Nokia IP Networks and Services Fundamentals 4A0-100 Exam Practice Test
Which of the following devices connects directly to the customer equipment?
Answer : A
In a typical MPLS/VPN service architecture:
PE (Provider Edge) router: Directly connects to the customer edge (CE) device.
P (Provider) router: Only forwards MPLS-labeled packets, does not touch customer routes.
LSR (Label Switch Router): General term, can be either PE or P depending on placement.
Correct Answer: A -- PE
It interfaces with CE devices and runs customer routing protocols (e.g., OSPF, BGP).
Nokia MPLS and VPN Guide -- PE vs P Role
Nokia SRA Study Guide -- PE-CE and Core Router Design
Which of the following statements about a physical router interface is FALSE?
Answer : D
In Nokia SR OS:
A physical interface refers to a physical port on the router (e.g., port 1/1/1).
It can be configured with IP addresses, associated with services (e.g., IES, VPRN), and connects to other routers or customer devices.
System and loopback interfaces are logical interfaces, not physical.
Option D is FALSE, because a physical interface cannot be of type 'system' or 'loopback' --- those are virtual/logical interfaces in the Nokia router architecture.
Nokia SRA Study Guide -- Chapter: ''Interfaces and Ports''
Nokia SR OS Interface Configuration Guide
Which of the following is a characteristic of a subnet created with a /31 prefix?
Answer : A
A /31 subnet in IPv4 provides exactly two IP addresses (e.g., 192.168.1.0/31 usable: 192.168.1.0 and 192.168.1.1). Traditionally, these would represent a network address and a broadcast address, but RFC 3021 redefines /31 subnets for point-to-point links, such as router-to-router connections.
In a /31 subnet:
Broadcast address is not used.
Both IPs are treated as usable host addresses.
It's ideal for point-to-point links, saving address space.
This is widely supported and standardized in Nokia IP and routing platforms.
Nokia IP Fundamentals Guide -- Subnetting Techniques
RFC 3021 -- 'Using 31-Bit Prefixes on IPv4 Point-to-Point Links'
Refer to the exhibit.
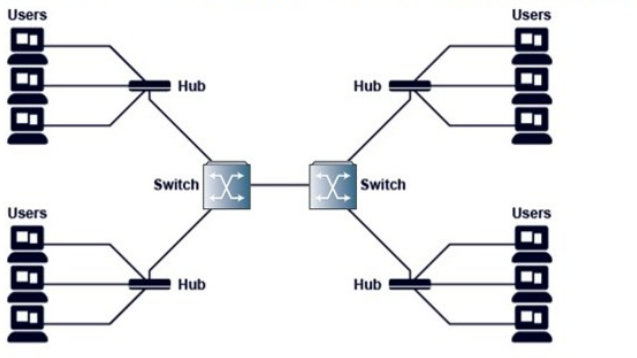
An Ethernet Local Area Network (LAN) consists of the components shown in the diagram. Assuming there are no VLANs, how many broadcast domains are on this LAN?
Answer : A
A broadcast domain is a logical division of a network in which all nodes can reach each other with broadcast frames (Layer 2). Devices within the same broadcast domain receive broadcast packets sent by others.
In the diagram:
Multiple users connect to hubs.
Hubs are Layer 1 devices and do not break broadcast domains. They simply replicate incoming electrical signals to all ports.
Hubs are then connected to switches.
Switches, unless VLANs are configured, forward broadcasts to all ports except the incoming one, effectively keeping all devices in the same broadcast domain.
The two switches are connected together without VLAN segmentation.
Therefore:
The entire LAN depicted is a single Layer 2 broadcast domain.
There are no routers or VLANs to break or separate the domain.
Correct answer: A. 1
Nokia IP Networking Fundamentals Study Guide -- Chapter: 'LAN Switching and Broadcast Domains'
Cisco and CompTIA Network+ materials on 'Hubs vs Switches vs Routers in Broadcast Domains'
Which of the following statements about ICMP functions is FALSE?
Answer : D
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) is used for network diagnostics and error messaging. Key uses include:
Ping (Echo Request/Reply) -- tests end-to-end connectivity
Traceroute -- uses ICMP time exceeded messages to identify hops
Error reporting -- returns various error types with different codes
However, ICMP does not re-route traffic. If a destination is unreachable, ICMP reports the error back to the sender; it doesn't instruct routers to re-route.
Option D is FALSE -- ICMP does not perform routing.
Nokia IP Fundamentals Guide -- Section: ''ICMP and Network Diagnostics''
RFC 792 -- ICMP Standard
In MAC address 00-20-60-CE-2B-28, which part is the Organisationally Unique Identifier (OUI)?
Answer : D
A MAC address (Media Access Control address) is a 48-bit identifier typically expressed in six groups of two hexadecimal digits (e.g., 00-20-60-CE-2B-28). It consists of two key parts:
OUI (Organizationally Unique Identifier) -- The first 24 bits (or first 3 octets, e.g., 00-20-60) are assigned by the IEEE to hardware manufacturers. This identifies the vendor or manufacturer.
Device Identifier (NIC Specific) -- The remaining 24 bits (e.g., CE-2B-28) are assigned uniquely by the vendor to each device/interface.
So in the address 00-20-60-CE-2B-28:
00-20-60 is the OUI
CE-2B-28 is the device-specific portion
Thus, the correct answer is D. 00-20-60.
IEEE MAC Address Standard (IEEE 802)
Nokia IP Networking Fundamentals Study Guide -- Chapter: 'Ethernet Addressing'
Which of the following statements best describes a hub?
Answer : B
A hub is a physical layer (Layer 1) networking device used to connect multiple Ethernet devices in a network. Unlike switches or routers, hubs do not inspect or process frame headers. Instead, they perform a simple task:
Receive a signal (electrical or optical) on one port
Replicate that signal identically to all other ports
This means the hub does not examine Layer 2 (MAC addresses) or Layer 3 (IP addresses) and does not perform intelligent forwarding. It merely broadcasts all incoming traffic to every other connected device, often resulting in high collision domains and poor efficiency.
Option A describes a repeater, not a hub.
Option C describes a switch (Layer 2 device).
Option D describes a router (Layer 3 device).
Option B is correct: A hub does not inspect headers and replicates traffic blindly.
Nokia IP Networking Fundamentals Study Guide -- Chapter: 'Network Devices and OSI Model'
CompTIA Network+ and Cisco CCNA foundational guides (for universally accepted hardware behavior)