OMG Certified UML Professional 2 (OCUP 2) - Advanced Level OMG-OCUP2-ADV300 Exam Questions
Choose the correct answer:
A project's requirements call for flexibility in the collection class design. Most of the collections will be a fixed length of 25 elements. However, allowance must be made in the design for collections that are a fixed length longer than 25.
Which model fragment supports the project's requirements?
A)
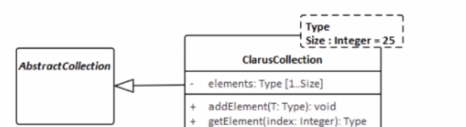
B)
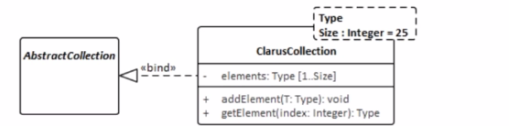
C)
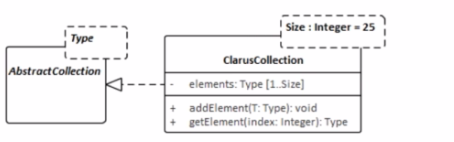
D)
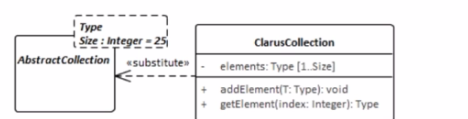
Answer : C
The UML model fragment that best supports the project's requirements for collection class design is one that allows the fixed length of the collections to be specified but also permits flexibility for collections longer than 25 elements. In Option C, the ClarusCollection class is shown as a template class with a template parameter Size set to a default of 25. However, the dashed lines and the separate box for Type and Size indicate that while there is a default value, it can be overridden. This means that the Size can be parameterized, thus allowing the creation of ClarusCollection instances with different fixed lengths, not just 25. This design will enable most collections to be created with the default size of 25, but also allows for creating collections with sizes greater than 25, providing the flexibility required by the project's requirements. This adheres to the UML 2.x specification on templates and parameterization.
Choose the correct answer:
What two protocol state machine interpretations can be defined?
Answer : C
Protocol State Machines in UML are used to specify the allowable protocol transitions that can be observed in the instances of a classifier. The interpretations that can be defined for protocol state machines are:
A . Behavioral and protocol are not specific types of interpretations but rather describe aspects of state machines in general.
B . Declarative and procedural describe styles or approaches to programming or specification, not specific to UML state machine interpretations.
C . Declarative and executable is the correct answer. Declarative interpretations specify the allowed sequences of events in a state machine, while executable interpretations are concerned with the actual implementation that can be executed by a machine.
D . Executable and non-executable are distinctions but not specifically pertaining to protocol state machine interpretations alone.
UML Specification: State Machines chapter, particularly sections on protocol state machines.
Further details can be found in the UML 2.5 Documentation discussing the differences between different state machine interpretations.
Choose the correct answer:
What characterizes the generalization relationship between two Classifiers where the child can NOT be substituted for the parent?
Answer : C
In UML, the isSubstitutable property of a generalization relationship indicates whether instances of the child classifier can be used wherever instances of the parent classifier are expected, that is, whether the subclass is substitutable for the superclass. When this property is set to false, it means that the child classifier cannot be substituted for the parent classifier. This property is part of the UML metamodel for generalization and affects how inheritance is interpreted in terms of substitutability, as described in the UML 2.x Superstructure Specification.
Choose the correct answer:
Consider the following template Operation:
addElement
Which Operation represents a binding of that template Operation?
Answer : A
The correct representation of a binding of the template operation addElement<E> with E being bound to the type Card is addElement (e : Card). This notation means that the template parameter E is being replaced by the concrete type Card, thus instantiating the template operation with that specific type. In UML, this instantiation does not require the bind keyword or the template brackets <> around the type in the operation signature itself; it is simply represented by using the concrete type as the type of the parameter in the operation. This usage is consistent with the UML 2.x Superstructure Specification, which explains how operations of a template classifier are instantiated when template parameters are bound to actual types.
Choose the correct answer:
Which capability Is provided by the Profile mechanism?
Answer : C
The Profile mechanism in UML provides the capability to adapt existing metamodel elements for specific purposes. Profiles allow modelers to extend the standard UML metamodel with additional semantics by defining stereotypes, tagged values, and constraints that are specific to a particular domain, platform, or methodology. This means that profiles tailor the existing UML metamodel elements to create domain-specific models without changing the underlying metamodel itself. This adaptation mechanism is described in the UML 2.x Superstructure and Infrastructure Specifications, which detail how profiles can be used to customize the UML for particular domains or purposes.
Choose the correct answer: What is the scope of fUML?
Choose the correct answer:
What is the main purpose of the concept of Extent in MOF?
Answer : B
The concept ofExtentin MOF serves the purpose of defining a set ofTagsthat can be associated with any number of model elements. These tags provide additional information or metadata about the elements. Extent allows you to annotate model elements with relevant information beyond their intrinsic properties. It provides a context for identifying and managing these annotations independently from the element's actual values.
Meta-Modeling and the OMG Meta Object Facility (MOF)