OMG Certified UML Professional 2 (OCUP 2) - Foundation Level OMG-OCUP2-FOUND100 Exam Questions
Choose the correct answer:
How would you refer lo element One of Package PI. when inside Package P2?
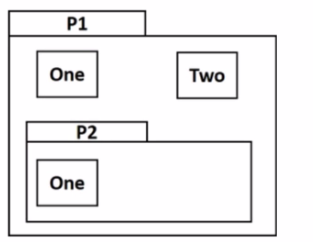
Answer : D
In UML, when you need to reference an element from another package while inside a different package, you use the qualified name. A qualified name includes the package name followed by two colons and then the element name. This ensures that the reference is clear and unambiguous, especially when different packages may have elements with the same name.
The correct syntax for referring to element One of Package P1 from inside Package P2 is P1::One, where :: is the scope resolution operator used to separate the package name from the element name.
Therefore, the correct answer is:
D . P1::One
Choose the correct answer:
Suppose you are using a programming language that knows the following basic types: byte, short, and long.
Which diagram defines them:
A)

B)

C)


Answer : A
In UML, basic types like byte, short, and long are represented as DataType elements. These are typically used to specify the types of attributes, parameters, or return values of operations in a model. Option A shows three separate classes named Byte, Short, and Long, which would represent these as distinct data types within the UML model.
Option B incorrectly uses stereotypes on objects, which is not the correct UML representation for data types. Option C shows a class with attributes of different types, but it does not define these types as basic types. Option D is incorrect because it uses stereotypes on DataType elements, which is not the standard way to represent basic types in UML.
According to the UML 2.5 specification, DataTypes are a kind of classifier that specifies a domain of values without identity (section 10.5.8). DataTypes are not classes; they do not have operations and cannot have instances that maintain an identity.
Choose the correct answer:
How many activities can feed an initial node at the beginning of an activity thread?
Answer : C
The initial node is depicted as a filled circle and is used to show where the control starts within the activity. When the activity is invoked, control tokens are placed on the initial node and can then traverse the outgoing edge to the first action or activity node. The specification clearly states that there should be only one outgoing edge, ensuring that the flow of control is unambiguous at the start of the activity.
It's important to note that while multiple initial nodes can exist within a single activity diagram, each initial node can only be the source of one outgoing edge, and thus, only one activity can feed each initial node.
Choose the correct answer:
Which statement is correct about Activity precondition and postcondition constraints?
Answer : B
Activitypreconditionandpostconditionconstraints are essential for specifying conditions that apply to an activity. Let's break down the concepts:
Precondition:
Apreconditionrepresents a condition that must betrue beforethe activity can start or be invoked.
It ensures that the necessary prerequisites are met before executing the activity.
For example, a precondition for an activity related to booking a flight might be that the user has already logged in to the system.
In UML, preconditions are typically expressed using natural language or constraints.
These constraints can be associated with the entire activity or specific actions within it.
Postcondition:
Apostconditionspecifies a condition that must betrue afterthe activity completes.
It captures the expected state or outcome resulting from the activity's execution.
For instance, a postcondition for the flight booking activity might be that the reservation has been successfully confirmed.
Similar to preconditions, postconditions can apply to the entire activity or individual actions within it.
Application Scope:
Bis the correct answer because preconditions and postconditions applyonly to specific invocationsof the activity.
They do not universally apply to all invocations of the same activity.
Different invocations of the same activity may have distinct preconditions and postconditions based on context or input parameters.
Constraining Actions vs. Flow of Objects:
OptionCis incorrect because preconditions and postconditions are not primarily used to constrain specific actions within the activity.
OptionDis also incorrect because they are not limited to constraining only the flow of objects within the activity.
Instead, preconditions and postconditions focus on the overall conditions for invoking and completing the activity.
Sparx Systems.''Use Case Diagram - UML 2 Tutorial.''2
Stack Overflow.''UML Use-case diagram postcondition implementation (with diagram).''3
Choose the correct answer:
Consider the following diagram:
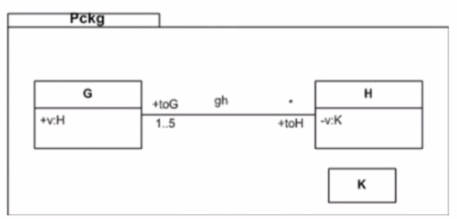
Which statement is true about the diagram?
Answer : D
The diagram you provided shows two classes, G and H, which are within a package named Pckg. Each class has an attribute named 'v' with different visibility and type indicators. The attribute 'v' in class G has visibility 'private' (denoted by '-'), and in class H, it is 'protected' (denoted by '#'). This suggests that the scope of each 'v' is limited to its respective class. Therefore, when you refer to 'v' within the package, its meaning depends on the context or the namespace from which it's accessed.
UML 2.x Superstructure Specification: This defines the rules for scopes and namespaces in UML. It clarifies how elements with the same name can coexist in different namespaces and how their references would differ based on the context.
UML 2.x Infrastructure Specification: Provides the foundational concepts for UML, including the semantics of structured classifiers and namespaces which pertain to the interpretation of the 'v' attribute in different classes.
Choose the correct answer:
What is the meaning of the relationship shown in the diagram below?
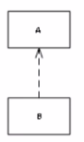
Answer : B
In UML 2, the dashed arrow with an open arrowhead represents a dependency relationship. In the context of class diagrams, a dependency relationship indicates that changes to one class (the independent class) may cause changes in the other class (the dependent class). The direction of the arrow specifies which class is dependent on which. In the given diagram, the arrow points from class A to class B, which means that class A is dependent on class B. This could manifest as class A using some services or functions of class B, for example.
UML 2.5 Specification Document: The official document by the Object Management Group (OMG), which defines the syntax and semantics of UML.
UML Distilled: A Brief Guide to the Standard Object Modeling Language, Third Edition by Martin Fowler: This book provides a clear guide to UML and includes examples of dependency relationships.
Choose the correct answer:
In your model, you need to represent accounts.
Which statement supports using a Class, rather than a DataType. lor this purpose''
Answer : C
In UML, a Class is a template that defines the structure and behavior of objects, whereas a DataType is a type of classifier which specifies a domain of values without identity. Operations (such as money transfers and withdrawals) are behaviors that change the state of an object and, therefore, are defined in Classes rather than DataTypes. This suggests that accounts, which require operations to transfer and withdraw money, should be modeled as Classes.
UML 2.x Superstructure Specification: Provides definitions for Classes and DataTypes, and details the circumstances under which each should be used. It specifically states that Classes can have operations while DataTypes cannot.
UML 2.x Infrastructure Specification: This foundational document provides an in-depth explanation of UML modeling constructs, supporting the use of Classes when operations are needed to manage an object's state.