Nokia IS-IS Routing Protocol 4A0-112 Exam Questions
Refer to the exhibit.
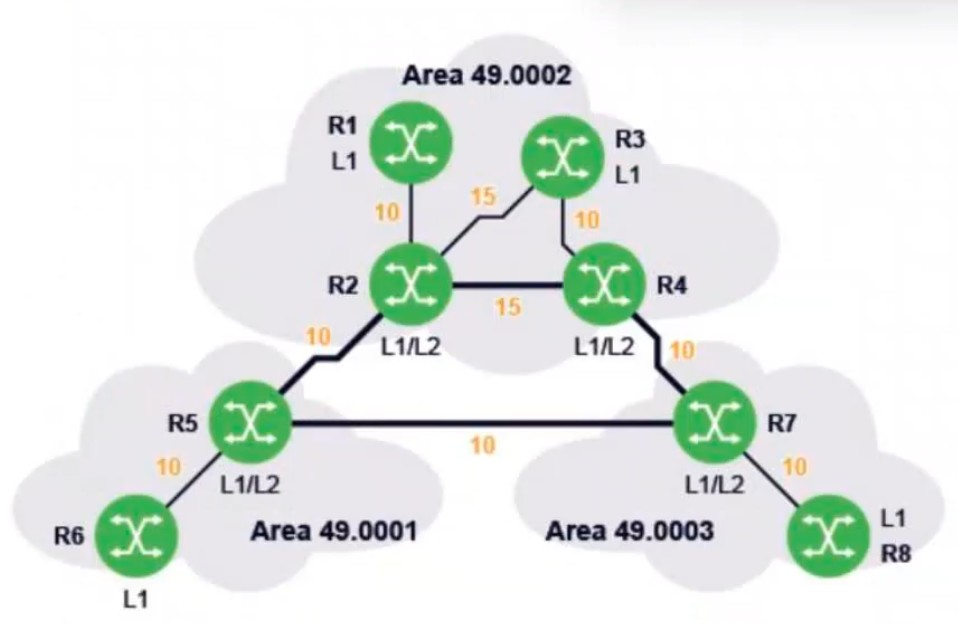
In the diagram, all routers are using IS-IS as their routing protocol. The number next to each link is its metric value.
What path will traffic follow from router R6 to router R3, and from router R3 to router R6?
Answer : A
The metric values between the routers dictate the routing paths, and IS-IS will calculate the shortest path based on these values.
R6 to R3: The path from R6 to R3 will go through R5 and R2, as this route has the least cumulative metric (10 + 10 + 15 = 35).
R3 to R6: The reverse path from R3 to R6 will follow R3 R2 R5 R6 because this route is also the shortest with a total metric of 10 + 10 + 10 = 30.
Which of the following is NOT a function of the control plane a router?
Answer : D
The data plane (or forwarding plane) is responsible for actually forwarding the data packets. It uses the information stored in the forwarding table to determine how to move packets from one interface to another toward their destination.
Refer to the exhibit.
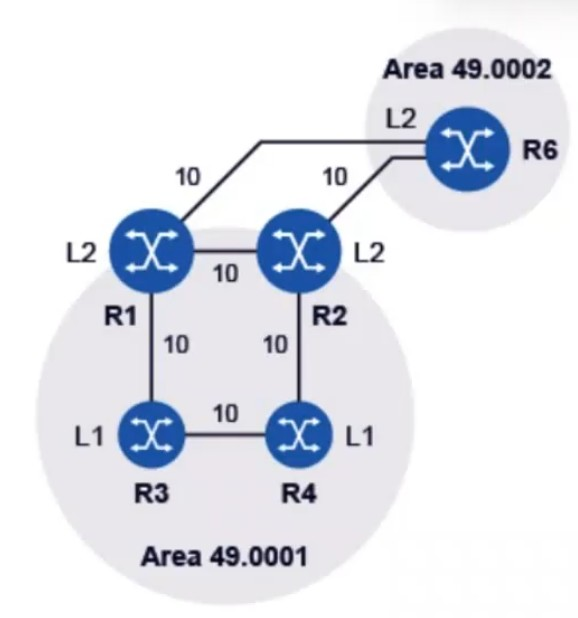
Examine the physical topology of the IS-IS network, the metrics of the links and the levels of the routers. All routers have their system interfaces included in IS-IS. Which of the following statements describes the route-table entry that router R4 will use to reach the system IP address of router R6?
