Salesforce Certified Tableau Consultant Analytics-Con-301 Exam Questions
A database contains two related tables at different levels of granularity. The client wants to make all data available in Tableau Prep at the original level of granularity.
Which two solutions in Tableau meet the client's requirements? Choose two.
Answer : A, C
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
The key requirement is:
Data must remain at the original grain in Tableau Prep
Tables are at different granularities
Tableau Prep does NOT support relationships, and automatically joins tables, which changes granularity (by duplicating or aggregating records).
Therefore, relationships (Option B) cannot preserve grain for Prep.
Also:
A physical join (Option D) changes the grain by combining rows, often multiplying results when grain differs.
Only two options preserve the original granularity:
Option A --- Two Separate Published Data Sources
Each data source represents one table.
In Tableau Prep, the user can choose:
Use tables separately
Join or clean them intentionally
Keep each table at its own grain
This keeps all data at its native level.
Option C --- Virtual Connection
A Virtual Connection:
Publishes entire tables from the database
Maintains each table independently at its native granularity
Makes all tables available to Tableau Prep without altering grain
Is specifically designed for governed, reusable multi-table access
Thus, it satisfies the requirement exactly.
Why the others are incorrect:
B --- Relationship
Relationships only exist in Tableau Desktop logical layer, NOT in Tableau Prep.
Prep flattens the data grain is lost.
D --- Physical join
Always modifies granularity when tables differ, often causing row multiplication.
Tableau Prep does not support logical relationships; only physical joins.
Virtual Connections preserve original tables and governance.
Published Data Sources can be separated to maintain original grain.
A Tableau consultant is tasked with creating a line graph that shows daily temperature fluctuations. The below set of data to use to create a dashboard.
How should the consultant manipulate the data to support the business need?
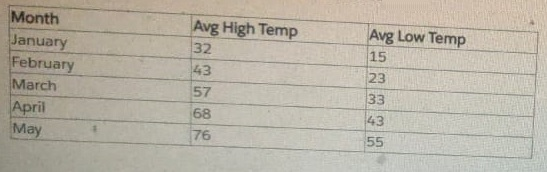
Answer : B
The business requirement is:
''Create a line graph that shows daily temperature fluctuations.''
The dataset provided contains:
Only 5 rows, one per month
Two aggregated columns: Avg High Temp and Avg Low Temp
No daily values in the dataset
Tableau's documentation states that:
Tableau cannot generate artificial granularity that does not exist in the underlying data.
LOD calculations cannot create detail that isn't present in the source. They can only roll up or fix existing grain; they cannot fabricate lower-grain data.
Pivoting only reshapes data; it does not create missing days or introduce new rows.
When the visualization requires detail that the dataset does not contain, the correct solution is to obtain data at the required level of granularity.
Because the dataset contains monthly averages, it is impossible to show day-to-day fluctuations without having the actual daily temperatures.
Therefore, the only way to support the business need is to request daily-level data from the data provider.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A . Pivot the data
Pivoting would convert the dataset from wide format to long format (e.g., ''Avg High Temp'' and ''Avg Low Temp'' into a single ''Temperature Type'' field).
This does not add daily rows, so the required daily line graph still cannot be built.
C . Create an LOD calculation
LOD expressions cannot create new lower-level detail.
They only aggregate or fix existing detail.
Because the dataset contains only monthly values, an LOD cannot generate daily temperatures.
Tableau granularity and data modeling guidance stating that detail must exist in the data to be visualized.
LOD expression documentation explaining that LODs cannot create lower granularity than the source data.
Pivoting documentation explaining pivots reshape fields but do not generate new rows or finer-grain data.
A client wants to see the average number of orders per customer per month, broken down by region. The client has created the following calculated field:
Orders per Customer: {FIXED [Customer ID]: COUNTD([Order ID])}
The client then creates a line chart that plots AVG(Orders per Customer) over MONTH(Order Date) by Region. The numbers shown by this chart are far higher
than the customer expects.
