PRMIA Exam I: Finance Theory, Financial Instruments, Financial Markets – 2015 Edition 8006 Exam Practice Test
Backwardation in commodity futures is explained by:
Answer : D
Backwardation is said to occur when futures prices are lower than the current spot prices. This would happen only when carrying costs are negative. Carrying costs are equal to interest, plus storage costs and less any 'convenience yield'. The existence of large convenience yields may explain backwardation in commodity futures prices. Therefore Choice 'd' is the correct answer.
Contango is the 'normal' market situation where forward prices are higher than spot prices. Storage costs explain contango, not backwardation. Risk free rates, or the cost of funding for the futures position, are always positive and do not explain backwardation.
According to the mean-variance criterion, which of the following statements are true in relation to an investor who does not borrow or lend?
1. The investor would select a portfolio of assets to minimize drawdowns
II. The investor would prefer a portfolio on the efficient frontier
III. The investor would prefer a portfolio with a higher return given the same level of risk
IV. The investor would maximize portfolio return alone as the mean-variance criterion assumes risk neutrality
Answer : D
According to the mean variance criterion, an investor would always:
- prefer less risk to more risk given a certain level of returns,
- prefer more returns to less returns given a certain level of risk,
- if two portfolios are such that one provides higher returns at a higher risk, and the other provides a lower return at a lower risk, then we cannot say which of the portfolios the investor would prefer as that would depend upon the investor's risk preference.
The implication of the above is that an investor will always prefer a portfolio on the efficient frontier (the first two points above), as the portfolios on the efficient frontier always represent the maximum return for any given level of risk (or lowest risk given a certain level of desired return). As between two portfolios both of which are on the efficient frontier (last point above), the investor will pick based upon his or her level of risk tolerance.
Therefore statement II and III are correct, and Choice 'd' is the correct answer. The reference to drawdowns and risk neutrality in statements I and IV are meaningless in the context and are incorrect.
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
The profit potential from the conversion of convertible bonds into stock is limited by
Answer : A
The profit potential from the conversion of convertible bonds into stock is limited by the issuer's option to call the security at short notice. Generally, the convertible debt security is convertible into a certain number of shares, and the debt holder will generally not convert the security to shares unless there is a profit to be made. The 'premium' is irrelevant, because as long as the premium exists, the debt holder has no incentive to convert, as he would be better off buying the shares in the market. It is only when share prices go beyond a level that it becomes advantageous convert the security into shares. However, the prospect of granting cheap shares to the debt holders is not too appealing to the issuer, and as soon as the share price goes beyond a point where the value of the shares exceeds the face value of the debt the issuer has an incentive to exercise its option to call the security.
Therefore the profit potential from the conversion of convertible bonds into shares is limited by the issuer's option to call the security, and Choice 'a' is the correct answer. The 'premium', or interest rates, or volatility are irrelevant.
Which of the following statements are true:
1. The swap rate, also called the swap spread, is initially calculated so that the value of the swap at inception is zero.
II. The value of a swap at initiation is different from zero and is equal to the difference between the NPV of the cash flows of the two legs of the swap
III. OTC swaps are standardized and limited to a defined set of standard contracts
IV. Interest rate and commodity swaps are the types of swaps that are most traded
Answer : C
Swaps rates are calculated such that the swap's value at inception is zero. Therefore statement I is correct and statement II is incorrect. OTC swaps are not standardized, in fact they are customized by the parties to suit their needs, which is why they are over-the-counter. Therefore statement III is incorrect. It is correct that interest rate and commodity swaps are the most traded, and statement IV is correct.
Therefore Choice 'c' is the correct answer.
Which of the following statements is true:
1. A high market beta implies a high degree of correlation with the market
II. Correlation coefficient and covariance between assets have the same sign
III. A correlation of zero indicates the absence of a linear relationship between the two assets
IV. Unless assets are perfectly correlated, diversification always reduces portfolio risk.
Answer : D
A high beta does not necessarily imply a high correlation with the market. The relationship
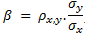

This means that a high market beta could be due to high volatility of the asset in question, and not because of a high correlation. Therefore statement I is not correct. Statement II is correct as correlation and covariance have the same sign. This is because correlation = covariance/product of standard deviations. Since standard deviation is always positive, correlation and covariance will have the same sign. A correlation of zero indicates the absence of a linear relationship between two variables - therefore statement III is correct. Statement IV is correct as well, because unless correlation is +1, diversification always reduces total portfolio risk.
[According to the PRMIA study guide for Exam 1, Simple Exotics and Convertible Bonds have been excluded from the syllabus. You may choose to ignore this question. It appears here solely because the Handbook continues to have these chapters.]
Which of the following best describes a shout option
Answer : A
Which of the following does not explain the shape of an yield curve?
Answer : C
The efficient markets hypothesis states that all known information is captured in the prices of a security. It does not explain the shape of the yield curve.
The expectations hypothesis, the LPT and the market segmentation theory are all attempts to explain the shape of the term structure of interest rates.
Therefore Choice 'c' is the correct answer as it does not explain the shape of the yield curve.