Answer : A
Router R4 is in Area 49.0001 and R6 is in Area 49.0002. Both routers are Level 2 (L2), meaning that they can communicate across areas using Level 2 IS-IS routing.
Since R2 is the L1/L2 router that connects both Area 49.0001 and Area 49.0002, it will be the next-hop for router R4 to reach R6's system IP address.
The IS-IS protocol will ensure that R4 will have a route to R6's system IP address via R2 as the next-hop.
Refer to the exhibit.
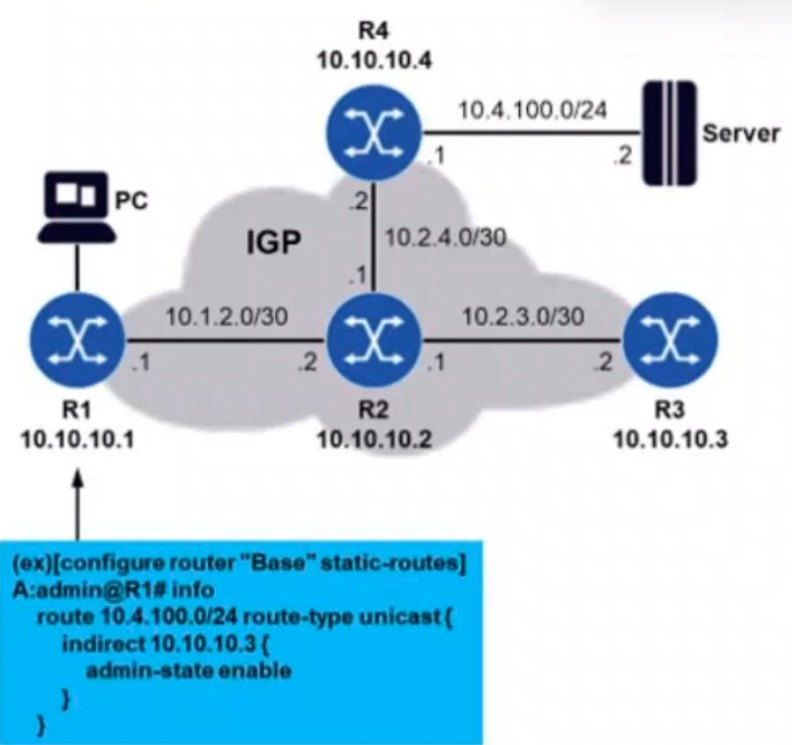
Routers R1 through R4 are running an IGP in such a way that they have each other's system IP addresses in their routing tables. A static route is configured on router R1 so that it can reach subnetwork 10.4.100.0/24. The network administrator decides to use an indirect static route, as shown in the diagram. However, pinging the server from router R1 fails. What may be the problem in this case?
Answer : D
The static route configured on router R1 uses an indirect next-hop, which is 10.10.10.3 (R3). While the echo request from R1 reaches the server through the IGP, the problem lies in the return path for the echo response.
The route 10.4.100.0/24 is reachable through R3, but there is no reciprocal route in R3's routing table that allows the response to flow back towards R1. This results in a failure to return the echo response to R1, causing the ping to fail.
Refer to the exhibit.
