Nokia Optical Networking Fundamentals 4A0-205 Exam Practice Test
How is it possible to check the activation status of GMRE on a node?
Answer : C
The GMRE activation status is reported in the supervision state column on the node list. The supervision state column displays the GMRE status of the node, which is either 'Activated' or 'Not Activated'. This allows the user to quickly check the GMRE activation status of a node without having to ping the node from the NFM-T platform.
Is it possible to open and manage EPT designs that are created with different releases than the release installed on the local workstation?
Answer : B
It is possible to open and manage EPT designs that are created with different releases than the release installed on the local workstation, however only designs created with current and older releases can be opened and edited. Designs created with an older release can be opened by a current release but changes cannot be made.
Which statement is correct about the NFM-T network map?
Answer : C
The NFM-T network map provides a graphical view of the network with different colors used to represent each node, physical connection, and active alarm. It allows the user to quickly identify any issues in the network and provides context sensitive navigation.
What is a degree-1 node?
Answer : A
A degree-1 node is a node that only has one direction, and it is therefore a terminal node. This means that the node only has one input and one output port. It does not have any other ports to connect to other nodes or fibers. This is a common feature of some optical transport networks, such as ring networks, where a degree-1 node serves as the endpoint of the ring.
Which of the following sentences about FlexGrid is false?
Answer : C
FlexGrid is a flexible grid technology that allows for variable channel spacing and bandwidth allocation. It uses the same sets of boards as the traditional fixed grid systems and it does not require upgrading the old generation WDM systems.
'Flexible Grid Optical Networks: From Concepts to Realizations' by Diomidis S. Michalopoulos and George K. Karagiannidis
'Flexible Grid and Flexible Spectrum Optical Networks' by Diomidis S. Michalopoulos and George K. Karagiannidis
'Flexible Grid Optical Networks' by Diomidis S. Michalopoulos and George K. Karagiannidis
With reference to the image, where is the OPS card placed to provide the OMSP protection?
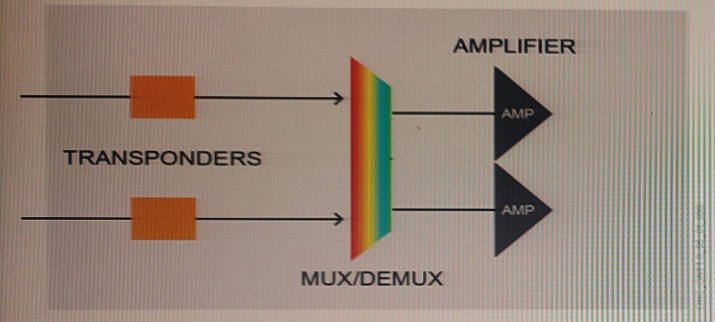
Answer : D
Which of the following is an example of optical protection mechanism?
Answer : B
It can be implemented through the use of a Y-cable or an optical protection switch (OPS) card, which allows for the switching of traffic to a secondary path in the event of a failure on the primary path. This type of protection is commonly used to protect against fiber cuts and other types of physical layer failures in the optical transport network.