The client asks a consultant to rewrite the calculation so the result meets their expectation.
Which calculation should the consultant use?
Answer : B
The calculation {FIXED [Customer ID], [Region]: COUNTD([Order ID])} is the correct one to use for this scenario. This Level of Detail (LOD) expression will calculate the distinct count of orders for each customer within each region, which is then averaged per month. This approach ensures that the average number of orders per customer is accurately calculated for each region and then broken down by month, aligning with the client's expectations.
The initial calculation provided by the client likely overestimates the average number of orders per customer per month by region due to improper granularity control. The revised calculation must take into account both the customer and the region to correctly aggregate the data:
FIXED Level of Detail Expression: This calculation uses a FIXED expression to count distinct order IDs for each customer within each region. This ensures that the count of orders is correctly grouped by both customer ID and region, addressing potential duplication or misaggregation issues.
Accurate Aggregation: By specifying both [Customer ID] and [Region] in the FIXED expression, the calculation prevents the overcounting of orders that may appear if only customer ID was considered, especially when a customer could be ordering from multiple regions.
Level of Detail Expressions in Tableau: These expressions allow you to specify the level of granularity you need for your calculations, independent of the visualization's level of detail, thus offering precise control over data aggregation.
Which technique should a Tableau consultant use to optimize workbook performance with a live data source?
Answer : A
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
When optimizing performance with live connections, Tableau documentation emphasizes minimizing the workload passed to the database. Key principles include:
Databases resolve numeric and Boolean fields significantly faster than strings and dates.
Using simpler data types reduces query parsing time and improves join and filter performance.
This is a standard Tableau recommendation for live query optimization.
Why the other answers are incorrect:
B: Table calculations add workload on Tableau, but live performance depends on database efficiency; granular table calc processing worsens performance.
C: Custom SQL often hurts performance because it disables query optimization, increases load times, and prevents Tableau from generating efficient queries.
D: Compute Calculations Now applies only to extracts, and has no effect on live connections.
Thus, the documented performance best practice for live sources is to use numbers and Booleans instead of strings and dates.
Live connection optimization guidance: prefer numeric and Boolean fields over strings/dates.
Best practices cautioning against Custom SQL for performance.
Documentation stating Compute Calculations Now applies only to extracts.
SIMULATION

From the desktop, open the NYC
Property Transactions workbook.
You need to record the performance of
the Property Transactions dashboard in
the NYC Property Transactions.twbx
workbook. Ensure that you start the
recording as soon as you open the
workbook. Open the Property
Transactions dashboard, reset the filters
on the dashboard to show all values, and
stop the recording. Save the recording in
C:\CC\Data\.
Create a new worksheet in the
performance recording. In the worksheet,
create a bar chart to show the elapsed
time of each command name by
worksheet, to show how each sheet in
the Property Transactions dashboard
contributes to the overall load time.
From the File menu in Tableau Desktop,
click Save. Save the performance
recording in C:\CC\Data\.
Answer : A
To record the performance of the Property Transactions dashboard in the NYC Property Transactions.twbx workbook and analyze it using a bar chart, follow these detailed steps:
Open the NYC Property Transactions Workbook:
From the desktop, double-click the NYC Property Transactions.twbx workbook to open it in Tableau Desktop.
Start Performance Recording:
Before doing anything else, navigate to the 'Help' menu in Tableau Desktop.
Select 'Settings and Performance', then choose 'Start Performance Recording'.
Open the Property Transactions Dashboard and Reset Filters:
Navigate to the Property Transactions dashboard within the workbook.
Reset all filters to show all values. This usually involves selecting the dropdown on each filter and choosing 'All' or using a 'Reset' button if available.
Stop the Performance Recording:
Go back to the 'Help' menu.
Choose 'Settings and Performance', then select 'Stop Performance Recording'.
Tableau will automatically open a new tab displaying the performance recording results.
Save the Performance Recording:
In the performance recording results tab, go to the 'File' menu.
