NFPA Certified Fire Plan Examiner CFPE Exam Practice Test
Exhibit.
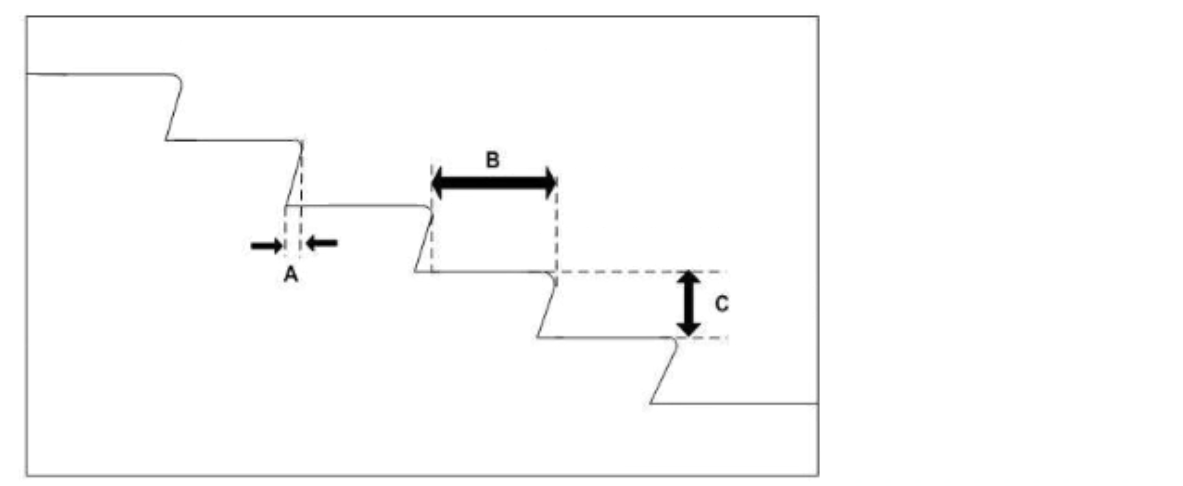
For the included figure, which dimension is the tread depth?
Answer : B
The tread depth is the horizontal distance from the front edge of a stair tread to the back edge of the same tread, which corresponds to dimension 'B' in the figure. According to NFPA 101, Life Safety Code, the tread depth is crucial in ensuring safe stairway design for proper footing and egress.
Exhibit.

Based on site plan C1 of the plan set what is the maximum depth the water lines are to be buried''
Answer : A
Based on site plan C1 of the plan set, the maximum depth for burying the water lines is 4 feet (1.2 meters). This depth is typically required to protect the pipes from freezing temperatures and mechanical damage while ensuring compliance with local codes and standards for water line installation.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
What is the maximum nominal spacing for spot type smoke detectors on smooth ceilings?
Answer : D
According to NFPA 72, National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code, the maximum nominal spacing for spot-type smoke detectors on smooth ceilings is 30 feet (9.1 meters). This spacing ensures adequate coverage for detecting smoke in large areas and complies with the performance criteria established in the standard to provide early warning of fire conditions.
Top of Form
Bottom of Form
What is the maximum travel distance to an exit that is permitted in a sprinklered movie theater'?
Answer : C
For a sprinklered movie theater, the maximum travel distance to an exit is typically 200 feet (61 meters), as stipulated by NFPA 101, Life Safety Code. This distance is determined based on the need to ensure safe egress for occupants in an emergency, balancing the need for quick evacuation with the layout and size of the building. The 200 ft maximum allows sufficient time for occupants to reach an exit while maintaining safety standards in a fully sprinklered environment.
The responsibilities of a Board of Appeals includes which of the following?
I . Interpreting the codes
II . Reviewing alternative methods and procedures
III . Ruling on challenges to the building or fire official regarding the applicability and interpretation of the codes
IV . Evaluating alternative proposals for compliance with the codes
Answer : D
The Board of Appeals typically has several responsibilities, including interpreting the codes (I), reviewing alternative methods and procedures (II), ruling on challenges to the building or fire official regarding the applicability and interpretation of the codes (III), and evaluating alternative proposals for compliance with the codes (IV). These responsibilities ensure that the board provides a fair process for resolving disputes related to code enforcement and allows for alternative solutions that meet the intent of the codes.
What is the minimum rating for visible indicating appliances in corridors'?
Answer : B
The minimum rating for visible indicating appliances in corridors is 15 cd (candela), as specified by NFPA 72, National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code. This requirement ensures that the visual signals are bright enough to be seen by occupants during an emergency, providing adequate warning to facilitate evacuation. The 15 cd rating is the standard for most corridors to ensure visibility over the required distance, especially in areas with no natural light or in emergency lighting conditions.
What is the maximum common path of travel permitted in a sprinklered educational occupancy?
Answer : C
According to NFPA 101, Life Safety Code, the maximum common path of travel in a sprinklered educational occupancy is 100 feet (30 meters). The common path of travel refers to the distance occupants must travel before having two separate means of egress. The code provides this limit to ensure that occupants have a reasonably short distance to safety, enhancing the likelihood of safe evacuation in an emergency.