Salesforce Build Applications Programmatically on the Salesforce Platform DEX-450 Exam Practice Test
Universal Containers wants to assess the advantages of declarative development versus programmatic customization for specific use cases in its Salesforce implementation.
What are two characteristics of declarative development over programmatic customization?
Choose 2 answers
Answer : A, C
In the following example, which sharing context will myMethod execute when it is invoked?
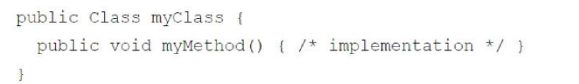
Answer : D
A developer needs to allow users to complete a form on an Account record that will create a record for a custom object.
The form needs to display different fields depending on the user's job role, The functionality should only be available to a small group of users.
Which three things should the developer do to satisfy these requirements?
Choose 3 answers
Answer : A, B, C, C
The following code snippet is executed by a Lightning web component in an environment with more than 2,000 lead records:

Which governor limit will likely be exceeded within the Apex transaction?
Answer : C
A developer considers the following snippet of code:

Based an this code, what is the value of x?
Answer : D
A developer identifies the following triggers on the Expense _c object:

The triggers process before delete, before insert, and before update events respectively.
Which two techniques should the developer implement to ensure trigger best practices are followed?
Choose 2 answers
Answer : A, C
A . Unify all three triggers in a single trigger on the Expense__c object that includes all events:
Salesforce best practices recommend having only one trigger per object to avoid redundancy and conflicts.
By combining all the events (before delete, before insert, and before update) into a single trigger, the developer can manage the logic in an organized and maintainable manner.
This also simplifies debugging and ensures that the trigger logic executes in a predictable order.
C . Create helper classes to execute the appropriate logic when a record is saved:
Using helper classes allows for a clean separation of concerns. The trigger becomes a dispatcher that delegates logic to dedicated classes.
For example, you can create methods like applyDefaultsToExpense(), validateExpenseUpdate(), and deleteExpense() in a helper class and invoke them from the trigger.
This improves reusability, readability, and testability of the code.
Why not the other options?
B . Unify the before insert and before update triggers and use Flow for the delete action:
While Flow is a powerful tool, it is not ideal for deleting records or replacing Apex trigger functionality, especially when triggers already exist for other events.
D . Maintain all three triggers on the Expense__c object but move the Apex logic out of the trigger definition:
Maintaining multiple triggers on the same object can lead to conflicts and execution order issues, even if the logic is moved to helper classes.
The Account object in an organization has a master-detail relationship to a child object called Branch. The following automations exist:
* Roll-up summary fields
* Custom validation rules
* Duplicate rules
developer created a trigger on the Account object.
Which two things should the developer consider while testing the trigger code?
Choose 2 answers
Answer : A, C
A . Roll-up summary fields can cause the parent record to go through Save:
When a roll-up summary field on a parent object (like Account) is updated due to changes in child records (like Branch), the parent record (Account) is implicitly saved again.
This can result in the execution of the trigger on the parent object. Developers must consider this behavior to avoid unintended recursion or infinite loops.
C . The trigger may fire multiple times during a transaction:
Triggers can execute multiple times within a single transaction, especially when there are operations such as updates to the parent record caused by roll-up summary fields or workflows.
Developers should implement logic to ensure that the trigger handles multiple executions correctly (e.g., using a static variable to prevent recursion).
Why not the other options?
B . Duplicate rules are executed once all DML operations commit to the database:
This is incorrect because duplicate rules execute before the DML operation is committed. Duplicate rules prevent duplicate records from being created or updated before the database operation occurs.
D . The validation rules will cause the trigger to fire again:
This is incorrect because validation rules do not cause triggers to fire again. Validation rules validate the record and may prevent DML operations, but they do not independently re-trigger the Apex trigger.