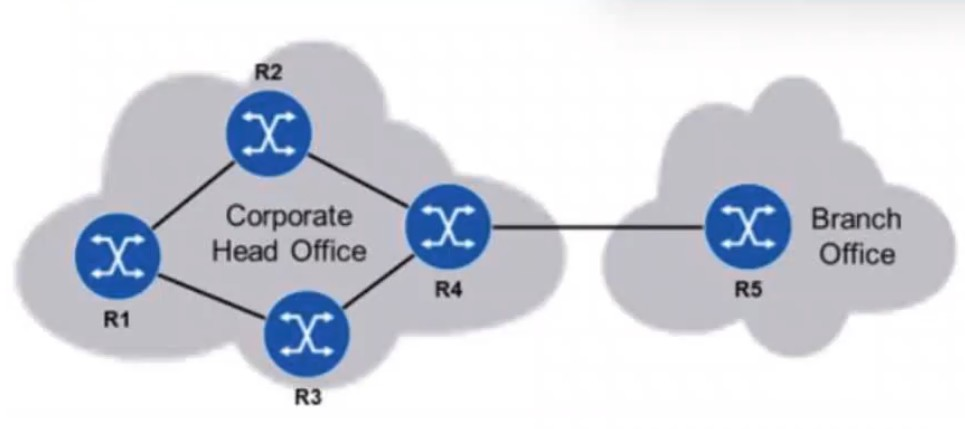
Static routing is to be used in a network between a corporate head office and a branch office. The head office has many connected subnetworks, whereas the branch office has one subnetwork and a single connection to the head office. Which of the following is the most likely configuration on the head office and branch office routers?
Answer : A
The head office has many connected subnetworks, so it will typically have a default route to forward traffic to the branch office (or external networks), since it may not need to define static routes for each branch network.
The branch office, which has only one subnetwork and a single connection to the head office, will have a specific static route to reach the head office subnet or other subnets at the head office, since it only needs to know the specific route to reach the head office's network.
Refer to the exhibit.
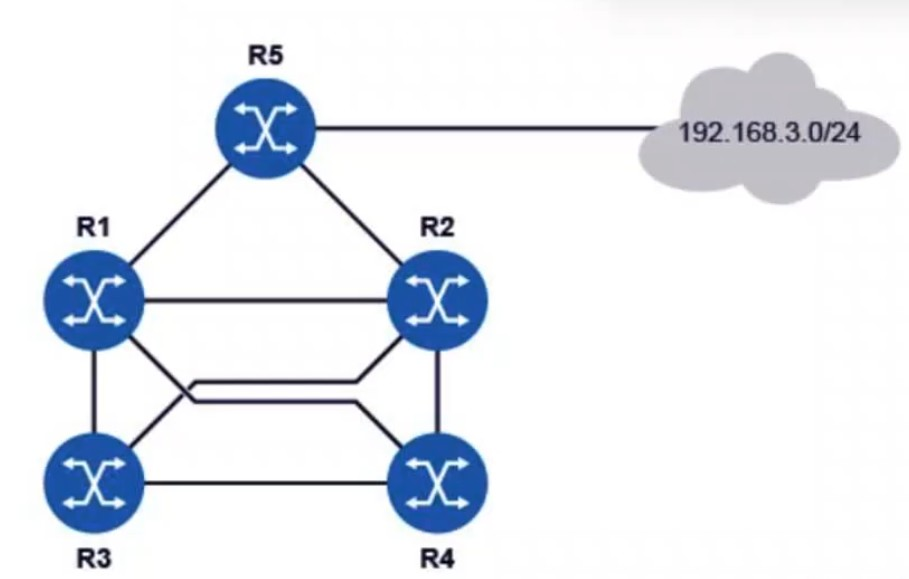
All routers in the diagram are running an interior gateway protocol (IGP) and have been configured with an ECMP value of 4. Router R5 advertises the prefix 192.168.3.0/24 using the IGP. Assuming all links have the same cost, how many entries for prefix 192.168.3.0/24 will be in router R3's routing table?
Answer : D
In this scenario, the routers are configured with an Equal-Cost Multi-Path (ECMP) value of 4, meaning they can utilize up to 4 equal-cost paths to reach a destination. Since Router R5 is advertising the 192.168.3.0/24 prefix and all links have the same cost, router R3 will receive multiple routes to reach this destination.
Given that all the routers (R1, R2, R3, R4, and R5) are connected in a way that can support multiple equal-cost paths, and assuming ECMP is set to 4, the routing table on Router R3 will have up to 4 entries for the prefix 192.168.3.0/24.
Thus, Router R3's routing table will contain 4 entries for the prefix 192.168.3.0/24.
There are several differences between IS-IS Hello packets used on broadcast interfaces and on point-to-point interfaces.
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
Answer : C
In both broadcast and point-to-point interfaces, IS-IS routers identify neighbors using system IDs, not interface MAC addresses. The system ID is a unique identifier assigned to each router, and it is used to identify neighbors in both types of interfaces.