus stop.
The site design addresses several challenges related to building orientation. The southeast facade, with excellent visibility from the highway, is the location of all service equipment. The
building entrance faces northwest, convenient to the parking but not visible from the highway.
The client believes future patient volumes will outgrow the clinic. The PD document allows for a planned Phase 2 development on the adjacent vacant site to the southwest. Phase 2 would
include a second building (2 story, 80,000 BGSF) and/or a parking deck.
Other considerations for the project include:
Protected tree requirements are defined in the PD document.
Easy pedestrian access must be provided from Sycamore Boulevard.
All required parking for the clinic must be accommodated on site.
Programmed area includes 109,450 Departmental Gross Square Feet (DGSF) / 130,184 Building Gross Square Feet (BGSF).
Exterior material percentages are dictated by the PD document and shall not exceed specific percentages for Primary and Secondary Finishes.
All service equipment needs to be screened; see PD document for restrictions.
Signage opportunities are important to the client.
Acoustical privacy is a concern of the healthcare system.
The following resources are available for your reference:
Drawings, including a perspective, plans, and exterior elevations
Building Program, including client's departmental program and detailed program for Treatment 01 (Infusion)
Exterior Material Cost Comparisons
Planned Development Document
IBC Excerpts, showing relevant code sections
ADA Excerpts, showing relevant sections from the ADA Standards for Accessible Design
Refer to the exhibit.
What is the required wall finish for rooms 1201 through 1206 on the first floor?
Answer : C
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
Rooms such as medical treatment or healthcare spaces require wall finishes that are smooth, scrubbable, and water-resistant to maintain hygiene and allow for regular cleaning and disinfection.
Tight, sealed seams (A) and absence of fissures (B) are important but part of broader requirements.
The key is surfaces that can withstand cleaning agents and moisture exposure without damage.
This ensures compliance with healthcare facility codes and infection control.
IBC -- Healthcare Facilities Chapter
ADA Standards for Accessible Design
ARE 5.0 PPD -- Codes and Regulations, Healthcare
Which of the following strategies is most appropriate for a new shopping center to be constructed on a nearly flat site flowing into a municipal subsurface storm-drainage system that is at capacity during a 5-year storm?
Answer : B
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
When the municipal storm-drain system is at capacity during frequent storms, site design must incorporate on-site stormwater management to reduce runoff and delay peak flows.
Option B is the most effective strategy: grading the site and positioning buildings and infrastructure to create retention basins allows water to be temporarily stored on site, reducing the volume and rate of runoff entering the municipal system. This also aids in groundwater recharge and helps comply with stormwater management regulations.
Extending storm sewers (A) without capacity improvements only increases burden on an already overloaded system.
Reducing runoff time (C) can exacerbate peak flows by quickly directing water to the storm drains.
Conducting drainage along curbs (D) is standard but does not solve capacity issues if the municipal system is overloaded.
Thus, on-site retention and detention through basin creation is preferred.
ARE 5.0 PPD -- Environmental Conditions and Context, Site and Stormwater Design
The Architect's Handbook of Professional Practice, 15th Edition -- Site Planning and Stormwater Management