Real Estate Licensing Virginia Real Estate Salesperson Exam Practice Test
The EGI of a building is $300,000. The operating costs are $30,000.
What is the NOI of the building?
Answer : C
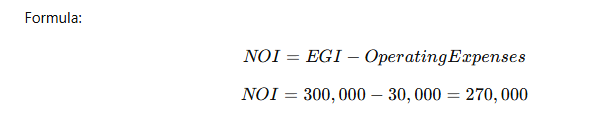
Other options are miscalculations.
Reference (Virginia Real Estate):
Appraisal & Finance curriculum
USPAP standards -- income approach
A490-02REGS.pdf -- Real Estate Math section
You're doing a CMA on a three-bedroom, two-bath, seven- year-old property. Choose the BEST comp from the following list:
Answer : B
When preparing a Comparative Market Analysis (CMA):
The best comp is most similar in location, age, size, and features.
Timeliness matters (more recent sales are preferred), but similarity in property type/size carries greater weight.
Analysis of options:
(A) Six-bedroom, new build = too dissimilar.
(B) Same size, age, and location --- best match, though sold 2 years ago.
(C) Too far (20 miles) and older property.
(D) Closer in time but has fewer bedrooms/baths and is older.
Thus, (B) is the closest comparable.
Virginia Real Estate Principles & Practices -- CMA and appraisal methods
Real Estate Exam Prep -- Valuation & Market Analysis
What is the legal doctrine by which the decedent's property will pass to the state without their consent if that individual dies without a will, a surviving spouse, lineal descendants, or other known heirs?
Answer : C
The doctrine of escheat applies when a person dies intestate (without a will) and has no surviving spouse, descendants, or heirs. In such cases, ownership of the property passes to the state.
Other doctrines:
(A) Police power = government authority to regulate land use.
(B) Eminent domain = taking private property for public use with just compensation.
(D) Variance = zoning exception.
Reference (Virginia Real Estate):
Virginia Code 55.1-2400 et seq. (Escheats)
A490-02REGS.pdf -- Government powers in real estate
Lola has an easement that allows her to cross her neighbor's back lot to reach her home. It runs with the land. What kind of easement does Lola have?
Answer : D
An easement appurtenant:
Attaches to the land and ''runs with the land.''
Involves two parcels: a dominant estate (benefited, here Lola's property) and a servient estate (burdened, neighbor's lot).
Example: Right-of-way across a neighbor's property for access.
Other options:
(A) Easement for light and air = very rare.
(B) Easement in gross = benefits a person/entity, not land (e.g., utility easement).
(C) Easement by prescription = acquired through long-term, open, notorious, hostile use (not the case here).
Reference (Virginia Real Estate):
Code of Virginia Title 55.1 -- Easements
Virginia Real Estate Principles -- Easements and property rights
A490-02REGS.pdf -- Property rights curriculum
Which of the following contracts has no legal effect and typically involves an illegal act, fraud, misrepresentation,duress, or undue influence?
Answer : A
A void contract is one that has no legal effect from the beginning. It is not enforceable by law because it lacks essential legal elements or involves unlawful acts. Common reasons:
Illegal act (e.g., contract to sell illegal drugs)
Fraud, misrepresentation, duress, undue influence
Lacks capacity or lawful purpose
Other options:
(B) Valid contract = fully enforceable by law.
(C) Implied contract = created by actions, not words, but still enforceable.
(D) Oral contract = valid (except when required in writing by the Statute of Frauds).
Reference (Virginia Real Estate):
Virginia Code 11-2 (Statute of Frauds)
Virginia Real Estate Principles -- Contract Law section
A490-02REGS.pdf -- Contracts & Legal Enforceability
The duty of obedience does not include requests or instructions that are:
Answer : D
The fiduciary duty of obedience requires an agent to follow all lawful instructions from their client.
However, the duty does not include following illegal or unethical requests.
Example: A client instructing a licensee to discriminate against buyers or falsify contract terms --- the licensee must refuse.
Other options:
(A) Instructions don't always need to be in writing to be valid.
(B) Ethical but unwise requests still require obedience.
(C) ''Unnecessary'' instructions are subjective and not an exception.
Reference (Virginia Real Estate):
Code of Virginia 54.1-2131 (Duties of licensees)
Virginia Real Estate Principles -- Fiduciary duties section
A490-02REGS.pdf -- Agency & fiduciary responsibilities
Which of these is a person who is licensed to represent one of the parties in a real estate transaction in exchange for a commission or other valuable consideration?
Answer : C
In Virginia, a real estate broker is the person licensed to represent one of the parties in a real estate transaction in exchange for commission or other valuable consideration.
Salesperson (A): Licensed to perform brokerage activities but only under the supervision of a broker; cannot independently represent a party for commission.
Assistant Broker (B): Not an official license category in Virginia.
Appraiser (D): Licensed to determine property value, not to represent parties in real estate transactions.
Thus, the correct answer is broker.
Code of Virginia 54.1-2100 (Definitions)
Virginia Real Estate Board Regulations (18 VAC 135-20)