Salesforce Certified MuleSoft Developer (Mule-Dev-201) Exam Questions
How can you call a subflow from Dataweave?
Answer : C
This is a trick question.
You can call only flows from DataWeave using lookup function. Note that lookup function does not support calling subflows.
A subflow needs a parent context to inherit behaviors from such as exception handling, which a flow does not need
Hence correct answer is Not possible in Mule 4
A RAML example fragment named StudentExample.raml is placed in the examples folder in an API specification project. What is the correct syntax to reference the fragment?
Answer : C
To include property. To keep the API definition concise, you can include external content, such as documentation, schemas, and frequently used patterns outside the definition itself. The parser interprets !include as if the content of the externally-hosted file or a URL were declared in-line.
To use the fragments in RAML you have to include the exact path(copy the path) of that fragment you want to use as shown below
Option 3 is the correct as correct syntax is
examples: !include examples/StudentExample.raml
How to import Core (dw::Core) module into your DataWeave scripts?
Answer : B
Correct answer is Not needed as dw::core module is included by default. We don't need to include it explicitly
Refer to the exhibits.


A web client sends a POST request to the HTTP Listener with the payload "Hello-". What response is returned to the web client?
What response is returned to the web client?
Answer : A
What payload is returned by a Database SELECT operation that does not match any rows in the database?
Answer : D
Empty array is returned when no rows are matched.
MuleSoft Doc Ref : https://docs.mulesoft.com/db-connector/1.9/database-connector-select
What should this endpoint return? http://dev.acme.com/api/patients?name=John&surname=Bell
Answer : D
Query parameters are a defined set of parameters attached to the end of a url. They are extensions of the URL that are used to help define specific content or actions based on the data being passed. To append query params to the end of a URL, a '?' Is added followed immediately by a query parameter.
To add multiple parameters, an '&' is added in between each.
Hence coming back to question, endpoint would return Patients with name as John and (and is very important here) surname as Bell
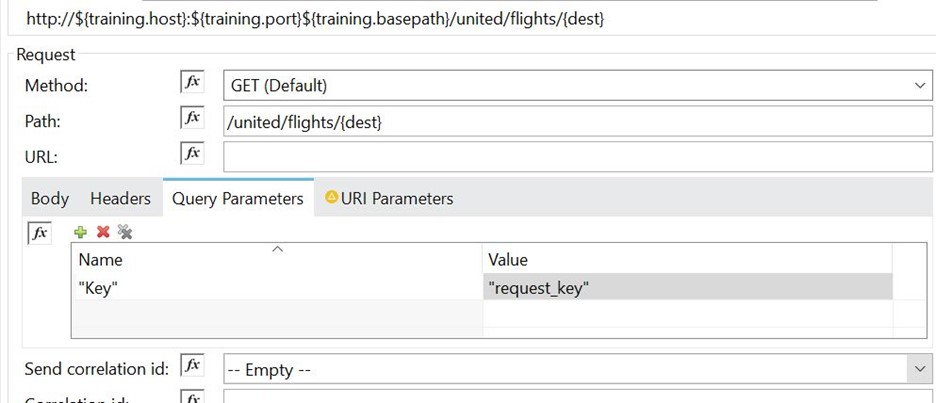
How are query parameters dynamically passed to an outbound REST request using an HTTP Request operation?
Answer : A
In General > Request > Query Parameters, click the plus icon (+) to add a parameter to a request. Type a name and value for the parameter or use a DataWeave expression to define the name and value.