Click 'Save As' and navigate to the C:\CC\Data\ directory.
Save the file, ensuring it is stored in the desired location.
Create a New Worksheet for Performance Analysis:
Return to the NYC Property Transactions workbook and create a new worksheet by clicking on the 'New Worksheet' icon.
Drag the 'Command Name' field to the Columns shelf.
Drag the 'Elapsed Time' field to the Rows shelf.
Ensure that the 'Worksheet' field is also included in the analysis to break down the time by individual sheets within the dashboard.
Choose 'Bar Chart' from the 'Show Me' options to display the data as a bar chart.
Customize and Finalize the Bar Chart:
Adjust the axes and labels to clearly display the information.
Format the chart to enhance readability, applying color coding or sorting as needed to emphasize sheets with longer load times.
Save Your Work:
Once the new worksheet and the performance recording are complete, ensure all work is saved.
Navigate to the 'File' menu and click 'Save', confirming that changes are stored in the workbook.
Tableau Help Documentation: Provides guidance on how to start and stop performance recordings and analyze them.
Tableau Visualization Techniques: Offers tips on creating effective bar charts for performance data.
By following these steps, you have successfully recorded and analyzed the performance of the Property Transactions dashboard, providing valuable insights into how each component of the dashboard contributes to the overall load time. This analysis is crucial for optimizing dashboard performance and ensuring efficient data visualization.
A client has a sales dataset that contains fields named Customer ID, Region, Item, and Sales Amount. Each row represents a single sale. There may be multiple sales for each Customer ID.
The client wants to visualize the average total customer sales by region.
Which Level of Detail (LOD) expression should a consultant recommend?
Answer : C
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract:
The requirement is:
Compute total sales per customer, not per transaction.
Then compute the average of those customer totals, grouped by region.
Tableau documentation states that FIXED LOD expressions are used to calculate values at a specific level of granularity regardless of the view.
To solve the business need:
Step 1:
Calculate total customer sales for each Customer ID within each Region:
{ FIXED [Customer ID], [Region] : SUM([Sales Amount]) }
This produces one number per customer per region.
Step 2:
Compute the average of those totals:
AVG( { FIXED [Customer ID], [Region] : SUM([Sales Amount]) } )
This yields:
Average total customer sales by region
This is exactly option C.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A . EXCLUDE Region: Would combine regions and incorrectly calculate overall totals.
B . FIXED Region: AVG(Sales Amount): Computes average of line-level sales, not customer totals.
D . FIXED Customer ID + Region: AVG(Sales Amount): Averages individual transactions, not customer totals.
Only option C matches the required two-step logic.
LOD Expressions: FIXED for computing customer-level aggregates.
Nested LOD usage for first calculating customer totals, then averaging them at a higher level.
Tableau guidance: SUM inside FIXED for per-customer totals, AVG outside for averaging customers.
A customer plans to do an in-place upgrade of their single node Tableau Server from 2023.1 to the most recent version.
What is the correct sequence to prepare for an in-place upgrade?
Answer : B
Tableau's official in-place upgrade steps for single-node Tableau Server require:
Disable scheduled tasks (to prevent extract failures during upgrade).
Run the upgrade script for the new version.
Validate and test the server after upgrade.
The critical detail:
An in-place upgrade means upgrading the existing production environment directly, not installing in a separate environment or cloning VMs.
Option B matches exactly the documented operational steps for an in-place upgrade.
Why the other options are incorrect:
A: Uninstalling Tableau Server is not part of an in-place upgrade workflow.
C: This describes a migration or test upgrade in a separate environment, not an in-place upgrade.
D: VM cloning and restoring is not required for in-place upgrades and is not part of Tableau's official procedure.
Only B represents the correct in-place upgrade sequence.
Tableau Server in-place upgrade instructions: disable tasks run upgrade script test.
Single-node upgrade guidelines noting that uninstalling is not required.
Tableau Server administration materials clarifying the difference between in-place upgrade and sandbox testing.